Beryllium On The Periodic Table Of Elements
listenit
Mar 25, 2025 · 7 min read
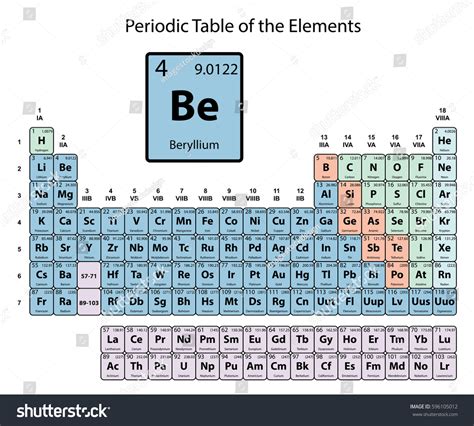
Table of Contents
Beryllium: A Deep Dive into the Element's Properties, Applications, and Significance
Beryllium, a fascinating and often overlooked element, holds a unique position on the periodic table. Its characteristics, both beneficial and challenging, have shaped its applications across diverse fields, from aerospace to nuclear technology. This comprehensive article explores the intriguing world of beryllium, delving into its atomic structure, physical and chemical properties, extraction methods, industrial uses, health implications, and environmental considerations.
Understanding Beryllium's Position on the Periodic Table
Beryllium (Be), atomic number 4, resides in Group 2 (alkaline earth metals) of the periodic table. Its location dictates many of its properties. Unlike the other alkaline earth metals, beryllium exhibits significantly different characteristics due to its small atomic size and high ionization energy. This smaller size leads to a higher charge density, influencing its chemical reactivity and bonding behavior. Its position as a bridging element between the alkaline earth metals and the transition metals further highlights its unique nature.
Atomic Structure and Electronic Configuration
Beryllium possesses a relatively simple atomic structure. Its nucleus contains four protons and typically four neutrons (although isotopes exist). It has two electrons in its outermost shell, giving it a valence of +2. This electronic configuration ([He] 2s²) explains its tendency to readily lose two electrons to achieve a stable, noble gas configuration similar to helium. This characteristic dictates its chemical reactivity and bonding preferences.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Beryllium
The physical and chemical properties of beryllium are largely dictated by its atomic structure and position on the periodic table. These properties are key to understanding its applications and limitations.
Unique Physical Properties:
- Lightweight: Beryllium is exceptionally lightweight, boasting a density approximately one-third that of aluminum. This makes it highly desirable in applications requiring minimal weight, such as aerospace components.
- High Strength: Despite its low density, beryllium possesses remarkable tensile strength, surpassing that of many other lightweight metals. This combination of lightness and strength is unparalleled.
- High Modulus of Elasticity: Beryllium exhibits an exceptionally high modulus of elasticity, meaning it resists deformation under stress better than most metals. This property is crucial in applications requiring structural rigidity.
- High Thermal Conductivity: It boasts impressive thermal conductivity, facilitating efficient heat dissipation. This characteristic is vital in applications involving high temperatures.
- Excellent Transparency to X-rays: Beryllium's unique atomic structure allows for exceptional transparency to X-rays and other forms of radiation, making it invaluable in X-ray windows and other radiation-related technologies.
- Low Electrical Conductivity: Despite being a metal, beryllium has relatively low electrical conductivity compared to other metals like copper or aluminum.
Important Chemical Properties:
- Amphoteric Nature: Beryllium oxide (BeO) is amphoteric, meaning it can react with both acids and bases. This dual reactivity complicates its chemical processing.
- Passivation: A thin, protective oxide layer forms on beryllium's surface upon exposure to air, preventing further oxidation. This passivation layer protects it from rapid corrosion.
- Reactivity with Water: Although relatively resistant to water at room temperature, beryllium reacts slowly with boiling water and more readily with steam to produce beryllium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
- Reaction with Acids: Beryllium readily dissolves in most dilute acids, except for nitric acid, where passivation interferes with dissolution.
- Formation of Complex Ions: Beryllium readily forms complex ions with many ligands, further influencing its chemical behavior.
Extraction and Production of Beryllium
Extracting beryllium from its ores is a complex and challenging process. The primary ore is beryl, a complex aluminosilicate mineral containing beryllium, aluminum, silicon, and oxygen.
Extraction Process:
- Ore Concentration: The first step involves concentrating the beryllium ore, often through physical methods like crushing, grinding, and flotation to separate beryl from other minerals.
- Beryl Decomposition: Next, the concentrated beryl undergoes decomposition to release beryllium. This often involves high-temperature processes like sintering or acid digestion using sulfuric acid or hydrofluoric acid.
- Purification: The resulting beryllium-containing solution requires extensive purification to remove impurities. Solvent extraction and ion-exchange techniques are commonly employed to achieve high-purity beryllium.
- Reduction: Finally, the purified beryllium compound is reduced to metallic beryllium using processes like electrolysis or metallothermic reduction. Electrolysis is particularly useful for high-purity beryllium production.
Applications of Beryllium in Various Industries
The unique combination of properties makes beryllium indispensable in various industries. However, its toxicity necessitates careful handling and specialized applications.
Aerospace Industry:
Beryllium's lightweight yet high-strength characteristics are highly valued in aerospace applications. It finds use in:
- Aircraft Components: Beryllium alloys are used in high-performance aircraft components, including structural parts, control surfaces, and braking systems, where weight reduction is critical for enhanced fuel efficiency and performance.
- Rocketry and Missiles: Its strength and thermal stability make it suitable for various rocket and missile components, enabling them to withstand the extreme conditions of launch and flight.
- Satellite Components: Beryllium's lightweight properties and resilience to radiation make it a valuable component in satellites and spacecraft.
Nuclear Industry:
Beryllium's transparency to X-rays and neutrons makes it essential in nuclear applications:
- Neutron Reflectors and Moderators: Beryllium's ability to reflect and moderate neutrons makes it a crucial component in nuclear reactors and weapons.
- X-Ray Windows: Its transparency to X-rays makes it ideal for X-ray windows in various nuclear research and medical applications.
Electronics Industry:
Beryllium's unique properties have earned it a place in the electronics industry:
- High-Frequency Applications: Beryllium's high modulus of elasticity and low density are utilized in high-frequency applications such as cell phones and other electronic devices that require minimal weight and high rigidity.
- Heat Sinks: Its excellent thermal conductivity makes it a suitable material for heat sinks, ensuring efficient dissipation of heat generated by electronic components.
Other Applications:
Beryllium's versatility extends beyond the aforementioned industries:
- Medical Applications: In specialized medical applications, it’s used in certain dental and surgical instruments due to its biocompatibility and high strength.
- Sporting Goods: The material's lightness and strength are used in a few high-end sporting goods like golf club heads and bicycle frames.
- Mirrors and Optics: Beryllium is being explored for highly precise mirrors and optics due to its dimensional stability and high reflectivity.
Health and Environmental Concerns Associated with Beryllium
Despite its many benefits, beryllium presents significant health and environmental concerns.
Health Effects:
Beryllium is a highly toxic element, particularly in its airborne form. Inhalation of beryllium dust or fumes can lead to a serious lung disease called berylliosis, which is characterized by chronic inflammation and scarring of lung tissue. The disease can range from mild to life-threatening, and early detection is critical. Skin contact can cause dermatitis, while ingestion can lead to gastrointestinal issues. The severity of the effects depends on factors like the concentration and duration of exposure.
Environmental Impact:
Beryllium's presence in the environment raises environmental concerns, primarily due to its toxicity. Disposal of beryllium-containing waste needs careful management to prevent environmental contamination. Regulations exist to minimize the risk of beryllium release into the environment.
Future Trends and Research in Beryllium
Research continues to explore new ways to utilize beryllium's unique properties while mitigating its inherent risks. Some areas of ongoing research include:
- Improved Safety Protocols: Research focuses on developing improved safety protocols and personal protective equipment to minimize occupational exposure to beryllium.
- New Alloys and Composites: Scientists are exploring the development of new beryllium alloys and composites to enhance its performance and reduce toxicity risks.
- Sustainable Extraction and Recycling: Efforts are underway to develop more sustainable extraction methods and efficient recycling processes to minimize environmental impact.
- Advanced Applications: Researchers continue to investigate the potential of beryllium in advanced applications, such as next-generation aerospace components and advanced nuclear technologies.
Conclusion: Beryllium - A Powerful Yet Perilous Element
Beryllium's unique combination of physical and chemical properties makes it invaluable in a variety of high-tech applications. However, its toxicity demands careful handling and robust safety measures. Ongoing research focuses on developing new approaches to utilize its potential while mitigating its risks. By carefully balancing its benefits against its inherent dangers, we can responsibly harness the unique power of this remarkable element.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Type Of Speech Is Is
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Order Does A Dog Belong To
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Is A Population Different From A Community
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Is 55 As A Fraction
Mar 29, 2025
-
40 Of What Number Is 24
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Beryllium On The Periodic Table Of Elements . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
