How Far Is Jupiter From The Sun In Astronomical Units
listenit
Mar 30, 2025 · 5 min read
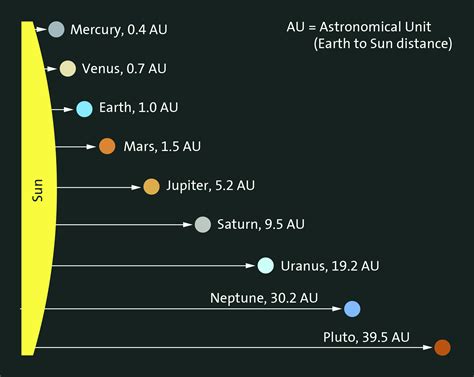
Table of Contents
How Far is Jupiter From the Sun in Astronomical Units? A Deep Dive into Jupiter's Orbit
Jupiter, the solar system's largest planet, holds a captivating place in our celestial neighborhood. Understanding its distance from the sun is crucial to comprehending its formation, characteristics, and influence on the surrounding planetary bodies. While the distance fluctuates due to its elliptical orbit, expressing it in Astronomical Units (AU) provides a convenient and standardized measure. This article delves deep into the specifics of Jupiter's distance from the sun, exploring the concept of AU, the factors influencing the distance variation, and the implications of this distance for Jupiter's environment and the broader solar system.
Understanding Astronomical Units (AU)
Before we delve into Jupiter's specific distance, let's define the fundamental unit of measurement: the Astronomical Unit (AU). An AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. It's approximately 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles). Using AU as a standard simplifies calculations and comparisons of distances within our solar system, making it a convenient and widely accepted unit in astronomy.
Jupiter's Average Distance from the Sun in AU
Jupiter's orbit isn't a perfect circle; it's slightly elliptical. This means its distance from the sun varies throughout its orbital period. However, we can define an average distance. Jupiter's average distance from the sun is approximately 5.2 AU. This means it's about 5.2 times farther from the sun than Earth.
Variations in Jupiter's Distance: Perihelion and Aphelion
Because Jupiter's orbit is elliptical, its distance from the sun fluctuates. These variations are defined by two key points:
Perihelion: Closest Approach
Perihelion is the point in Jupiter's orbit where it is closest to the sun. At perihelion, Jupiter is approximately 4.95 AU from the sun.
Aphelion: Farthest Point
Aphelion, on the other hand, represents the point in Jupiter's orbit where it's farthest from the sun. At aphelion, Jupiter's distance from the sun reaches approximately 5.45 AU.
Calculating Jupiter's Distance at Any Given Time
Determining Jupiter's precise distance from the sun at any particular moment requires sophisticated calculations involving Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion and precise orbital elements. These calculations consider the planet's orbital eccentricity (a measure of how elliptical the orbit is), its semi-major axis (half of the longest diameter of the ellipse), and its current position along its orbital path. Astronomers and space agencies regularly use these calculations for navigation and mission planning involving spacecraft exploring the Jovian system.
The Implications of Jupiter's Distance
Jupiter's significant distance from the sun profoundly affects its environment and characteristics.
Sunlight and Temperature
The intensity of sunlight diminishes with distance. Being 5.2 AU from the sun, Jupiter receives considerably less sunlight than Earth. This results in a significantly lower average temperature, although the planet's internal heat source plays a crucial role in maintaining its atmospheric dynamics.
Orbital Period
Due to its greater distance from the sun, Jupiter's orbital period—the time it takes to complete one revolution around the sun—is much longer than Earth's. A Jovian year is equivalent to roughly 11.86 Earth years.
Atmospheric Composition and Dynamics
The lower solar energy flux at Jupiter's distance influences the composition and dynamics of its atmosphere. The planet's massive size and strong internal heat contribute to its characteristic swirling storms, including the Great Red Spot, a massive anticyclonic storm that has persisted for centuries.
Magnetic Field
Jupiter possesses an incredibly powerful magnetic field, much stronger than Earth's. The distance from the sun doesn't directly determine the strength of the magnetic field, but it does influence the interaction between the magnetic field and the solar wind. The solar wind, a stream of charged particles from the sun, interacts differently with Jupiter's magnetosphere at its distance compared to the interaction with Earth's magnetosphere.
Jupiter's Influence on the Solar System
Jupiter's significant mass and distance play a key role in shaping the solar system's dynamics:
Gravitational Influence
Jupiter's immense gravitational pull influences the orbits of other planets, asteroids, and comets. It acts as a gravitational shepherd, influencing the distribution of objects in the asteroid belt and protecting the inner planets from potentially hazardous asteroid impacts. The gravitational interactions between Jupiter and other planets are crucial in maintaining the overall stability of the solar system.
Protection of the Inner Solar System
Jupiter's immense gravity acts as a shield for the inner planets. It captures many comets and asteroids that would otherwise have collided with Earth and other inner planets. This protective role has been suggested as a crucial factor in the development of life on Earth.
Formation of the Solar System
The distance of Jupiter from the sun played a significant role in the initial formation of the solar system. Its formation and migration within the early solar system significantly influenced the distribution of mass and the formation of other planets.
Observing Jupiter
Jupiter's brightness makes it easily visible to the naked eye, even at its considerable distance from the sun. With binoculars or a small telescope, its four largest moons (Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto), also known as the Galilean moons, can be observed. Larger telescopes reveal the planet's atmospheric details, such as the Great Red Spot and cloud bands.
Conclusion
Jupiter's average distance from the sun, approximately 5.2 AU, is a fundamental aspect of its nature and its impact on the solar system. This distance determines the intensity of sunlight it receives, its orbital period, and its atmospheric characteristics. Moreover, its gravitational influence, related to both its mass and its location, significantly shapes the dynamics of the entire solar system, contributing to its overall stability and even potentially influencing the conditions that allowed life to flourish on Earth. By understanding Jupiter's distance and its implications, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and interconnectedness of our celestial neighborhood. Further exploration and observation of Jupiter will undoubtedly continue to unveil new insights into this magnificent planet and its vital role in the solar system's story.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 30 And 45
Apr 01, 2025
-
How To Go From Grams To Molecules
Apr 01, 2025
-
3 As A Percentage Of 8
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is 20 Off Of 600
Apr 01, 2025
-
Why Is Dna Replication Described As Semi Conservative
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Far Is Jupiter From The Sun In Astronomical Units . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
