2 2 7 As An Improper Fraction
listenit
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
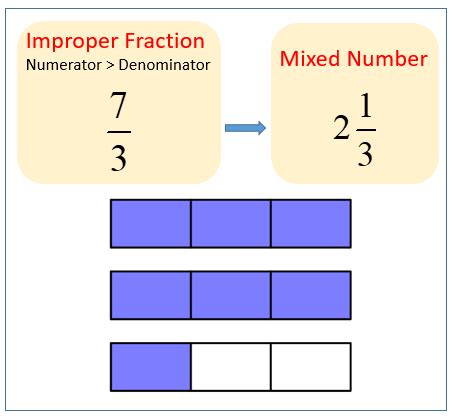
Table of Contents
Understanding 2 2/7 as an Improper Fraction: A Comprehensive Guide
The mixed number 2 2/7 represents a combination of a whole number (2) and a proper fraction (2/7). Converting this mixed number into an improper fraction is a fundamental skill in arithmetic, crucial for various mathematical operations and problem-solving. This comprehensive guide will not only explain the process of converting 2 2/7 to an improper fraction but also delve deeper into the underlying concepts, providing you with a solid understanding of fractions and their manipulations.
What is a Mixed Number?
A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction is a fraction where the numerator (the top number) is smaller than the denominator (the bottom number). For example, 1/2, 3/4, and 5/8 are all proper fractions. Mixed numbers are useful for representing quantities that are greater than one but not whole numbers. Think of having two whole pizzas and two-sevenths of another pizza – this would be represented as 2 2/7.
What is an Improper Fraction?
An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. Examples include 7/4, 5/5, and 11/3. Improper fractions represent values greater than or equal to one. While they might seem less intuitive than mixed numbers, they are essential for performing many mathematical calculations, especially multiplication and division of fractions.
Converting 2 2/7 to an Improper Fraction: The Step-by-Step Process
The conversion of a mixed number to an improper fraction involves a simple two-step process:
Step 1: Multiply the whole number by the denominator.
In our case, the whole number is 2, and the denominator of the fraction is 7. Therefore, we multiply 2 by 7: 2 * 7 = 14.
Step 2: Add the numerator to the result from Step 1.
The numerator of our fraction is 2. Adding this to the result from Step 1 (14), we get: 14 + 2 = 16.
Step 3: Keep the same denominator.
The denominator remains unchanged throughout the conversion process. Therefore, our denominator stays as 7.
The final result: Combining the results from Steps 2 and 3, we get the improper fraction 16/7. This signifies that 2 2/7 is equivalent to 16/7.
Visualizing the Conversion
Imagine you have two whole pizzas and two-sevenths of another pizza. To represent this as an improper fraction, consider dividing each of the two whole pizzas into seven equal slices. This gives you 14 slices (2 pizzas * 7 slices/pizza). Adding the two slices from the remaining two-sevenths of a pizza, you have a total of 16 slices. Since each pizza was divided into 7 slices, the total number of slices is represented as 16/7.
Why is Converting to an Improper Fraction Important?
Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions is vital for several reasons:
-
Simplifying Calculations: Many mathematical operations, particularly multiplication and division of fractions, are significantly easier to perform with improper fractions. Attempting these operations with mixed numbers often leads to more complex calculations.
-
Consistency in Operations: Using improper fractions ensures consistency in calculations, avoiding the need to handle whole numbers and fractions separately.
-
Solving Equations: Improper fractions are often necessary when solving equations involving fractions, especially those where the unknown variable is part of a fraction.
-
Advanced Mathematical Concepts: A strong grasp of improper fractions is crucial for understanding more advanced mathematical concepts like rational numbers, complex numbers, and calculus.
Practice Problems: Converting Mixed Numbers to Improper Fractions
Let's practice converting some more mixed numbers to improper fractions to solidify your understanding:
-
3 1/4: (3 * 4) + 1 = 13. The improper fraction is 13/4.
-
1 5/6: (1 * 6) + 5 = 11. The improper fraction is 11/6.
-
5 2/3: (5 * 3) + 2 = 17. The improper fraction is 17/3.
-
4 3/8: (4 * 8) + 3 = 35. The improper fraction is 35/8.
-
10 1/2: (10 * 2) + 1 = 21. The improper fraction is 21/2.
By working through these examples, you'll reinforce your ability to confidently convert mixed numbers into their improper fraction equivalents.
Converting Improper Fractions back to Mixed Numbers
While converting to improper fractions is often necessary for calculations, it's equally important to know how to convert them back to mixed numbers for easier interpretation. This is done through division:
-
Divide the numerator by the denominator. For example, with 16/7, 16 divided by 7 is 2 with a remainder of 2.
-
The quotient becomes the whole number. In our example, the quotient is 2.
-
The remainder becomes the numerator of the fraction. The remainder is 2.
-
The denominator remains the same. The denominator remains 7.
Therefore, 16/7 converts back to the mixed number 2 2/7.
Real-World Applications of Improper Fractions
Improper fractions aren't just abstract mathematical concepts; they find practical applications in various real-world scenarios:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often involve fractional amounts of ingredients. Using improper fractions can simplify calculations when dealing with larger quantities.
-
Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements are crucial in construction and engineering. Improper fractions are often used to represent measurements that are not whole numbers.
-
Finance and Accounting: Financial calculations often involve fractions, particularly when dealing with percentages, interest rates, and stock prices.
-
Data Analysis: In statistical analysis and data interpretation, improper fractions are frequently encountered when dealing with ratios and proportions.
Advanced Concepts Related to Improper Fractions
Understanding improper fractions lays a foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts:
-
Rational Numbers: Improper fractions, along with proper fractions and integers, form the set of rational numbers. Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as the ratio of two integers.
-
Algebraic Expressions: Improper fractions appear frequently in algebraic expressions and equations, requiring manipulation and simplification.
-
Calculus: The concept of limits and derivatives in calculus often involve manipulating fractions, including improper fractions.
By mastering the conversion between mixed numbers and improper fractions, you significantly enhance your ability to perform a wide range of mathematical operations and tackle various problem-solving scenarios. Remember the simple yet powerful process: multiply, add, and keep the denominator. Practice makes perfect, so continue working through examples to build your confidence and expertise in this fundamental arithmetic skill. The ability to effortlessly convert between mixed numbers and improper fractions will undoubtedly serve you well in your academic pursuits and everyday life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Square Root Of 39
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Percent Of 400 Is 20
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 4 And 16
Mar 17, 2025
-
Is 3 Pi A Rational Number
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is 50 As A Fraction
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 2 7 As An Improper Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
