How Many Electrons Are In O2
listenit
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
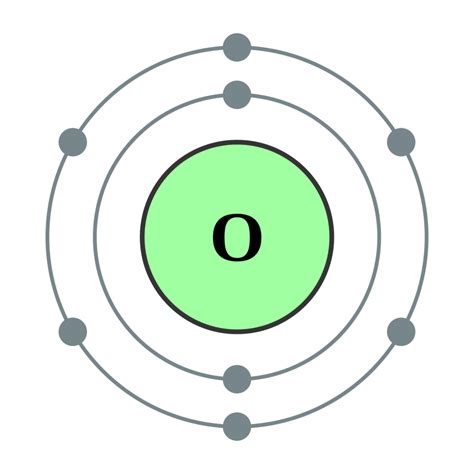
Table of Contents
How Many Electrons Are in O₂? A Deep Dive into Molecular Oxygen
Determining the number of electrons in a molecule like O₂ (dioxygen or molecular oxygen) might seem simple at first glance, but understanding the underlying principles reveals a deeper appreciation for atomic structure and chemical bonding. This article will explore not just the answer but the why behind it, delving into relevant concepts of atomic number, electron configuration, and covalent bonding.
Understanding Atomic Structure: The Foundation
Before we tackle the O₂ molecule, let's revisit the fundamentals of atomic structure. An atom is composed of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by orbiting electrons. The number of protons defines the element's atomic number and determines its identity. For oxygen (O), the atomic number is 8, meaning each oxygen atom possesses 8 protons in its nucleus. Crucially, in a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons. Therefore, a neutral oxygen atom has 8 electrons.
Electron Shells and Subshells: Organizing Electrons
Electrons don't orbit randomly; they occupy specific energy levels called shells and subshells. These shells are arranged in increasing energy levels, with electrons filling the lower energy levels first. The arrangement of electrons in an atom's shells is known as its electron configuration. For oxygen, the electron configuration is 1s²2s²2p⁴. Let's break this down:
- 1s²: The first shell (n=1) contains one subshell (s), holding a maximum of two electrons. Oxygen has two electrons in this subshell.
- 2s²: The second shell (n=2) contains two subshells (s and p). The 2s subshell holds a maximum of two electrons, and oxygen fills this subshell completely.
- 2p⁴: The 2p subshell can hold a maximum of six electrons, but oxygen only has four electrons in this subshell. This incompletely filled 2p subshell is crucial for understanding oxygen's reactivity.
Covalent Bonding in O₂: Sharing Electrons
Oxygen, being highly reactive, doesn't exist as individual atoms under normal conditions. Instead, it forms a stable diatomic molecule, O₂, through covalent bonding. Covalent bonding occurs when two atoms share electrons to achieve a more stable electron configuration, usually resembling a noble gas (full outer shell).
The Formation of the O₂ Double Bond
In O₂, each oxygen atom contributes its six valence electrons (electrons in the outermost shell). To achieve a stable octet (eight electrons in the outer shell), each oxygen atom shares two electrons with the other. This sharing forms a double covalent bond between the two oxygen atoms.
Imagine two oxygen atoms approaching each other. Each atom has four unpaired electrons in its 2p subshell. These unpaired electrons participate in the bond formation. Through the overlap of atomic orbitals, two pairs of electrons are shared between the two oxygen atoms, creating a double bond. This double bond is crucial for the stability and properties of the O₂ molecule.
Calculating the Total Number of Electrons in O₂
Now, let's answer the central question: How many electrons are in O₂?
Since each oxygen atom contributes 8 electrons, and there are two oxygen atoms in the molecule, the total number of electrons in O₂ is 16 electrons.
Deeper Dive into Molecular Orbital Theory
While the simplified Lewis structure and valence bond theory provide a good understanding of the O₂ double bond, a more accurate description requires molecular orbital theory. This theory describes the combination of atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals that encompass the entire molecule.
Molecular Orbitals and Bonding/Antibonding Orbitals
In molecular orbital theory, atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. These molecular orbitals can be bonding orbitals (lower energy, stabilizing the molecule) or antibonding orbitals (higher energy, destabilizing the molecule).
For O₂, the 2s and 2p atomic orbitals combine to form sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. The electron configuration of O₂ in molecular orbital terms is (σ₂s)²(σ₂s*)²(σ₂p)²(π₂p)⁴(π₂p*)². The asterisks (*) indicate antibonding orbitals.
Notice that despite the presence of antibonding electrons, the overall bond order (the difference between bonding and antibonding electrons divided by 2) is 2, corresponding to the double bond in the Lewis structure. This subtle difference highlights the increased accuracy of molecular orbital theory in explaining the properties of O₂ (such as its paramagnetism, a property due to the presence of unpaired electrons in the antibonding orbitals).
The Significance of Oxygen's Electron Configuration and Bonding
The specific electron configuration and bonding in O₂ explain its crucial role in biological processes and its chemical reactivity. The high electronegativity of oxygen, resulting from its electron configuration, enables it to form strong bonds with other elements and participate in various oxidation reactions.
Oxygen's involvement in respiration, where it acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, is a prime example of its importance. The energy released during this process is vital for powering cellular activities.
Conclusion: More Than Just a Number
While the simple answer to "How many electrons are in O₂?" is 16, the journey to arrive at that answer provides a deeper understanding of atomic structure, chemical bonding, and the fundamental principles of chemistry. Exploring the electron configuration of individual oxygen atoms, the formation of covalent bonds, and the intricacies of molecular orbital theory illuminates the underlying reasons behind O₂'s properties and its crucial role in our world. The number 16 isn't just a count; it's a representation of the intricate dance of electrons that creates one of the most important molecules on Earth. This knowledge empowers a deeper comprehension of chemistry and its relevance to the world around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Conjugate Acid Of Oh
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Are The Raw Materials For Photosynthesis
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is An Equivalent Fraction To 3 4
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Two Elements Have Similar Characteristics
Mar 25, 2025
-
5r 2 44r 120 30 11r
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Electrons Are In O2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
