How Many Protons Are In Carbon 14
listenit
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
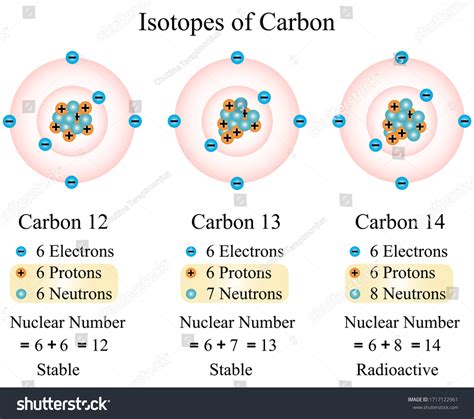
Table of Contents
- How Many Protons Are In Carbon 14
- Table of Contents
- How Many Protons are in Carbon-14? Understanding Isotopes and Atomic Structure
- Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
- Isotopes: Variations in Neutron Number
- Carbon-14: The Radioactive Isotope
- Radiocarbon Dating: Utilizing Carbon-14's Decay
- Significance of Protons in Defining Carbon-14's Properties
- The Role of Neutrons in Carbon-14's Radioactivity
- Applications of Carbon-14 Beyond Radiocarbon Dating
- Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Isotopes
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
How Many Protons are in Carbon-14? Understanding Isotopes and Atomic Structure
The question, "How many protons are in carbon-14?" seems simple, but it opens the door to understanding fundamental concepts in chemistry and physics, specifically isotopes and atomic structure. The answer itself is straightforward, but exploring the 'why' behind it reveals a fascinating world of nuclear properties and their implications.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Every atom, the basic building block of matter, is composed of three subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element; it's the atomic number.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles (no charge) also residing in the nucleus. They contribute to the atom's mass but not its charge.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells. They are significantly lighter than protons and neutrons and determine the atom's chemical properties.
The number of protons dictates the element's identity. All atoms of a specific element have the same number of protons. For instance, all hydrogen atoms have one proton, all oxygen atoms have eight, and so on. This is a fundamental principle in chemistry.
Isotopes: Variations in Neutron Number
While the number of protons defines the element, the number of neutrons can vary. Atoms of the same element with differing numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. These isotopes have the same number of protons and electrons but different mass numbers (the total number of protons and neutrons).
Carbon, for example, has several isotopes, the most common being carbon-12 (¹²C) and carbon-13 (¹³C). Both contain six protons (defining them as carbon), but ¹²C has six neutrons, while ¹³C has seven.
Carbon-14: The Radioactive Isotope
Carbon-14 (¹⁴C) is a naturally occurring radioisotope of carbon. This means it has the same number of protons as other carbon isotopes (six), but it has a different number of neutrons. Specifically, ¹⁴C has eight neutrons.
Therefore, carbon-14 has six protons.
The extra two neutrons in ¹⁴C compared to the most common isotope, ¹²C, make it unstable. This instability leads to radioactive decay, where ¹⁴C emits radiation over time, eventually transforming into nitrogen-14 (¹⁴N). This radioactive decay is the basis of radiocarbon dating, a technique used to determine the age of organic materials.
Radiocarbon Dating: Utilizing Carbon-14's Decay
The radioactive decay of ¹⁴C follows a predictable pattern, with a half-life of approximately 5,730 years. This means that after 5,730 years, half of the ¹⁴C in a sample will have decayed into ¹⁴N. By measuring the ratio of ¹⁴C to ¹²C in a sample of organic material (like wood or bone), scientists can estimate its age. This technique has revolutionized archaeology and other fields.
Significance of Protons in Defining Carbon-14's Properties
While the neutron count differentiates carbon isotopes, the six protons remain the defining characteristic of carbon-14. These six protons determine:
- Chemical Behavior: The number of protons and electrons dictate how an atom interacts chemically with other atoms. Because ¹⁴C has the same number of electrons as ¹²C, it participates in the same chemical reactions. This allows it to be incorporated into living organisms during photosynthesis and other metabolic processes, making radiocarbon dating possible.
- Atomic Number: The atomic number (6) uniquely identifies carbon-14 as a carbon isotope. This atomic number is fundamental to its position on the periodic table and understanding its properties.
- Nuclear Properties: The protons and neutrons together determine the nucleus's stability and thus the isotope's radioactivity. The extra neutrons in ¹⁴C contribute to its instability and radioactive decay.
The Role of Neutrons in Carbon-14's Radioactivity
Although the number of protons defines the element, the number of neutrons plays a crucial role in determining the isotope's stability. In ¹⁴C, the presence of eight neutrons makes the nucleus unstable, causing it to undergo beta decay. During beta decay, a neutron transforms into a proton, an electron (beta particle), and an antineutrino. This process changes ¹⁴C into ¹⁴N (which has seven protons and seven neutrons).
This radioactive decay is a key characteristic that distinguishes ¹⁴C from other carbon isotopes. It's the basis for the application of ¹⁴C in various scientific and technological fields.
Applications of Carbon-14 Beyond Radiocarbon Dating
The unique properties of carbon-14, stemming from its nuclear structure, have led to applications beyond radiocarbon dating. These include:
- Medical Research: Carbon-14 is used as a tracer in metabolic studies and other biological research. The radioactive nature allows researchers to track the movement and fate of molecules in living systems.
- Industrial Applications: Carbon-14 is employed in various industrial processes, such as measuring wear and tear in machinery or determining the effectiveness of chemical treatments.
- Environmental Studies: The presence and concentration of ¹⁴C in environmental samples can provide valuable insights into environmental processes and pollution.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Isotopes
The simple question of how many protons are in carbon-14 leads to a rich exploration of atomic structure, isotopes, and radioactive decay. While the answer – six protons – is essential, the understanding of the role of neutrons in determining the isotope's properties and its applications is crucial. The existence of isotopes and their distinct properties expands our comprehension of the world around us, impacting fields ranging from archaeology to medicine to environmental science. The study of isotopes, such as carbon-14, emphasizes the fascinating interplay between subatomic particles and their macroscopic consequences. It highlights the power of fundamental scientific principles in solving real-world problems and advancing our knowledge. The number of protons, while seemingly a small detail, provides the foundation for understanding the unique characteristics and applications of this vital radioisotope.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Percent Is 8 Out Of 40
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Many Ounces Is In 3 4
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 30
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 170
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Long Does A Sensory Memory Last
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Protons Are In Carbon 14 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
