Area Of A Circle With A Radius Of 6
listenit
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
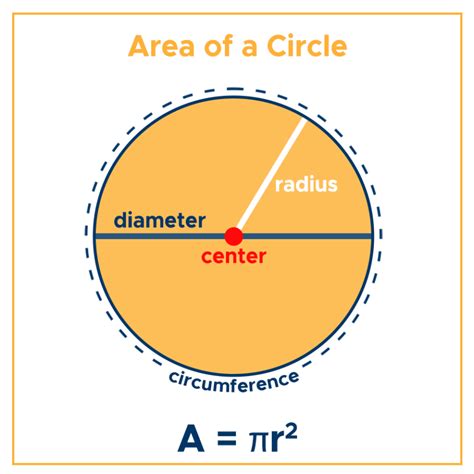
Table of Contents
Delving Deep into the Area of a Circle with a Radius of 6: A Comprehensive Guide
The seemingly simple calculation of the area of a circle with a radius of 6 units opens a door to a fascinating exploration of geometry, mathematical formulas, and their real-world applications. This article will not only provide the answer but will also delve into the underlying principles, explore related concepts, and discuss practical uses of this fundamental calculation.
Understanding the Formula: πr²
The area of any circle is calculated using the formula A = πr², where:
- A represents the area of the circle.
- π (pi) is a mathematical constant, approximately equal to 3.14159. It represents the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. The value of π is irrational, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation goes on forever without repeating.
- r represents the radius of the circle, which is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference.
In our case, the radius (r) is given as 6 units. Therefore, the calculation becomes:
A = π * 6² = π * 36 ≈ 36π
Using a more precise approximation of π (e.g., 3.14159), we get:
A ≈ 3.14159 * 36 ≈ 113.097 square units.
Therefore, the area of a circle with a radius of 6 units is approximately 113.097 square units. The units will depend on the units used to measure the radius (e.g., square centimeters, square meters, square inches).
Beyond the Calculation: Exploring the Concept of π
The constant π plays a pivotal role in understanding circles and spheres. Its ubiquity extends far beyond simple geometry problems. It appears in various areas of mathematics, physics, and engineering, highlighting its fundamental importance in describing natural phenomena and patterns. Understanding its significance helps to appreciate the elegance and power of mathematical concepts.
The Irrationality of π: A Mathematical Mystery
The irrationality of π, the fact that its decimal representation never ends or repeats, has fascinated mathematicians for centuries. The pursuit of more accurate approximations of π has driven advancements in computational power and algorithm development. The quest to understand its nature remains a captivating area of mathematical research.
π in Real-World Applications
The applications of π are vast and far-reaching:
- Engineering and Architecture: Calculating the volume and surface area of cylindrical structures like pipes, tanks, and silos heavily relies on π.
- Physics: π appears frequently in physics equations related to waves, oscillations, and circular motion. It's crucial in understanding concepts like gravitational forces and planetary orbits.
- Probability and Statistics: π surprisingly emerges in various probabilistic calculations and statistical distributions, demonstrating its unexpected connections across different mathematical branches.
- Computer Science: Algorithms for generating random numbers and simulating natural processes often incorporate π.
Practical Applications of Calculating Circle Area
The ability to accurately determine the area of a circle has a wealth of real-world applications:
Landscaping and Gardening
Determining the amount of fertilizer, grass seed, or mulch needed for a circular garden bed requires calculating its area. Knowing the area allows for precise and efficient resource allocation.
Construction and Manufacturing
Calculating the area of circular components is crucial in various manufacturing processes. It helps in determining material requirements, optimizing cutting patterns, and ensuring accurate production. For example, in designing circular components for machinery or constructing circular structures, understanding area is essential for both design and material estimation.
Science and Research
In scientific research, understanding the area of a circle is crucial for various experiments and measurements. For example, in biology, calculating the area of a circular cell culture dish is essential for controlling experimental conditions and analyzing results. In physics experiments involving circular motion or circular waves, understanding the area is paramount for accurate modeling and analysis.
Art and Design
In art and design, understanding the area of a circle is crucial for creating balanced and aesthetically pleasing compositions. Artists and designers use circles and circular elements in many of their creations, and calculating the area can influence their design choices and the overall effect of their work.
Expanding the Understanding: Related Geometric Concepts
Understanding the area of a circle with a radius of 6 helps build a foundation for grasping more complex geometrical concepts.
Circumference
The circumference of a circle (the distance around the circle) is calculated using the formula C = 2πr. For a circle with a radius of 6, the circumference would be approximately 37.699 units.
Diameter
The diameter (the distance across the circle through the center) is twice the radius. For our circle, the diameter is 12 units.
Sector Area
A sector is a portion of a circle enclosed by two radii and an arc. The area of a sector can be calculated using the formula: Area of sector = (θ/360) * πr², where θ is the central angle in degrees.
Segment Area
A segment is the area between a chord and an arc. Calculating the area of a segment involves subtracting the area of a triangle from the area of a sector.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
For those interested in delving deeper, consider exploring:
Calculus and the Area of a Circle
Calculus provides alternative methods for calculating the area of a circle, using integration techniques. This approach offers a more rigorous and powerful way of understanding area calculation.
Higher Dimensions: Spheres and Hyperspheres
The concept of area extends to higher dimensions. The surface area of a sphere (a three-dimensional circle) and the "hyper-surface area" of hyperspheres (higher-dimensional generalizations of spheres) are calculated using formulas that are related to the area of a circle but involve more complex mathematical concepts.
Non-Euclidean Geometry
The formula for the area of a circle, A = πr², is valid in Euclidean geometry. In non-Euclidean geometries (like spherical or hyperbolic geometry), the formula for the area of a circle differs, reflecting the different properties of these geometric spaces.
Conclusion: The Enduring Relevance of a Simple Formula
The seemingly straightforward calculation of the area of a circle with a radius of 6 units unveils a wealth of mathematical concepts, practical applications, and connections to various scientific disciplines. From landscaping to engineering, from art to advanced calculus, the ability to calculate the area of a circle remains a fundamental skill with far-reaching implications. By exploring this seemingly simple concept, we gain a deeper appreciation for the beauty and power of mathematics and its role in shaping our understanding of the world around us. This comprehensive guide serves as a starting point for those seeking to further explore the fascinating world of circles and their mathematical properties.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Do Parallelograms Have 4 Right Angles
Mar 29, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 10 And 8
Mar 29, 2025
-
Name 3 Ways To Dissolve Something Faster
Mar 29, 2025
-
Charged Language In I Have A Dream
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Percentage Is 38 Out Of 40
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Area Of A Circle With A Radius Of 6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
