Graph Of X 2 Y 2 4
listenit
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
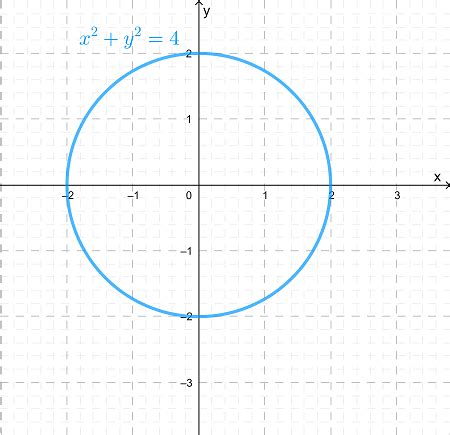
Table of Contents
Exploring the Graph of x² + y² = 4: A Comprehensive Guide
The equation x² + y² = 4 represents a fundamental concept in coordinate geometry: the circle. Understanding its graph involves exploring its properties, characteristics, and the broader mathematical context within which it resides. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of this equation, providing a detailed analysis suitable for students and enthusiasts alike.
Understanding the Equation x² + y² = 4
At its core, x² + y² = 4 is the equation of a circle centered at the origin (0, 0) with a radius of 2. Let's break down why:
The Pythagorean Theorem and the Circle
The equation is a direct application of the Pythagorean theorem, a cornerstone of geometry. Recall that the Pythagorean theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
In the context of our equation, consider a point (x, y) on the circle. The distance from this point to the origin (0, 0) forms the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle. The horizontal distance (x) and the vertical distance (y) are the other two sides. Therefore, applying the Pythagorean theorem, we get:
x² + y² = r²
where 'r' represents the radius of the circle. In our equation, x² + y² = 4, we can see that r² = 4, meaning the radius r = 2.
Key Characteristics of the Circle
Several key characteristics define the circle represented by x² + y² = 4:
-
Center: The circle is centered at the origin (0, 0). This is evident because the equation is in the standard form (x - h)² + (y - k)² = r², where (h, k) represents the center and r represents the radius. In our case, h = 0, k = 0, and r = 2.
-
Radius: The radius of the circle is 2. This is the distance from the center to any point on the circle.
-
Diameter: The diameter of the circle is twice the radius, therefore 4.
-
Circumference: The circumference (the distance around the circle) is calculated using the formula 2πr, which in this case is 4π.
-
Area: The area enclosed by the circle is calculated using the formula πr², which gives us 4π.
Graphing the Circle
Graphing x² + y² = 4 is relatively straightforward:
-
Plot the Center: Mark the point (0, 0) on the coordinate plane.
-
Mark the Radius: From the center, measure a distance of 2 units in all four directions (up, down, left, and right). This gives you four points on the circle: (2, 0), (-2, 0), (0, 2), and (0, -2).
-
Draw the Circle: Connect these four points with a smooth curve to form the circle. A compass can be helpful for accuracy.
Transformations of the Circle Equation
The basic equation x² + y² = 4 can be transformed to represent circles with different centers and radii. Understanding these transformations is crucial for a complete grasp of the concept.
Translations
Translating the circle involves shifting its center. The general equation for a circle with center (h, k) and radius r is:
(x - h)² + (y - k)² = r²
For instance, (x - 3)² + (y + 2)² = 4 represents a circle with a center at (3, -2) and a radius of 2. This is simply the original circle shifted 3 units to the right and 2 units down.
Scaling
Scaling affects the radius of the circle. Multiplying the entire equation by a constant changes the radius. For example, 2x² + 2y² = 8 is equivalent to x² + y² = 4 and represents the same circle. However, an equation like x² + y² = 9 represents a circle with a radius of 3, a larger circle than our original.
Applications of the Circle Equation
The equation x² + y² = 4, and its more general form, finds applications in numerous fields:
Geometry and Trigonometry
Circles are fundamental shapes in geometry, used extensively in trigonometry to define angles and relationships between sides of triangles.
Physics
Circular motion, projectile motion, and wave phenomena often involve equations representing circles or parts of circles.
Computer Graphics and Game Development
Circles are essential elements in computer graphics for creating images, animations, and user interfaces. Game development utilizes circular equations for collision detection and pathfinding.
Engineering
Many engineering applications, such as designing gears, wheels, and other circular components, rely on understanding the properties of circles.
Advanced Concepts and Related Topics
Exploring the equation x² + y² = 4 leads to more advanced mathematical concepts:
Polar Coordinates
The equation of a circle can be expressed more simply using polar coordinates. In polar coordinates, a point is defined by its distance from the origin (r) and its angle (θ) from the positive x-axis. The equation x² + y² = 4 becomes simply r = 2 in polar coordinates.
Parametric Equations
A circle can also be defined using parametric equations. A common set of parametric equations for a circle with radius r is:
x = r cos(t) y = r sin(t)
where t is a parameter ranging from 0 to 2π. For x² + y² = 4, the parametric equations would be:
x = 2 cos(t) y = 2 sin(t)
Complex Numbers
The equation x² + y² = 4 can be interpreted in the context of complex numbers. If we let z = x + iy (where i is the imaginary unit), then |z|² = x² + y² = 4 represents a circle in the complex plane with radius 2 centered at the origin.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple equation x² + y² = 4 unlocks a wealth of mathematical concepts, illustrating the power of basic geometric principles. From its connection to the Pythagorean theorem to its applications in various fields, understanding this equation provides a strong foundation for further exploration in mathematics and related disciplines. By mastering the graph and transformations of this equation, one develops a deeper understanding of circles and their significance within a broader mathematical framework. The journey from a simple equation to a deeper comprehension of its implications underscores the elegance and power of mathematical reasoning.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Valence Electrons In Argon
Mar 17, 2025
-
1 1 X 2 Power Series
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Percent Of 75 Is 40
Mar 17, 2025
-
Translating Graph Up By 4 Units
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 3 2
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Graph Of X 2 Y 2 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
