Energy Measured In Units Is Called
listenit
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
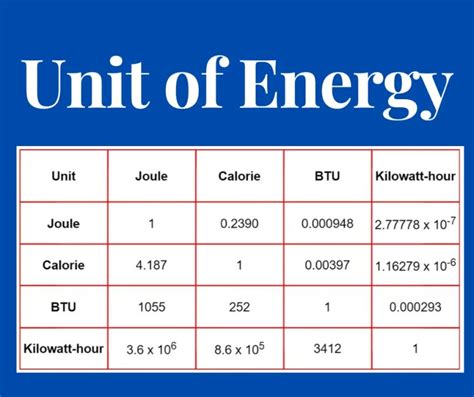
Table of Contents
Energy Measured in Units: A Comprehensive Guide
Energy is a fundamental concept in physics, representing the capacity of a system to perform work. Understanding energy, its various forms, and how it's measured is crucial across numerous scientific disciplines and everyday life. This comprehensive guide delves into the units used to measure energy, exploring their origins, applications, and interrelationships.
What is Energy?
Before diving into the units, let's briefly revisit the concept of energy itself. Energy exists in many forms, including:
- Kinetic Energy: The energy of motion. A moving car, a flying bird, even the atoms vibrating within a solid possess kinetic energy.
- Potential Energy: Stored energy due to position or configuration. A stretched rubber band, water held behind a dam, and a ball held high above the ground all possess potential energy.
- Thermal Energy (Heat): The energy associated with the random motion of atoms and molecules. This is related to temperature, with hotter objects possessing more thermal energy.
- Chemical Energy: Energy stored in the bonds between atoms and molecules. This energy is released during chemical reactions, such as burning fuel or digestion.
- Nuclear Energy: Energy stored within the nucleus of an atom. Nuclear reactions, like fission and fusion, release vast amounts of this energy.
- Radiant Energy (Electromagnetic Radiation): Energy that travels in the form of waves, such as light, radio waves, and X-rays.
- Electrical Energy: The energy associated with the flow of electric charge. This powers our homes, appliances, and electronic devices.
Energy can be converted from one form to another, but the total amount of energy in a closed system remains constant (this is the principle of conservation of energy).
Units of Energy: A Global Perspective
The units used to measure energy vary depending on the context and the system of units being used. However, all units represent the same fundamental quantity: the capacity to do work.
1. Joule (J) - The SI Unit of Energy
The joule (J) is the standard unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). One joule is defined as the energy transferred to an object when a force of one newton acts on that object in the direction of its motion through a distance of one meter. This can be expressed mathematically as:
1 J = 1 N⋅m (newton-meter)
The joule is a versatile unit, applicable across all forms of energy. It's widely used in physics, engineering, and other scientific fields. Its versatility stems from its fundamental definition based on force, distance, and work.
2. Other Common Units of Energy
While the joule is the primary SI unit, other units are commonly used, particularly in specific contexts:
- Calorie (cal): Originally defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius. The calorie is often used in nutrition and thermodynamics. It's important to note the distinction between the "small calorie" (cal) and the "large calorie" (kcal or Calorie), where 1 kcal = 1000 cal.
- Kilowatt-hour (kWh): This unit is commonly used in the context of electricity. One kilowatt-hour represents the energy consumed by a 1-kilowatt device operating for one hour. It's a practical unit for measuring energy consumption in homes and industries. The conversion to joules is: 1 kWh = 3.6 x 10⁶ J.
- Electronvolt (eV): This unit is frequently used in atomic and nuclear physics. One electronvolt is the energy gained by a single electron when it accelerates through a potential difference of one volt. It's a very small unit, often expressed in multiples like keV (kilo-electronvolt) or MeV (mega-electronvolt). 1 eV = 1.602 x 10⁻¹⁹ J.
- British Thermal Unit (BTU): This unit is primarily used in the United States and some other countries. One BTU is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. It's often used in heating and cooling calculations.
3. Understanding Unit Conversions
Converting between different units of energy is often necessary. This requires using appropriate conversion factors. For example:
- Joules to Calories: 1 cal ≈ 4.184 J
- Joules to Kilowatt-hours: 1 kWh = 3.6 x 10⁶ J
- Calories to BTU: 1 BTU ≈ 252 cal
Mastering these conversions is crucial for accurate calculations and comparisons in various energy-related applications.
Applications of Energy Units in Different Fields
The choice of energy unit often depends on the specific application.
1. Physics and Engineering
In physics and engineering, the joule (J) is the predominant unit due to its direct relationship to work and force. Calculations involving kinetic energy, potential energy, work done, and power all frequently utilize the joule.
2. Thermodynamics
In thermodynamics, both joules and calories (or kilocalories) are common. Calories are often used when dealing with heat transfer and specific heat capacities.
3. Electrical Engineering
Kilowatt-hours (kWh) are widely used in electrical engineering and power systems to measure electricity consumption and generation. This unit is practical for billing purposes and large-scale energy management.
4. Nuclear Physics
In nuclear physics, the electronvolt (eV) and its multiples are preferred. These units are convenient for describing the energies of particles and the energy released in nuclear reactions.
5. Nutrition and Food Science
Calories (kcal or Calorie) are the standard unit for measuring the energy content of food. This allows individuals to track their energy intake and manage their weight.
Energy Measurement Techniques
Measuring energy often involves indirect measurements related to the effects of energy. Some common techniques include:
- Calorimetry: This technique measures heat transfer to determine the energy content of substances. A calorimeter measures the temperature change of a known mass of water to calculate the heat absorbed or released.
- Photometry: This measures the radiant energy (light) by determining the intensity of light sources.
- Power Meters: These devices measure the rate of energy consumption or production (power) over a period, allowing for the calculation of total energy usage.
The Importance of Energy Units and Conservation
Accurate measurement of energy is critical for numerous reasons:
- Efficient Resource Management: Understanding energy consumption helps in optimizing energy usage in homes, industries, and transportation, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
- Technological Advancement: Precise energy measurements are essential for developing and improving energy-efficient technologies, renewable energy sources, and energy storage systems.
- Scientific Understanding: Accurate energy measurements are fundamental to advancing our knowledge in physics, chemistry, and other scientific fields. They underpin our understanding of fundamental processes and interactions in the universe.
- Environmental Sustainability: Precise measurements are crucial for monitoring energy production and consumption patterns, enabling informed decisions about sustainable energy practices and reducing carbon emissions.
In conclusion, understanding the various units of energy and their applications is crucial for navigating the complexities of the modern world. From calculating the energy content of food to designing efficient power systems, mastering energy units is essential for scientific advancement, technological innovation, and environmental sustainability. The joule, as the SI unit, provides a fundamental framework for understanding and quantifying this vital aspect of the universe. However, the choice of the most appropriate unit depends heavily on the specific context and application.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 5 9 In Decimal Form
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Many Grams In 8 Kilograms
Apr 02, 2025
-
12x 4y 20 Solve For Y
Apr 02, 2025
-
Most Reactive Group On The Periodic Table
Apr 02, 2025
-
How To Solve Multi Step Inequalities
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Energy Measured In Units Is Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
