How Many Neutrons Does Chromium Have
listenit
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
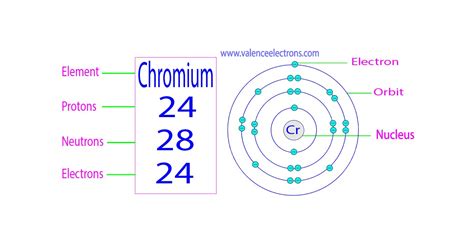
Table of Contents
How Many Neutrons Does Chromium Have? A Deep Dive into Isotopes and Nuclear Structure
Chromium, a lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal, is a fascinating element with a rich variety of applications, from stainless steel production to nutritional supplements. But beyond its practical uses lies a complex nuclear structure, and a key aspect of this structure is the number of neutrons found in its various isotopes. This article will delve deep into the world of chromium isotopes, exploring the number of neutrons each possesses and the factors influencing this number. We'll also touch on the implications of neutron count for chromium's properties and applications.
Understanding Isotopes and Atomic Structure
Before we dive into the specifics of chromium's neutron count, it's crucial to understand the fundamental concepts of isotopes and atomic structure. Every atom consists of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by orbiting electrons.
- Protons: Positively charged particles that determine the element's atomic number. Chromium's atomic number is 24, meaning every chromium atom has 24 protons.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles residing in the nucleus alongside protons. The number of neutrons can vary within the same element, giving rise to isotopes.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus. The number of electrons generally equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
- Isotopes: Atoms of the same element (same number of protons) but with different numbers of neutrons. This difference in neutron number affects the atom's mass and sometimes its stability.
The mass number of an atom is the total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. Since the number of protons is fixed for a given element, isotopes are identified by their mass number. For example, Chromium-52 (⁵²Cr) indicates a chromium isotope with a mass number of 52.
Chromium Isotopes: A Spectrum of Neutron Counts
Chromium exhibits several naturally occurring isotopes, each with a different number of neutrons. The most common isotopes and their neutron counts are:
- ⁵⁰Cr: Mass number 50. Number of neutrons: 50 - 24 (protons) = 26 neutrons. This isotope accounts for a small percentage of naturally occurring chromium.
- ⁵¹Cr: Mass number 51. Number of neutrons: 51 - 24 = 27 neutrons. This isotope is radioactive and has a relatively short half-life.
- ⁵²Cr: Mass number 52. Number of neutrons: 52 - 24 = 28 neutrons. This is the most abundant isotope of chromium, making up approximately 83.79% of naturally occurring chromium.
- ⁵³Cr: Mass number 53. Number of neutrons: 53 - 24 = 29 neutrons. This isotope makes up a significant portion of naturally occurring chromium.
- ⁵⁴Cr: Mass number 54. Number of neutrons: 54 - 24 = 30 neutrons. This isotope is less abundant than ⁵²Cr and ⁵³Cr but still present in appreciable amounts.
It's important to note that several other chromium isotopes exist, but these are either extremely rare in nature or artificially produced in laboratories. These less common isotopes also possess varying numbers of neutrons, often making them radioactive.
Factors Influencing Neutron Number in Isotopes
The number of neutrons in a chromium isotope is not arbitrary; it's governed by several factors, including:
-
Nuclear Stability: The ratio of protons to neutrons plays a crucial role in determining the stability of an atomic nucleus. For lighter elements, a roughly equal number of protons and neutrons often leads to stability. However, as the atomic number increases, the optimal neutron-to-proton ratio shifts, favoring a higher neutron count for stability. Isotopes with neutron numbers significantly deviating from this optimum tend to be radioactive.
-
Nuclear Forces: The strong nuclear force holds protons and neutrons together in the nucleus. This force is short-ranged, meaning it only operates effectively over very small distances. The number of neutrons influences the strength and effectiveness of this force, impacting nuclear stability.
-
Shell Model of the Nucleus: Similar to how electrons are arranged in shells around the nucleus, neutrons and protons also occupy distinct energy levels or shells within the nucleus. Certain neutron numbers corresponding to filled shells lead to enhanced stability, while partially filled shells can result in instability.
The Importance of Neutron Number in Chromium's Properties
The number of neutrons in a chromium atom significantly impacts several of its properties:
-
Mass: The most obvious effect is on the atomic mass. Isotopes with more neutrons are heavier. This difference in mass can be relevant in various applications, such as isotopic separation techniques.
-
Nuclear Stability and Radioactivity: As mentioned, isotopes with neutron numbers outside the stable range tend to be radioactive. This radioactivity can have implications for safety, handling, and potential applications in areas like medical imaging or radiotherapy.
-
Chemical Properties: While the number of neutrons doesn't directly impact the chemical behavior of an element, the isotopic composition can influence the overall properties of a chromium sample. This is particularly relevant in high-precision applications where subtle differences in mass or radioactivity can affect performance.
Applications of Chromium and its Isotopes
Chromium's various isotopes find applications in diverse fields:
-
Metallurgy: Chromium's high hardness and corrosion resistance make it an essential component of stainless steel and various alloys. The isotopic composition of the chromium used in these alloys typically isn't a critical factor, but it could subtly influence the material's properties.
-
Chromium Plating: Chromium plating is used to enhance the surface hardness, corrosion resistance, and appearance of metal objects. Again, the isotopic composition generally isn't a crucial factor for this application.
-
Nutritional Supplements: Chromium is an essential trace mineral involved in glucose metabolism. Supplements often use naturally occurring chromium, with its mixture of stable isotopes. The isotopic composition is not a primary concern here.
-
Nuclear Research: Radioactive chromium isotopes, such as ⁵¹Cr, find uses as tracers in various scientific studies and industrial applications. The controlled radioactivity allows scientists to track the movement and distribution of chromium in different systems.
Conclusion: The Significance of Neutron Count in Chromium
Understanding the number of neutrons in chromium's various isotopes is essential for comprehending the element's properties and behavior. While the number of protons dictates the element's identity, the varying neutron counts lead to differences in mass, stability, and potentially, subtle variations in the element's macroscopic properties. The most abundant isotope, ⁵²Cr, has 28 neutrons, showcasing the strong influence of the neutron-to-proton ratio in determining nuclear stability. The diverse applications of chromium, from everyday materials to specialized scientific research, highlight the importance of understanding its isotopic composition, including the number of neutrons each isotope possesses. Future research continues to explore the fine details of nuclear structure and the influence of neutron count on the properties and applications of elements like chromium. This knowledge continues to drive advancements in various scientific and technological fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
5 Converted To A Decimal Is
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Long Does It Take To Get To The Venus
Apr 02, 2025
-
03 Miles Is How Many Feet
Apr 02, 2025
-
Ions How Are Ions Made From Neutral Atoms
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Many Ounces Is 280 Grams
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Neutrons Does Chromium Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
