12x 3 2x 2 30x 5
listenit
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
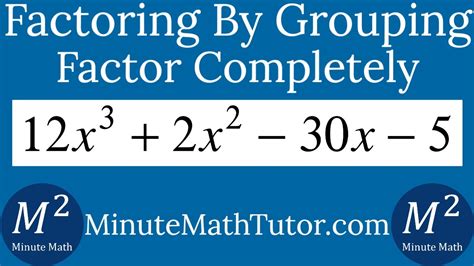
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: 12x3, 2x2, and 30x5 – A Deep Dive into Multiplication and its Applications
This seemingly simple sequence of multiplications – 12 x 3, 2 x 2, and 30 x 5 – opens a door to a vast world of mathematical concepts and real-world applications. While the calculations themselves are straightforward, understanding the underlying principles and exploring their relevance across different fields allows us to appreciate the power and versatility of multiplication. This article will delve into each equation individually, exploring their solutions, and then broadening the scope to consider the broader implications of multiplication in various contexts.
Understanding the Basics: Solving 12 x 3, 2 x 2, and 30 x 5
Let's begin by solving each multiplication problem:
1. 12 x 3: This multiplication problem involves multiplying the number 12 by 3. We can solve this using several methods:
- Traditional Multiplication: We can break down 12 into 10 and 2. Then, (10 x 3) + (2 x 3) = 30 + 6 = 36.
- Repeated Addition: Adding 12 three times (12 + 12 + 12) also results in 36.
Therefore, 12 x 3 = 36
2. 2 x 2: This is a fundamental multiplication problem. Multiplying 2 by itself gives us:
- Traditional Multiplication: A simple calculation yields 4.
- Visual Representation: Imagine two rows with two items each; the total is 4.
Therefore, 2 x 2 = 4
3. 30 x 5: This multiplication problem involves multiplying 30 by 5. Again, we can use several methods:
- Traditional Multiplication: Multiplying 30 by 5 gives us 150.
- Multiplication by 10 and 5: We can multiply 30 by 10 (300) and then divide by 2 (300/2 = 150).
Therefore, 30 x 5 = 150
Beyond the Basics: Exploring the Concepts of Multiplication
These three simple problems showcase the fundamental concept of multiplication: repeated addition. However, the concept expands far beyond simple calculations. Let's explore some key aspects:
Commutative Property:
Multiplication is commutative, meaning the order of the numbers doesn't change the result. For example, 3 x 12 = 12 x 3 = 36. This property simplifies calculations and provides flexibility in problem-solving.
Associative Property:
The associative property allows us to group numbers in different ways without changing the final result. For instance, (2 x 3) x 4 = 2 x (3 x 4) = 24. This is particularly useful when dealing with multiple multiplications.
Distributive Property:
The distributive property allows us to simplify more complex multiplications. It states that a(b + c) = ab + ac. For example, 3 x (10 + 2) = (3 x 10) + (3 x 2) = 36.
Real-World Applications: Where Multiplication Matters
Multiplication is not just a theoretical concept; it's a fundamental tool used across numerous fields:
Everyday Life:
- Shopping: Calculating the total cost of multiple items (e.g., 3 apples at $1.20 each).
- Cooking: Scaling recipes (e.g., doubling a recipe that calls for 2 cups of flour).
- Travel: Determining distances (e.g., driving 60 mph for 3 hours).
- Finance: Calculating interest, taxes, and discounts.
Science and Engineering:
- Physics: Calculating forces, velocities, and accelerations often involves multiplication.
- Chemistry: Determining the number of molecules in a chemical reaction.
- Engineering: Calculating areas, volumes, and other geometrical properties often involves multiplication.
Business and Economics:
- Profit Calculation: Determining profit margins involves multiplying costs and quantities.
- Sales Forecasting: Predicting future sales often involves multiplying projected sales per unit by the number of units sold.
- Investment Analysis: Calculating returns on investment often involves multiplying initial investment by the rate of return.
Computer Science:
- Data Structures: Multiplication is frequently used in algorithms and data structures, such as matrix multiplication.
- Image Processing: Image manipulation often involves multiplication of pixel values.
- Graphics Programming: 3D graphics rely heavily on matrix multiplication for transformations and projections.
Advanced Concepts Related to Multiplication
Moving beyond the elementary examples, we can explore more complex mathematical concepts related to multiplication:
Exponents and Powers:
Repeated multiplication of the same number is represented using exponents (e.g., 2 x 2 x 2 = 2³ = 8). Understanding exponents is crucial for many scientific and mathematical calculations.
Factors and Multiples:
Understanding factors and multiples helps in simplifying fractions, solving equations, and working with divisibility rules. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
Prime Numbers and Factorization:
Prime numbers are numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves. Prime factorization involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors (e.g., 12 = 2 x 2 x 3). This concept is fundamental in cryptography and number theory.
Multiplication in Different Number Systems
While we've primarily focused on the decimal system (base 10), multiplication also applies to other number systems, such as binary (base 2) which is the foundation of computer operations. Understanding multiplication across different bases provides a deeper appreciation of the concept's universality.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Multiplication
The seemingly simple equations 12 x 3, 2 x 2, and 30 x 5 represent a gateway to a powerful and versatile mathematical operation. Its applications extend far beyond the classroom, playing a crucial role in our daily lives, scientific advancements, and technological innovations. Mastering multiplication is not merely about calculating numbers; it's about developing a foundational understanding that empowers us to solve complex problems and navigate a world increasingly reliant on quantitative reasoning. From calculating the cost of groceries to understanding complex scientific models, multiplication remains an indispensable tool for navigating our world. The exploration of these simple examples reveals the depth and breadth of this fundamental mathematical operation, highlighting its profound importance across numerous fields and aspects of human endeavor. Understanding these concepts enables us to appreciate the elegance and practicality of mathematics in shaping our understanding and interaction with the world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
If The Ka Of A Monoprotic Weak Acid Is
Mar 23, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 12 And 8
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is The Percent Of 7 9
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Grams Are In 1200 Mg
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Do You Write 80 As A Fraction
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 12x 3 2x 2 30x 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
