How Many Electrons Are Shared In A Double Covalent Bond
listenit
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
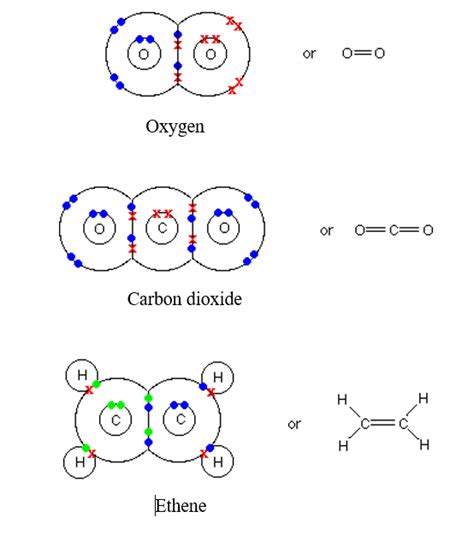
Table of Contents
How Many Electrons are Shared in a Double Covalent Bond? A Deep Dive into Chemical Bonding
Understanding chemical bonding is fundamental to grasping the behavior of matter. Covalent bonds, formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms, are particularly prevalent in organic chemistry and many other areas of the chemical sciences. This article will delve into the specifics of double covalent bonds, explaining exactly how many electrons are involved in their formation and the implications for molecular structure and properties.
What is a Covalent Bond?
Before exploring double covalent bonds, let's establish a firm understanding of the basic principle. A covalent bond arises from the electrostatic attraction between two atoms and the shared electrons that lie between their nuclei. This sharing allows each atom to achieve a more stable electron configuration, often resembling a noble gas (a full outer electron shell). The stability gained from achieving a complete octet (eight valence electrons) is the driving force behind covalent bond formation. Atoms achieve this stability by sharing electrons, as opposed to the transfer of electrons seen in ionic bonds.
Types of Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds aren't all the same. They can be classified based on the number of electron pairs shared between atoms:
-
Single Covalent Bond (Single Bond): This involves the sharing of one pair of electrons (two electrons) between two atoms. A classic example is the bond in a hydrogen molecule (H₂), where each hydrogen atom contributes one electron to the shared pair.
-
Double Covalent Bond (Double Bond): This involves the sharing of two pairs of electrons (four electrons) between two atoms. This stronger bond significantly influences the molecular geometry and reactivity of the molecule.
-
Triple Covalent Bond (Triple Bond): This, the strongest type of covalent bond, involves the sharing of three pairs of electrons (six electrons) between two atoms. Nitrogen gas (N₂) is a prime example, with each nitrogen atom contributing three electrons to the shared pool.
The Double Covalent Bond: A Detailed Examination
Now, let's focus on the core question: how many electrons are shared in a double covalent bond? The answer, simply put, is four. Two pairs of electrons are shared between the two bonded atoms. This creates a stronger bond than a single covalent bond due to the increased electrostatic attraction between the nuclei and the greater electron density between them.
Visualizing the Double Bond
Representing double bonds in chemical formulas and diagrams is crucial. Several methods exist:
-
Lewis Structures: These diagrams use dots to represent valence electrons. A double bond is shown as two pairs of dots between the bonded atoms. For example, in the oxygen molecule (O₂), each oxygen atom is represented with two pairs of dots, showing the double bond formed by the sharing of four electrons.
-
Dash Notation: In this simpler notation, a single dash represents a single bond, and a double dash (or =) represents a double bond. So, the oxygen molecule (O₂) would be written as O=O.
Examples of Double Bonds in Molecules
Double bonds are ubiquitous in organic chemistry and occur in many inorganic compounds as well. Here are some notable examples:
-
Ethylene (C₂H₄): The carbon atoms in ethylene are joined by a double bond, accounting for the molecule's reactivity. The double bond influences its planar geometry.
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): This molecule features two double bonds, one between each oxygen atom and the central carbon atom. This linear geometry results from the strong electron repulsion between the double bonds.
-
Ozone (O₃): The ozone molecule possesses a resonance structure, where a double bond resonates between two oxygen-oxygen bonds. The delocalization of electrons contributes to ozone's unique properties.
-
Alkenes: The defining characteristic of alkenes is the presence of at least one carbon-carbon double bond within their structure. The double bond is crucial for many of their chemical properties.
-
Ketones and Aldehydes: These carbonyl-containing functional groups have a carbon-oxygen double bond, called a carbonyl group (C=O). This group contributes significantly to the reactivity and properties of ketones and aldehydes.
The Strength and Stability of Double Bonds
The increased electron density and stronger electrostatic attraction in double bonds translates to several key characteristics:
-
Higher Bond Energy: Double bonds have higher bond energies than single bonds. This means more energy is required to break a double bond.
-
Shorter Bond Length: The stronger attraction between the nuclei in a double bond results in a shorter bond length compared to a single bond.
-
Increased Rigidity: The presence of a double bond restricts rotation around the bond axis, leading to greater rigidity in the molecule. This is crucial in determining the three-dimensional shape and reactivity of the molecule. Rotation around a double bond would require breaking the pi bond, which is energetically unfavorable.
-
Planar Geometry (often): Molecules containing double bonds often exhibit planar (or nearly planar) geometry around the atoms involved in the double bond. This is due to the constraints imposed by the p-orbital overlap that forms the pi bond.
Implications for Molecular Properties
The presence of double bonds significantly impacts the physical and chemical properties of molecules. These impacts include:
-
Boiling Point and Melting Point: Double bonds contribute to higher boiling and melting points compared to molecules with only single bonds, due to the stronger intermolecular forces arising from increased electron density.
-
Reactivity: Double bonds are more reactive than single bonds, particularly prone to addition reactions where atoms or groups add across the double bond. This is because the pi bond is weaker than the sigma bond and is more readily broken.
-
Spectroscopic Properties: Double bonds exhibit unique signatures in various spectroscopic techniques (e.g., infrared and ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy), enabling their identification and characterization in molecules.
Differentiating Double Bonds from Other Bond Types
It's important to differentiate double covalent bonds from other types of bonding interactions:
-
Ionic Bonds: These bonds involve the complete transfer of electrons from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of ions. There's no sharing of electrons, unlike in covalent bonds.
-
Metallic Bonds: In metallic bonds, electrons are delocalized across a lattice of metal atoms, forming a "sea" of electrons. This is distinctly different from the localized sharing of electrons in covalent bonds.
-
Coordinate Covalent Bonds (Dative Bonds): While still a type of covalent bond, a dative bond involves both electrons in the shared pair originating from the same atom, rather than one electron from each atom. The overall number of shared electrons, however, can still contribute to double bonds if a coordinate bond and a regular covalent bond are both involved.
Conclusion: The Significance of Double Covalent Bonds
The double covalent bond, involving the sharing of four electrons, is a cornerstone of chemical structure and reactivity. Its presence profoundly influences molecular geometry, bond strength, reactivity, and physical properties. Understanding the intricacies of double bonds is essential for comprehending the vast array of molecules and their interactions in the world around us, across numerous fields of science and engineering. From the synthesis of polymers to the study of biological molecules, the knowledge of how many electrons are shared in a double bond (four) underpins a significant portion of our understanding of the chemical world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Monomers Of Nucleic Acids
Mar 15, 2025
-
Atoms Of The Same Element With Varying Number Of Neutrons
Mar 15, 2025
-
Find The Most General Antiderivative Of The Function
Mar 15, 2025
-
All Organic Compounds Contain The Element Carbon
Mar 15, 2025
-
12 Is What Percent Of 20
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Electrons Are Shared In A Double Covalent Bond . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
