How Many Degrees Fahrenheit In 1 Degree Celsius
listenit
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
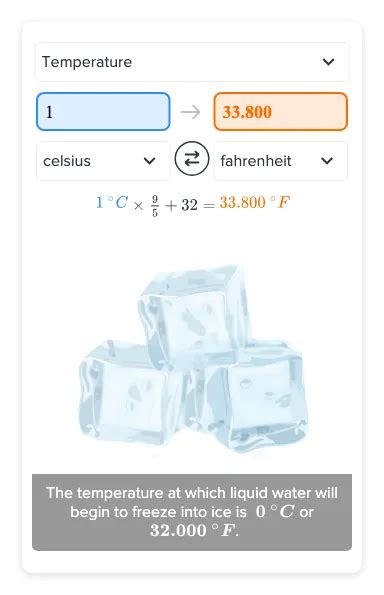
Table of Contents
How Many Degrees Fahrenheit are in 1 Degree Celsius? A Deep Dive into Temperature Conversions
The question, "How many degrees Fahrenheit are in 1 degree Celsius?" seems simple at first glance. However, a deeper understanding reveals a fascinating relationship between these two common temperature scales, involving more than just a simple conversion factor. This article will delve into the intricacies of Celsius and Fahrenheit, explaining their origins, differences, and the precise mathematical relationship between them, ultimately providing a comprehensive answer to the core question and exploring related concepts.
Understanding the Celsius and Fahrenheit Scales
Before tackling the conversion, let's understand the foundation of each scale.
The Celsius Scale: A Centigrade System
The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is a metric system temperature scale named after Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius. It's based on the freezing and boiling points of water at standard atmospheric pressure.
- 0°C: The freezing point of water.
- 100°C: The boiling point of water.
The scale is divided into 100 equal degrees between these two points, making it a relatively straightforward and easily understood system. Its widespread use globally stems from its integration within the metric system, promoting consistency in scientific measurements and everyday applications.
The Fahrenheit Scale: A More Complex History
The Fahrenheit scale, developed by German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, uses a different reference point.
- 32°F: The freezing point of water.
- 212°F: The boiling point of water.
The scale is divided into 180 degrees between these points, resulting in smaller degree increments compared to Celsius. The choice of these specific reference points in Fahrenheit is somewhat arbitrary, historically linked to Fahrenheit's experiments using brine solutions and human body temperature. Its continued use, primarily in the United States, is a testament to historical inertia and established usage.
The Conversion Formula: Unraveling the Relationship
The relationship between Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F) is not a simple ratio. It's a linear relationship, meaning that a change in one scale corresponds to a proportional change in the other, but the proportionality constant is not 1. The conversion formula is:
°F = (9/5)°C + 32
This equation reveals several key aspects:
-
(9/5) Multiplier: This factor accounts for the difference in the size of a degree between the two scales. A Fahrenheit degree is smaller than a Celsius degree (180 degrees span the same range as 100 degrees).
-
+32 Offset: This constant adds the difference in the zero points between the two scales. The freezing point of water is 0°C but 32°F. This offset ensures the conversion accurately reflects the different starting points.
Now, let's apply the formula to answer our core question:
How Many Degrees Fahrenheit are in 1 Degree Celsius?
Substituting °C = 1 into the conversion formula:
°F = (9/5) * 1 + 32 = 1.8 + 32 = 33.8°F
Therefore, there are 33.8 degrees Fahrenheit in 1 degree Celsius. This means that a 1°C increase corresponds to a 1.8°F increase. This is not intuitive, and understanding the formula is crucial to avoid common conversion errors.
Practical Applications and Examples
Understanding this conversion isn't just an academic exercise; it has numerous practical applications:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes frequently specify temperatures in either Celsius or Fahrenheit. Accurate conversion is vital for successful cooking. For instance, a recipe calling for 175°C would require converting to Fahrenheit for ovens calibrated using that scale.
-
Weather Reporting: Many countries use Celsius, while others use Fahrenheit. Converting between the scales is essential for understanding weather forecasts accurately. Knowing that a temperature of 20°C is equivalent to 68°F allows for a clear comparison.
-
Scientific Research: Researchers often work with data expressed in different temperature scales. Converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit is necessary to ensure consistency and comparability of results. Many scientific instruments may offer output in either scale, requiring users to readily convert between them.
-
Engineering and Industry: Many industrial processes and engineering calculations depend on accurate temperature measurements. Conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit is essential for ensuring equipment functions correctly and meets specified parameters. For example, processes involving specific heat transfer calculations would require consistent temperature units.
Beyond the Basic Conversion: Exploring Further Concepts
While the basic conversion formula suffices for most situations, a deeper understanding involves additional concepts:
-
Absolute Zero: Both Celsius and Fahrenheit are relative scales. Absolute zero, the theoretical lowest possible temperature, is represented differently on each scale. In Kelvin (K), the absolute temperature scale, absolute zero is 0 K. The conversion from Celsius to Kelvin is: K = °C + 273.15. A similar conversion exists for Fahrenheit and Rankine (R), another absolute scale.
-
Temperature Gradients: Understanding the relationship between temperature changes in Celsius and Fahrenheit is crucial in applications involving heat transfer and thermal expansion. The consistent 9/5 ratio highlights the difference in the sensitivity of each scale to temperature changes.
-
Nonlinear Effects: At extremely high or low temperatures, the relationship between Celsius and Fahrenheit may not perfectly adhere to the linear conversion formula, due to physical phenomena influencing the behavior of materials under extreme thermal conditions.
Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversions
Mastering the conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit is an essential skill across various fields. This article has provided a detailed explanation of the conversion formula, its practical applications, and broader concepts related to temperature measurement. Remembering that 1 degree Celsius is equal to 33.8 degrees Fahrenheit provides a quick answer to the core question, but understanding the underlying principles of the conversion ensures accurate and meaningful interpretation of temperature data in any context. While a simple numerical answer can be easily found, understanding the mathematical reasoning behind the conversion makes the difference between simple knowledge and true comprehension of this important scientific concept. The ability to seamlessly convert between these scales empowers accurate data analysis and fosters a deeper appreciation of the interplay between these two fundamentally different systems of temperature measurement.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
45 As A Fraction In Simplest Form
Mar 21, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Scalar Quantity
Mar 21, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 14 21
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is The Correct Formula For Cellular Respiration
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Cr Have
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Degrees Fahrenheit In 1 Degree Celsius . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
