How Many Neutrons Does Uranium 238 Have
listenit
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
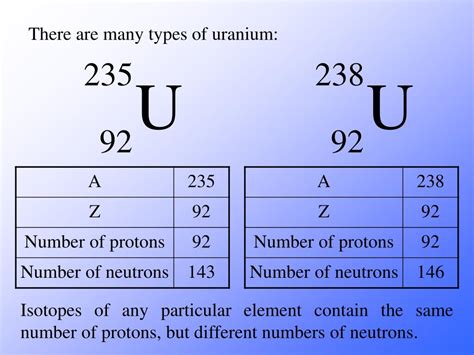
Table of Contents
How Many Neutrons Does Uranium-238 Have? Delving into Isotopes and Nuclear Structure
Uranium-238 (²³⁸U), a naturally occurring isotope of uranium, plays a significant role in various fields, from nuclear power generation to geological dating. Understanding its atomic structure, particularly the number of neutrons it possesses, is crucial for comprehending its properties and applications. This article will comprehensively explore the number of neutrons in Uranium-238, explaining the concepts of isotopes, atomic number, mass number, and their relevance to nuclear physics. We’ll also touch upon the significance of Uranium-238 in different contexts.
Understanding Isotopes: The Key to Understanding Uranium-238's Neutron Count
Before determining the neutron count in Uranium-238, let's clarify the concept of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons. This means they have the same atomic number (number of protons) but different mass numbers (total number of protons and neutrons).
All atoms of a given element have the same number of protons, defining their position on the periodic table. However, the number of neutrons can vary, resulting in different isotopes of that element. These isotopes may exhibit similar chemical properties but can have vastly different nuclear properties. This difference in nuclear properties significantly impacts their applications in various scientific and technological fields.
Atomic Number and Mass Number: Deciphering the Uranium-238 Structure
The notation ²³⁸U provides crucial information about the uranium atom's structure. The number 238 represents the mass number (A), which is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. The symbol U represents the element uranium, whose atomic number (Z) – the number of protons – is 92. This is a constant value for all uranium atoms.
To determine the number of neutrons (N), we simply subtract the atomic number (Z) from the mass number (A):
N = A - Z
In the case of Uranium-238:
N = 238 - 92 = 146
Therefore, Uranium-238 has 146 neutrons.
The Significance of Uranium-238's Neutron Count
The 146 neutrons in Uranium-238 are not just a number; they significantly influence its properties and applications. Let's explore some key aspects:
1. Nuclear Stability and Radioactivity:
The neutron-to-proton ratio is a critical factor in determining the stability of an atomic nucleus. Uranium-238, with its high neutron-to-proton ratio, is radioactive. It undergoes alpha decay, emitting an alpha particle (two protons and two neutrons), gradually transforming into thorium-234. This decay process is fundamental to its use in radioactive dating techniques.
2. Nuclear Fission and Power Generation:
While Uranium-238 itself is not directly fissile (meaning it doesn't readily undergo fission with thermal neutrons), it plays a vital role in nuclear reactors. It can capture a neutron and become Uranium-239, which subsequently decays to Plutonium-239, a fissile isotope used as fuel in nuclear reactors. This process, known as breeding, extends the fuel cycle and improves the efficiency of nuclear power generation.
3. Uranium Enrichment and Nuclear Weapons:
Uranium enrichment is a process of increasing the proportion of Uranium-235 (a fissile isotope) in natural uranium. Natural uranium consists mainly of Uranium-238 (approximately 99.3%) and a small amount of Uranium-235 (approximately 0.7%). Separating these isotopes is a complex process, essential for both nuclear power generation (where a higher concentration of Uranium-235 is required) and nuclear weapons (which rely heavily on highly enriched Uranium-235). The abundance of Uranium-238 presents both opportunities (through breeding) and challenges (in terms of enrichment).
4. Geological Dating:
The radioactive decay of Uranium-238 to Lead-206 is used in radiometric dating to determine the age of rocks and minerals. By analyzing the ratio of Uranium-238 to Lead-206, scientists can estimate the time elapsed since the rock's formation. This technique is fundamental to understanding geological history and the age of the Earth.
5. Medical Applications:
Although less prominent than other isotopes, Uranium-238 finds limited use in medical applications, mostly in radiation therapy. Its decay products and their associated radiation are utilized in certain targeted cancer treatments, although the use of Uranium itself is less common compared to other radioisotopes.
Comparing Uranium-238 with Other Uranium Isotopes
Uranium has several isotopes, each with a different number of neutrons and, consequently, different properties. Comparing Uranium-238 with other key isotopes highlights the significance of neutron count:
-
Uranium-235 (²³⁵U): This isotope has 143 neutrons (235 - 92 = 143). Unlike Uranium-238, Uranium-235 is fissile, meaning it readily undergoes nuclear fission with thermal neutrons, making it the primary fuel for many nuclear reactors. The lower neutron count contributes to its higher reactivity.
-
Uranium-234 (²³⁴U): This isotope has 142 neutrons (234 - 92 = 142). It's present in trace amounts in natural uranium and is also radioactive, decaying through alpha decay. Its lower neutron count compared to Uranium-238 leads to slightly different decay characteristics.
Understanding Nuclear Reactions Involving Uranium-238
Uranium-238 participates in various nuclear reactions, many of which are crucial in different technological applications. Let's explore a few key examples:
-
Neutron Capture: Uranium-238 readily captures neutrons, converting into Uranium-239. This reaction is essential in breeder reactors, where the Uranium-238 acts as a fertile material, ultimately producing Plutonium-239, a fissile material.
-
Alpha Decay: Uranium-238 undergoes alpha decay, emitting an alpha particle and transforming into Thorium-234. This decay chain continues through a series of radioactive decays, ultimately leading to stable Lead-206. This process is fundamental in radiometric dating.
-
Photofission: At sufficiently high energies, Uranium-238 can undergo photofission, splitting into smaller nuclei when bombarded with gamma rays. This process is less common than neutron-induced fission but is relevant in specific research contexts.
The Future of Uranium-238 Research
Research on Uranium-238 continues to be vital for several reasons:
-
Improving Nuclear Reactor Efficiency: Ongoing research focuses on optimizing the use of Uranium-238 in breeder reactors, maximizing the energy production from natural uranium and minimizing nuclear waste.
-
Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles: Development of advanced nuclear fuel cycles aims to effectively utilize Uranium-238, improving the sustainability and safety of nuclear power.
-
New Applications of Uranium-238's Properties: Researchers continue to investigate potential applications of Uranium-238's unique properties in various fields, including advanced materials science and medical applications.
Conclusion: The Importance of Neutron Count in Understanding Uranium-238
In conclusion, Uranium-238's 146 neutrons are not merely a numerical detail; they fundamentally determine its properties and applications. Understanding its atomic structure, particularly the neutron-to-proton ratio, is essential for comprehending its role in nuclear power generation, radioactive dating, and various other scientific and technological applications. Ongoing research continuously reveals new aspects of this crucial isotope, paving the way for advancements in energy production, materials science, and our understanding of the natural world. The careful study of Uranium-238's neutron count and its consequent properties remains a significant area of scientific endeavor.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Unit Of Energy In Si Units Is
Apr 02, 2025
-
How To Find The Mean Of A Probability Distribution
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Do Producers Get Their Energy
Apr 02, 2025
-
The Number Of Protons In An Atom Is That Elements
Apr 02, 2025
-
Is Magnesium Oxide Ionic Or Covalent
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Neutrons Does Uranium 238 Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
