Effects Of Acid Rain In Germany
listenit
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
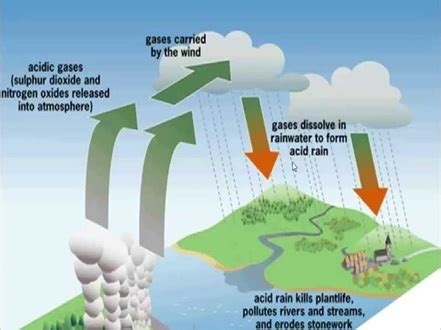
Table of Contents
- Effects Of Acid Rain In Germany
- Table of Contents
- The Devastating Effects of Acid Rain in Germany: A Comprehensive Overview
- Understanding Acid Rain: Causes and Chemistry
- Sources of SO2 and NOx Emissions:
- The Devastating Impact on German Forests
- 1. Soil Acidification and Nutrient Depletion:
- 2. Direct Damage to Foliage:
- 3. Increased Susceptibility to Pests and Diseases:
- Effects on German Lakes and Waterways
- 1. Acidification of Lakes and Streams:
- 2. Loss of Biodiversity:
- 3. Damage to Infrastructure:
- The Economic Consequences of Acid Rain in Germany
- 1. Forestry and Timber Industry:
- 2. Fisheries and Tourism:
- 3. Infrastructure Repair and Maintenance:
- Mitigation and Remediation Efforts in Germany
- 1. Emission Control Policies:
- 2. Vehicle Emission Standards:
- 3. International Cooperation:
- 4. Reforestation and Ecosystem Restoration:
- 5. Liming of Acidified Lakes:
- Conclusion: An Ongoing Challenge
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Devastating Effects of Acid Rain in Germany: A Comprehensive Overview
Germany, a nation known for its rich forests, pristine lakes, and vibrant ecosystems, faces a significant environmental challenge: acid rain. This phenomenon, primarily caused by the emission of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into the atmosphere, has profoundly impacted Germany's natural landscape and infrastructure for decades. This article delves deep into the effects of acid rain in Germany, exploring its causes, consequences, and the ongoing efforts to mitigate its damaging impact.
Understanding Acid Rain: Causes and Chemistry
Acid rain isn't just rain; it encompasses all forms of precipitation with acidic components, including snow, fog, and even dry deposition of acidic particles. The primary culprits behind acid rain are the aforementioned SO2 and NOx emissions. These gases react with water molecules in the atmosphere to form sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) and nitric acid (HNO₃), which then fall to the earth as acid rain.
Sources of SO2 and NOx Emissions:
-
Industrial Activities: Historically, the burning of fossil fuels (coal and oil) in power plants and industrial processes has been a major contributor to SO2 emissions. While Germany has made significant strides in reducing these emissions, industrial activities remain a factor.
-
Transportation: Vehicle exhaust is a significant source of NOx emissions, particularly in densely populated urban areas and along major highways. Diesel vehicles, in particular, have historically been a significant contributor.
-
Agriculture: Ammonia (NH₃) emissions from agricultural activities, though not a direct contributor to acid rain formation, can react in the atmosphere to form secondary pollutants that contribute to acidity.
-
International Transport: Transboundary pollution plays a significant role. Emissions from neighboring countries can be transported by wind patterns, contributing to acid rain in Germany. This highlights the need for international cooperation in addressing acid rain.
The Devastating Impact on German Forests
Germany's vast forests, a cornerstone of its natural heritage, are particularly vulnerable to acid rain. The acidic precipitation damages trees in several ways:
1. Soil Acidification and Nutrient Depletion:
Acid rain lowers the pH of soil, leaching essential nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and potassium. This nutrient depletion weakens trees, making them more susceptible to disease, pests, and harsh weather conditions. The acidic environment also mobilizes toxic metals like aluminum, which can further damage tree roots and hinder nutrient uptake. This effect is particularly pronounced in forests with thin or poorly buffered soils.
2. Direct Damage to Foliage:
The acidic components in rain directly damage the delicate tissues of tree leaves and needles. This damage reduces the tree's ability to photosynthesize, impacting its growth and overall health. Visible signs of damage include leaf discoloration, needle loss, and stunted growth.
3. Increased Susceptibility to Pests and Diseases:
Weakened trees by acid rain are more vulnerable to attacks from insects, fungi, and other pathogens. The compromised immune system of the trees makes them unable to effectively fight off these threats, leading to further damage and even mortality.
Effects on German Lakes and Waterways
Acid rain doesn't stop at the forests; its acidic nature also significantly impacts Germany's lakes and rivers:
1. Acidification of Lakes and Streams:
The acidic precipitation directly lowers the pH of surface waters. This acidification harms aquatic life by disrupting delicate ecosystems and making the water unsuitable for many species.
2. Loss of Biodiversity:
Many aquatic organisms, including fish, amphibians, and invertebrates, are highly sensitive to changes in water pH. Acidification leads to a decline in biodiversity, with some species disappearing completely from affected lakes and streams. The loss of these species has cascading effects on the entire aquatic food web.
3. Damage to Infrastructure:
Acid rain also corrodes infrastructure, including bridges, buildings, and pipelines, made of materials sensitive to acidic environments. This leads to increased maintenance costs and potential safety hazards. The corrosive effects are particularly noticeable on structures made of limestone, marble, and certain metals.
The Economic Consequences of Acid Rain in Germany
The effects of acid rain extend far beyond ecological damage. The economic implications are substantial:
1. Forestry and Timber Industry:
Reduced tree growth and increased tree mortality lead to decreased timber yields, affecting the forestry industry and local economies reliant on it. The costs associated with reforestation and restoring damaged forest ecosystems are also significant.
2. Fisheries and Tourism:
The decline in fish populations due to lake acidification impacts the fishing industry. The aesthetic damage to lakes and forests also reduces tourism revenue, impacting local communities.
3. Infrastructure Repair and Maintenance:
The corrosive effects of acid rain necessitate increased spending on infrastructure repair and maintenance, placing an additional burden on taxpayers and public budgets.
Mitigation and Remediation Efforts in Germany
Germany has implemented various strategies to mitigate the effects of acid rain:
1. Emission Control Policies:
Stricter emission control regulations for power plants and industrial facilities have drastically reduced SO2 and NOx emissions. The use of cleaner fuels and technologies like flue-gas desulfurization has played a vital role.
2. Vehicle Emission Standards:
Stringent vehicle emission standards have significantly reduced NOx emissions from automobiles. The promotion of electric vehicles and other alternative transportation modes is an ongoing effort.
3. International Cooperation:
Germany participates in international agreements and collaborations to address transboundary air pollution. Working with neighboring countries to reduce emissions is crucial in effectively combating acid rain.
4. Reforestation and Ecosystem Restoration:
Efforts to reforest damaged areas and restore degraded ecosystems are underway. Planting acid-tolerant tree species and employing soil remediation techniques are crucial for long-term recovery.
5. Liming of Acidified Lakes:
In some cases, the liming of acidified lakes is undertaken to neutralize acidity and improve water quality. This is a costly and time-consuming process, but it can be effective in restoring aquatic life in severely affected areas.
Conclusion: An Ongoing Challenge
Acid rain remains a significant environmental challenge in Germany, demanding continuous monitoring, research, and collaborative efforts. While substantial progress has been made in reducing emissions and mitigating the damage, the long-term effects of past pollution and the need for sustained environmental protection remain crucial considerations. The ongoing commitment to cleaner energy sources, sustainable transportation, and international cooperation is essential for securing a healthier environment for future generations in Germany. The success of these efforts will not only safeguard the nation's natural beauty but also its economic stability and the well-being of its citizens. Continued vigilance and proactive measures are vital in ensuring that the devastating legacy of acid rain is effectively addressed and ultimately overcome.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Inches In Square Yard
Mar 26, 2025
-
When Nucleotides Polymerize To Form A Nucleic Acid
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Charge For Iron
Mar 26, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple 3 And 8
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is 1 8 In Fraction Form
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Effects Of Acid Rain In Germany . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
