Albr3 K2so4 Kbr Al2 So4 3
listenit
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
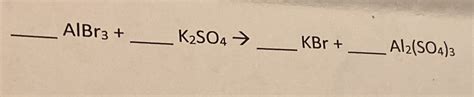
Table of Contents
Delving into the World of Aluminum Bromide, Potassium Sulfate, Potassium Bromide, and Aluminum Sulfate
This article explores the fascinating world of four inorganic compounds: Aluminum Bromide (AlBr₃), Potassium Sulfate (K₂SO₄), Potassium Bromide (KBr), and Aluminum Sulfate (Al₂(SO₄)₃). We'll delve into their individual properties, synthesis methods, applications, safety considerations, and the interesting relationships between them. Understanding these compounds requires examining their chemical structures, reactivity, and the unique roles they play in various scientific and industrial applications.
Aluminum Bromide (AlBr₃): Properties and Applications
Aluminum bromide is a colorless to pale-yellow crystalline solid with a pungent odor. Its anhydrous form is highly hygroscopic, readily absorbing moisture from the air. Key properties include:
- Chemical Formula: AlBr₃
- Molar Mass: 266.69 g/mol
- Melting Point: 97.5 °C
- Boiling Point: 263 °C
- Solubility: Soluble in water, ethanol, and other polar solvents.
Synthesis of Aluminum Bromide: AlBr₃ can be synthesized through the direct reaction of aluminum metal with bromine:
2Al(s) + 3Br₂(l) → 2AlBr₃(s)
This reaction is highly exothermic and requires careful control to prevent runaway heating.
Applications of Aluminum Bromide:
- Organic Synthesis: AlBr₃ serves as a powerful Lewis acid catalyst in various organic reactions, including Friedel-Crafts alkylation and acylation. Its ability to accept electron pairs allows it to activate substrates and facilitate reactions.
- Material Science: It finds applications in the synthesis of certain aluminum-containing materials.
- Catalysis: Its Lewis acidity makes it suitable for use in various catalytic processes.
Potassium Sulfate (K₂SO₄): A Versatile Compound
Potassium sulfate is a white crystalline solid, odorless, and readily soluble in water. It's a crucial source of potassium and sulfur for plants, making it a key component in fertilizers. Its properties include:
- Chemical Formula: K₂SO₄
- Molar Mass: 174.26 g/mol
- Melting Point: 1069 °C
- Boiling Point: 1689 °C
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol.
Synthesis of Potassium Sulfate: K₂SO₄ can be synthesized via several methods:
- Reaction of Potassium Hydroxide with Sulfuric Acid: 2KOH(aq) + H₂SO₄(aq) → K₂SO₄(aq) + 2H₂O(l)
- Neutralization of Potassium Carbonate with Sulfuric Acid: K₂CO₃(aq) + H₂SO₄(aq) → K₂SO₄(aq) + H₂O(l) + CO₂(g)
Applications of Potassium Sulfate:
- Agriculture: As a fertilizer, providing potassium and sulfur to plants, vital for growth and yield.
- Food Industry: Used as a food additive, acting as a firming agent in some foods.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Used in some pharmaceutical preparations.
- Glassmaking: A component in certain types of glass.
Potassium Bromide (KBr): Properties and Uses
Potassium bromide is a white crystalline salt, odorless, and soluble in water. It's used in various applications, ranging from medical to industrial. Its properties include:
- Chemical Formula: KBr
- Molar Mass: 119.00 g/mol
- Melting Point: 734 °C
- Boiling Point: 1435 °C
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol.
Synthesis of Potassium Bromide: KBr can be produced by reacting potassium hydroxide or potassium carbonate with hydrobromic acid:
KOH(aq) + HBr(aq) → KBr(aq) + H₂O(l)
K₂CO₃(aq) + 2HBr(aq) → 2KBr(aq) + H₂O(l) + CO₂(g)
Applications of Potassium Bromide:
- Medicine: Historically used as an anticonvulsant and sedative, although its use has declined due to the availability of safer alternatives.
- Photography: Previously used in photographic emulsions as a light-sensitive material.
- Spectroscopy: Used in infrared spectroscopy as an optical material due to its transparency in the infrared region.
- Industrial Applications: Employed in certain drilling fluids and as a catalyst in some chemical processes.
Aluminum Sulfate (Al₂(SO₄)₃): A Widely Used Compound
Aluminum sulfate, also known as alum, is a white crystalline solid, usually found as a hydrate (Al₂(SO₄)₃·xH₂O). It's highly soluble in water and has several significant applications. Its properties include:
- Chemical Formula: Al₂(SO₄)₃
- Molar Mass: 342.15 g/mol (anhydrous)
- Melting Point: Decomposes upon heating
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water.
Synthesis of Aluminum Sulfate: Aluminum sulfate is typically produced through the reaction of aluminum hydroxide or aluminum oxide with sulfuric acid:
2Al(OH)₃(s) + 3H₂SO₄(aq) → Al₂(SO₄)₃(aq) + 6H₂O(l)
Al₂O₃(s) + 3H₂SO₄(aq) → Al₂(SO₄)₃(aq) + 3H₂O(l)
Applications of Aluminum Sulfate:
- Water Treatment: A key coagulant in water purification processes, facilitating the removal of suspended solids and impurities.
- Papermaking: Used as a sizing agent in paper production, strengthening the paper and improving its printing properties.
- Textile Industry: Acts as a mordant in dyeing processes, helping dyes adhere to fabrics.
- Other Applications: Found in various other applications, including leather tanning, cosmetics, and as a food additive (e.g., in baking powder).
Interrelationships and Reactions
While these four compounds appear distinct, there are interesting interrelationships. For example, the sulfate ion (SO₄²⁻) is present in both potassium sulfate and aluminum sulfate. Similarly, the bromide ion (Br⁻) appears in both aluminum bromide and potassium bromide. However, direct reactions between these compounds are generally not significant under normal conditions. For instance, a simple aqueous mixture of potassium sulfate and aluminum bromide would likely result in a solution containing the constituent ions without significant precipitation or other noteworthy reactions. More complex reactions might occur under specific conditions (high temperature, presence of a catalyst, etc.), but these are generally not straightforward and are beyond the scope of this introductory overview.
Safety Considerations
All four compounds require careful handling. Aluminum bromide, in its anhydrous form, is highly hygroscopic and reacts violently with water. Appropriate safety precautions, including the use of gloves and eye protection, are essential. Potassium sulfate is generally considered relatively safe, but inhalation of dust should be avoided. Potassium bromide requires careful handling, as excessive ingestion can be harmful. Aluminum sulfate, while less hazardous than aluminum bromide, can cause skin and eye irritation. Proper handling and disposal procedures are critical when working with these chemicals. Always refer to relevant Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for detailed safety information before handling any of these compounds.
Conclusion
Aluminum bromide, potassium sulfate, potassium bromide, and aluminum sulfate represent a diverse group of inorganic compounds with a wide array of applications. Understanding their individual properties, synthesis methods, and safety considerations is crucial for their safe and effective utilization in various scientific and industrial processes. Though they share some common ionic components, they are distinct compounds with unique characteristics and roles. Further research into their applications and potential interactions would enhance their practical utility and deepen our understanding of their chemical behavior. The information presented here offers a solid foundation for exploring the fascinating chemistry of these important inorganic compounds.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 6 Percent Of 15
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 162
Mar 19, 2025
-
Is Salad Dressing A Homogeneous Mixture
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Happens To The Atoms In A Chemical Reaction
Mar 19, 2025
-
Taylor Expansion Of Sqrt 1 X 2
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Albr3 K2so4 Kbr Al2 So4 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
