How Many Protons Are In Sulfur
listenit
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
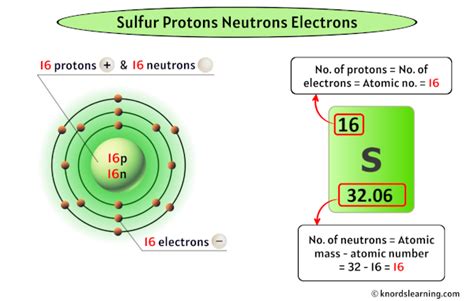
Table of Contents
How Many Protons are in Sulfur? Understanding Atomic Structure and Sulfur's Properties
Determining the number of protons in an atom of any element is fundamental to understanding its chemical behavior and its place within the periodic table. This article delves into the specifics of sulfur, explaining how many protons it possesses, and exploring the broader implications of atomic structure in determining an element's properties. We'll also touch upon related concepts and applications.
Understanding Atomic Structure: The Foundation of Chemistry
Before we pinpoint the number of protons in sulfur, let's briefly review the fundamental components of an atom. Atoms, the basic building blocks of matter, are composed of three primary subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element. Each element has a unique number of protons.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles (no charge) also residing in the nucleus. The number of neutrons can vary within an element, leading to isotopes.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels. The number of electrons typically equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. This number is unique to each element and is what distinguishes one element from another. It's found on the periodic table, typically displayed above the element's symbol.
How Many Protons Does Sulfur Have?
Sulfur, a nonmetal with the chemical symbol S, occupies a significant place in various natural processes and industrial applications. Its atomic number is 16. Therefore, a sulfur atom contains 16 protons. This is a fundamental characteristic of sulfur and is unchanging regardless of its physical state (solid, liquid, gas) or its chemical bonding with other elements.
Isotopes of Sulfur: Variations in Neutron Count
While the number of protons remains constant at 16, sulfur exhibits isotopic variation. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that possess the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons. This difference affects the atom's mass but not its chemical properties significantly.
Naturally occurring sulfur consists of several stable isotopes, including:
- Sulfur-32 (³²S): The most abundant isotope, comprising about 95% of natural sulfur. It contains 16 protons and 16 neutrons.
- Sulfur-33 (³³S): A less abundant isotope, with 16 protons and 17 neutrons.
- Sulfur-34 (³⁴S): Another stable isotope, containing 16 protons and 18 neutrons.
- Sulfur-36 (³⁶S): A naturally occurring, albeit rare, isotope with 16 protons and 20 neutrons.
The variations in neutron number lead to slight differences in the atomic mass of sulfur. The atomic mass listed on the periodic table is a weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes, taking into account their relative abundances.
The Importance of Sulfur's 16 Protons: Implications for its Properties
The presence of 16 protons in sulfur's nucleus profoundly impacts its chemical and physical properties. These properties make sulfur crucial in various areas:
Chemical Properties:
- Reactivity: Sulfur's six valence electrons (electrons in the outermost shell) determine its reactivity. It readily forms covalent bonds with other atoms to achieve a stable octet (eight electrons in the outermost shell). This is evident in the formation of compounds like sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
- Oxidation States: Sulfur can exhibit various oxidation states, ranging from -2 to +6, depending on the chemical environment and bonding partners. This versatility allows it to participate in numerous redox reactions.
- Formation of Polyatomic Ions: Sulfur forms polyatomic ions like sulfate (SO₄²⁻) and sulfite (SO₃²⁻), which are vital components in various chemical processes and biological systems.
Physical Properties:
- Allotropes: Sulfur exists in several allotropic forms, meaning it can exist in different physical forms (e.g., rhombic, monoclinic) with different crystal structures, demonstrating the influence of its atomic structure on its macroscopic properties.
- Melting and Boiling Points: The relatively weak intermolecular forces between sulfur atoms influence its relatively low melting and boiling points compared to other elements.
- Electrical Conductivity: Sulfur is a poor conductor of electricity due to the strong covalent bonds within its molecular structure.
Sulfur's Role in Various Applications
Sulfur's unique properties have made it indispensable in numerous industrial and biological applications:
- Vulcanization of Rubber: Sulfur plays a pivotal role in vulcanizing rubber, improving its strength, elasticity, and durability. This is a critical process in tire manufacturing and other rubber-related industries.
- Production of Sulfuric Acid: Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), one of the most important industrial chemicals, is produced largely from sulfur. Its uses span fertilizer production, petroleum refining, metal processing, and many other industrial processes.
- Fertilizers: Sulfur is an essential nutrient for plant growth and is included in various fertilizers to promote healthy plant development.
- Pharmaceuticals: Sulfur compounds are used in the synthesis of certain drugs and pharmaceuticals.
- Matches: Historically and even today in some applications, sulfur is a component in the head of matches, contributing to its ignition.
- Fungicides and Pesticides: Certain sulfur compounds have fungicidal and pesticidal properties and are used in agriculture and horticulture.
Beyond Sulfur: Understanding the Periodic Table and Atomic Structure
Understanding the atomic structure of sulfur, particularly the fact that it has 16 protons, provides a strong foundation for understanding its chemical behavior and its numerous applications. This principle extends to all elements in the periodic table. The periodic table itself is organized based on the atomic number (number of protons) and the resulting electron configurations, which dictate the recurring trends in elemental properties.
Exploring other elements and their proton counts allows for a deeper understanding of the periodic trends and the fascinating relationships between atomic structure and macroscopic properties. These relationships enable scientists to predict and understand the behavior of matter, driving innovations across various fields.
Conclusion: The Significance of 16 Protons
The simple fact that sulfur contains 16 protons underpins its unique properties and its essential role in various aspects of our lives. From the vulcanization of rubber to the production of sulfuric acid, sulfur's impact is undeniable. Understanding its atomic structure provides invaluable insights into its behavior and applications, highlighting the profound connection between the subatomic world and our macroscopic experience. By learning about sulfur and its 16 protons, we gain a more profound understanding of chemistry and the fundamental principles that govern the world around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Electrons Are Shared In A Double Covalent Bond
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 8 And 2
Mar 15, 2025
-
An Atom That Gains Or Loses An Electron Is Called
Mar 15, 2025
-
Write A System Of Equations With The Solution 4
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Do You Punctuate A Tv Show Title
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Protons Are In Sulfur . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
