Greatest Common Factor Of 72 And 54
listenit
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
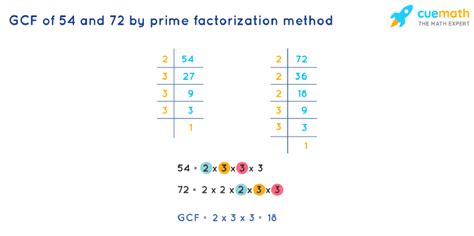
Table of Contents
Finding the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) of 72 and 54: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the greatest common factor (GCF), also known as the greatest common divisor (GCD), of two numbers is a fundamental concept in mathematics with applications across various fields, from simplifying fractions to solving algebraic equations. This comprehensive guide will delve into the process of determining the GCF of 72 and 54, exploring multiple methods and providing a deeper understanding of the underlying principles. We'll also touch upon the broader applications and significance of finding the GCF in different mathematical contexts.
Understanding the Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
Before we dive into calculating the GCF of 72 and 54, let's clarify the definition. The greatest common factor (GCF) of two or more integers is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the biggest number that perfectly divides both numbers.
Why is finding the GCF important?
The GCF plays a crucial role in numerous mathematical operations and problem-solving scenarios:
- Simplifying Fractions: The GCF helps in reducing fractions to their simplest form. By dividing both the numerator and denominator by their GCF, we obtain an equivalent fraction with smaller, more manageable numbers.
- Solving Equations: The GCF is frequently used in solving algebraic equations, particularly those involving factoring expressions.
- Geometry: The concept is applied in geometry when dealing with problems related to area, volume, and finding common dimensions.
- Number Theory: GCF is a cornerstone concept in number theory, forming the basis for more advanced topics like modular arithmetic and Diophantine equations.
Methods for Finding the GCF of 72 and 54
Several methods exist for determining the GCF of two numbers. We'll explore three prominent approaches:
1. Listing Factors Method
This method involves listing all the factors of each number and identifying the largest common factor.
Factors of 72: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 72
Factors of 54: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18, 27, 54
By comparing the two lists, we observe that the common factors are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18. The greatest of these common factors is 18. Therefore, the GCF of 72 and 54 is 18.
This method is straightforward for smaller numbers but can become cumbersome for larger numbers with numerous factors.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method involves expressing each number as a product of its prime factors. The GCF is then found by multiplying the common prime factors raised to the lowest power.
Prime Factorization of 72:
72 = 2 x 36 = 2 x 2 x 18 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 9 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 = 2³ x 3²
Prime Factorization of 54:
54 = 2 x 27 = 2 x 3 x 9 = 2 x 3 x 3 x 3 = 2 x 3³
Now, let's identify the common prime factors: both numbers have one factor of 2 and two factors of 3.
GCF = 2¹ x 3² = 2 x 9 = 18
Therefore, the GCF of 72 and 54 is 18. This method is generally more efficient than the listing factors method, especially for larger numbers.
3. Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean algorithm is a highly efficient method for finding the GCF, especially for larger numbers. It's based on the principle that the GCF of two numbers does not change if the larger number is replaced by its difference with the smaller number. This process is repeated until the two numbers become equal, which represents their GCF.
Let's apply the Euclidean algorithm to 72 and 54:
- 72 ÷ 54 = 1 with a remainder of 18
- Now, we replace the larger number (72) with the remainder (18): 54 ÷ 18 = 3 with a remainder of 0
Since the remainder is 0, the GCF is the last non-zero remainder, which is 18.
Applications of GCF: Real-World Examples
The concept of the greatest common factor extends beyond theoretical mathematics and finds practical applications in various real-world scenarios. Here are a few examples:
-
Dividing items evenly: Imagine you have 72 apples and 54 oranges, and you want to divide them into identical bags such that each bag contains the same number of apples and oranges, and no fruit is left over. The GCF (18) tells us that you can create 18 bags, each containing 4 apples (72/18) and 3 oranges (54/18).
-
Simplifying measurements: In construction or engineering, you might need to work with measurements expressed in different units. Finding the GCF helps simplify these measurements to their simplest form. For example, if you have two pieces of wood measuring 72 inches and 54 inches, you could divide them into identical smaller pieces of 18 inches each.
-
Recipe scaling: Let's say you have a recipe that requires 72 grams of flour and 54 grams of sugar. To reduce the recipe's size, you can divide both quantities by their GCF (18). This would give you a smaller recipe that still maintains the same proportions: 4 grams of flour and 3 grams of sugar.
Beyond Two Numbers: Extending the GCF Concept
While we've focused on finding the GCF of two numbers, the concept can be extended to three or more numbers. The prime factorization method remains particularly useful in these cases. For example, to find the GCF of 72, 54, and 36:
- Prime factorization of 72: 2³ x 3²
- Prime factorization of 54: 2 x 3³
- Prime factorization of 36: 2² x 3²
The common prime factors are 2 and 3. The lowest powers are 2¹ and 3². Therefore, the GCF of 72, 54, and 36 is 2¹ x 3² = 18.
Conclusion: Mastering the GCF
Understanding and applying the GCF is a crucial skill in various mathematical contexts. Whether you're simplifying fractions, solving equations, or tackling real-world problems, mastering the different methods for finding the GCF – including listing factors, prime factorization, and the Euclidean algorithm – empowers you to approach these challenges with efficiency and confidence. The ability to identify and utilize the GCF not only enhances your mathematical proficiency but also lays a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. This detailed exploration of finding the GCF of 72 and 54, along with its diverse applications, serves as a solid starting point for deeper mathematical explorations. Remember to practice consistently to solidify your understanding and develop fluency in applying these techniques.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is An Arithmetic Sequence
Mar 24, 2025
-
Taylor Series Expansion Of Ln 1 X
Mar 24, 2025
-
45 Is What Percent Of 36
Mar 24, 2025
-
How Does A Igneous Rock Become A Sedimentary Rock
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is 1 6 Of A Cup
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Greatest Common Factor Of 72 And 54 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
