Common Multiples Of 2 And 4
listenit
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
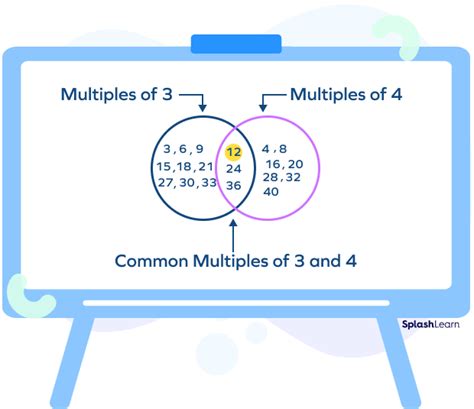
Table of Contents
Delving Deep into the Common Multiples of 2 and 4: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding common multiples might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying principles and exploring their applications can reveal a fascinating world of mathematical concepts. This article dives deep into the common multiples of 2 and 4, exploring their properties, methods for finding them, and their relevance in various mathematical contexts. We'll go beyond basic definitions and uncover the intricacies of this seemingly straightforward topic.
Understanding Multiples and Common Multiples
Before we delve into the specifics of 2 and 4, let's establish a clear understanding of the core concepts.
What is a Multiple? A multiple of a number is the product of that number and any integer (whole number). For example, multiples of 2 include 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and so on. Each of these numbers is obtained by multiplying 2 by a whole number (2 x 1, 2 x 2, 2 x 3, etc.).
What is a Common Multiple? A common multiple of two or more numbers is a number that is a multiple of all of the numbers. For instance, 12 is a common multiple of 2 and 3 because it's a multiple of both (2 x 6 = 12 and 3 x 4 = 12).
Finding Common Multiples of 2 and 4: Methods and Strategies
Since 4 is a multiple of 2 (2 x 2 = 4), finding the common multiples of 2 and 4 simplifies considerably. Every multiple of 4 is automatically a multiple of 2. Therefore, the common multiples of 2 and 4 are simply the multiples of 4.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
The most straightforward method is to list the multiples of both numbers and identify the common ones.
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30...
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40...
Notice that every number in the "Multiples of 4" list is also present in the "Multiples of 2" list. This confirms our earlier statement: the common multiples of 2 and 4 are just the multiples of 4.
Method 2: Using the Larger Number
Because 4 is a multiple of 2, you can directly generate the common multiples by simply listing the multiples of the larger number (4). This is a more efficient approach.
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40, 44, 48, 52, 56, 60...
This list represents all the common multiples of 2 and 4.
Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 2 and 4
The Least Common Multiple (LCM) is the smallest positive common multiple of two or more numbers. In the case of 2 and 4, the LCM is 4. This is because 4 is the smallest number that is a multiple of both 2 and 4.
Exploring the Relationship Between Factors and Multiples
Understanding factors helps clarify the relationship between 2 and 4. A factor is a number that divides another number without leaving a remainder.
- Factors of 4: 1, 2, and 4
- Factors of 2: 1 and 2
Notice that 2 is a factor of 4. This directly explains why all multiples of 4 are also multiples of 2. When a number is a factor of another number, all multiples of the larger number will also be multiples of the smaller number.
Applications of Common Multiples
The concept of common multiples isn't just a theoretical exercise; it has practical applications in various fields:
1. Scheduling and Time Management: Imagine two buses arrive at a bus stop. One bus arrives every 2 hours, and the other arrives every 4 hours. Finding the common multiples helps determine when both buses will arrive simultaneously. The common multiples (multiples of 4) represent the times when both buses are at the stop.
2. Measurement and Conversions: Converting units often involves common multiples. For example, converting inches to feet requires understanding that there are 12 inches in a foot. Finding common multiples helps in efficient conversion.
3. Fractions and Least Common Denominator (LCD): When adding or subtracting fractions, the least common denominator (LCD) is crucial. The LCD is the LCM of the denominators. For example, to add 1/2 and 1/4, the LCD is 4 (the LCM of 2 and 4).
4. Real-World Scenarios: Many real-world problems, from tiling floors to scheduling events, rely on the principles of common multiples and LCM for efficient solutions. Consider arranging chairs in rows where you need a multiple of both 2 and 4. The number of chairs must be a multiple of 4.
Expanding the Concept: Common Multiples of More Than Two Numbers
The principles discussed extend to finding common multiples of more than two numbers. For instance, finding the common multiples of 2, 4, and 6 involves identifying numbers divisible by all three. While this task becomes slightly more complex, the fundamental approach remains the same; it's about identifying numbers that are multiples of all the given numbers. Again, understanding the factors and prime factorization of the numbers provides a structured approach.
Prime Factorization and Common Multiples
Prime factorization is a powerful tool for determining common multiples, especially for larger numbers. Prime factorization breaks a number down into its prime factors (numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves).
Let's consider finding the common multiples of 6 and 8:
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
- Prime factorization of 8: 2 x 2 x 2
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations: 2³ x 3 = 24. Therefore, the LCM of 6 and 8 is 24, and all common multiples of 6 and 8 will be multiples of 24.
Advanced Techniques for Finding Common Multiples
For larger numbers or sets of numbers, more advanced techniques might be employed:
- Euclidean Algorithm: This algorithm is used to efficiently find the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The LCM can then be calculated using the relationship: LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b).
- Prime Factorization (for more than two numbers): This extends the earlier prime factorization method to handle multiple numbers, offering a systematic way to find the LCM.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Common Multiples
Understanding common multiples, from their basic definitions to advanced techniques for calculating LCMs, reveals a rich mathematical landscape. It's a concept that transcends simple arithmetic exercises; it forms the foundation for various practical applications and more complex mathematical concepts. Whether you are tackling simple scheduling problems or sophisticated mathematical challenges, grasping the intricacies of common multiples equips you with a valuable tool for problem-solving and a deeper appreciation for the elegance of mathematics. The seemingly simple exploration of the common multiples of 2 and 4 serves as a gateway to a more profound understanding of number theory and its diverse applications in the real world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Much Is 67 Kilos In Pounds
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Secant Line
Mar 17, 2025
-
Is Water A Good Leaving Group
Mar 17, 2025
-
480 Cm Equals How Many M
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is 8 In Fraction Form
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Common Multiples Of 2 And 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
