How Many Electrons Does Cobalt Have
listenit
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
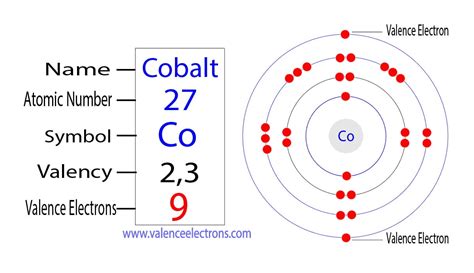
Table of Contents
How Many Electrons Does Cobalt Have? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Cobalt, a transition metal with the symbol Co and atomic number 27, plays a fascinating role in various scientific fields, from chemistry and materials science to biology and medicine. Understanding its atomic structure, particularly the number of electrons it possesses, is fundamental to grasping its properties and behavior. This comprehensive article delves into the specifics of cobalt's electron configuration, exploring its implications for chemical bonding, magnetic properties, and its diverse applications.
The Simple Answer: 27 Electrons
The most straightforward answer to the question, "How many electrons does cobalt have?" is 27. This directly corresponds to its atomic number, which represents the number of protons in its nucleus and, in a neutral atom, the number of electrons orbiting the nucleus.
Diving Deeper: Electron Shells and Subshells
However, simply stating that cobalt has 27 electrons doesn't fully capture the complexity of its atomic structure. Electrons are arranged in specific energy levels, or shells, around the nucleus. These shells are further subdivided into subshells, denoted by the letters s, p, d, and f. Each subshell can hold a specific number of electrons:
- s subshell: Holds a maximum of 2 electrons.
- p subshell: Holds a maximum of 6 electrons.
- d subshell: Holds a maximum of 10 electrons.
- f subshell: Holds a maximum of 14 electrons.
Cobalt's Electron Configuration: A Detailed Look
The electron configuration of cobalt, which describes the arrangement of its 27 electrons across the shells and subshells, is [Ar] 3d⁷ 4s². Let's break this down:
-
[Ar]: This represents the electron configuration of argon, a noble gas with 18 electrons. This notation is a shorthand way of indicating that the first 18 electrons of cobalt are arranged identically to those in argon. This is because the first three electron shells are filled completely.
-
3d⁷: This indicates that there are seven electrons in the 3d subshell. The "3" represents the principal quantum number, signifying the energy level, while "d" represents the type of subshell.
-
4s²: This indicates that there are two electrons in the 4s subshell. This subshell fills before the 3d subshell is completely filled, due to subtle energy level differences.
Therefore, the complete electron configuration of cobalt is: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d⁷ 4s².
Implications of the Electron Configuration
Cobalt's electron configuration is crucial to understanding its properties:
-
Chemical Bonding: The seven electrons in the 3d subshell and the two electrons in the 4s subshell are valence electrons, meaning they participate in chemical bonding. Cobalt can readily lose these electrons to form various cations (positively charged ions), commonly Co²⁺ and Co³⁺. This explains its ability to form a wide range of compounds.
-
Magnetic Properties: The partially filled 3d subshell is responsible for cobalt's strong magnetic properties. The unpaired electrons in this subshell create a net magnetic moment, making cobalt a ferromagnetic material, meaning it can be permanently magnetized. This property is exploited in numerous applications, including magnets and magnetic storage devices.
-
Catalytic Activity: Cobalt's ability to easily change its oxidation state (lose or gain electrons) makes it an excellent catalyst. It's used in various catalytic processes, such as the Fischer-Tropsch process for synthesizing hydrocarbons.
Isotopes and Electron Variations
While the most common isotope of cobalt, Cobalt-59, has 27 electrons, isotopes exist with varying numbers of neutrons. The number of protons and thus electrons remains constant, defining the element itself. However, different isotopes might have slightly different properties due to the differing neutron numbers, though the electronic structure remains largely consistent.
Cobalt's Role in Biology and Medicine
Cobalt also plays a vital role in biological systems. It's a component of vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, which is essential for human health. Vitamin B12 is crucial for red blood cell formation, nerve function, and DNA synthesis. The cobalt ion in vitamin B12 is coordinated to a corrin ring and is involved in crucial enzymatic reactions.
The radioactive isotope Cobalt-60 is widely used in radiotherapy to treat cancer. Its gamma rays can damage cancer cells, effectively destroying them. This application highlights another facet of cobalt’s significant impact on human lives.
Applications of Cobalt and its Compounds
The unique properties stemming from its electron configuration lead to a wide array of cobalt applications:
-
Magnets: Powerful permanent magnets are made from cobalt alloys, such as Alnico (aluminum, nickel, cobalt) magnets, renowned for their high magnetic strength.
-
Superalloys: Cobalt-based superalloys are used in high-temperature applications, such as gas turbine blades in jet engines and industrial gas turbines. Their high strength and resistance to oxidation make them suitable for such demanding conditions.
-
Batteries: Cobalt is a crucial component in lithium-ion batteries, which power many portable electronic devices and electric vehicles. Its ability to readily accept and release electrons allows it to contribute to the battery’s high energy density. However, ethical sourcing of cobalt for batteries is a growing concern.
-
Catalysis: Cobalt catalysts find applications in various chemical processes, from petroleum refining to the production of synthetic fuels.
-
Pigments: Cobalt compounds are used to produce various blue and green pigments, used in paints, ceramics, and glass. Cobalt blue, for example, is a highly valued and stable pigment.
-
Electroplating: Cobalt electroplating is used to create a hard, wear-resistant coating on metal parts.
Conclusion: A Versatile Element
In conclusion, cobalt's 27 electrons are not just a number; they represent a fundamental aspect of its atomic structure that dictates its versatile properties. The specific arrangement of these electrons in shells and subshells, particularly the partially filled 3d subshell, is responsible for its magnetic properties, its catalytic activity, and its ability to form a variety of compounds. This has led to its extensive use in various industries, from high-tech applications to essential biological processes, solidifying its position as a vital element in modern society. Further research into cobalt's properties continues to uncover new applications and possibilities, highlighting the continuing importance of understanding its fundamental atomic structure. From the simple answer of 27 electrons to the complex interplay of its electronic configuration with its chemical and physical properties, the story of cobalt is one of scientific fascination and practical significance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Square Root Of 150 In Simplest Radical Form
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Are The Basic Units Of Living Matter
Mar 28, 2025
-
34 As A Fraction In Simplest Form
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Electrons Can P Orbital Hold
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 3
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Electrons Does Cobalt Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
