X 3y 6 In Slope Intercept Form
listenit
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
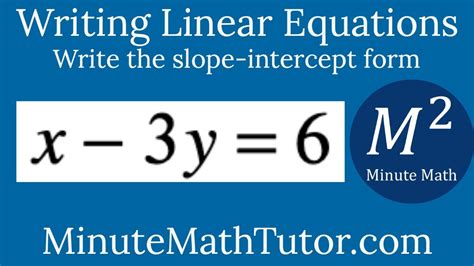
Table of Contents
Understanding and Applying the Equation x = 3y + 6 in Slope-Intercept Form
The equation x = 3y + 6 represents a linear relationship between two variables, x and y. While not initially presented in slope-intercept form (y = mx + b), we can easily transform it to reveal valuable insights about its slope and y-intercept. Understanding this transformation is crucial for graphing the equation and analyzing its properties. This comprehensive guide will delve into the process, exploring various related concepts and providing practical applications.
From Standard Form to Slope-Intercept Form
The given equation, x = 3y + 6, is in a form often called standard form (Ax + By = C), although it's slightly rearranged. The slope-intercept form, y = mx + b, provides a more intuitive understanding of the line's characteristics. 'm' represents the slope (the steepness of the line), and 'b' represents the y-intercept (the point where the line crosses the y-axis).
To convert x = 3y + 6 into slope-intercept form, we need to isolate 'y':
-
Subtract 6 from both sides: x - 6 = 3y
-
Divide both sides by 3: (x - 6) / 3 = y
-
Simplify: y = (1/3)x - 2
Now we have the equation in slope-intercept form: y = (1/3)x - 2.
Identifying Key Features: Slope and Y-Intercept
From the slope-intercept form, y = (1/3)x - 2, we can immediately identify:
-
Slope (m): The slope is 1/3. This means that for every 3 units increase in the x-coordinate, the y-coordinate increases by 1 unit. The slope indicates the line's direction and steepness. A positive slope indicates an upward trend from left to right.
-
Y-intercept (b): The y-intercept is -2. This means the line crosses the y-axis at the point (0, -2).
Graphing the Equation
Now that we have the slope and y-intercept, graphing the equation becomes straightforward.
-
Plot the y-intercept: Start by plotting the point (0, -2) on the coordinate plane.
-
Use the slope to find another point: The slope of 1/3 means we can move 3 units to the right and 1 unit up from the y-intercept to find another point on the line. This gives us the point (3, -1).
-
Draw the line: Draw a straight line through the two points (0, -2) and (3, -1). This line represents the graph of the equation x = 3y + 6 (or equivalently, y = (1/3)x - 2).
Understanding the Relationship Between x and y
The equation x = 3y + 6, or its equivalent y = (1/3)x - 2, describes a linear relationship. This means that changes in x are directly proportional to changes in y. The constant of proportionality is the slope, 1/3. For every unit increase in x, y increases by 1/3 of a unit. Conversely, for every unit increase in y, x increases by 3 units.
This linear relationship can be useful in various applications, from predicting outcomes based on known data to modeling real-world phenomena that exhibit linear trends.
Applications and Real-World Examples
Linear equations have extensive applications across numerous fields:
-
Physics: Describing the motion of objects with constant velocity (where x might represent distance and y represents time).
-
Economics: Modeling supply and demand relationships (where x might represent price and y represents quantity).
-
Engineering: Analyzing structural behavior, calculating forces, and designing systems.
-
Finance: Predicting investment growth or calculating loan repayments.
-
Computer Science: Algorithms and data structures often involve linear relationships.
Let's consider a simple example: Suppose a taxi charges a fixed fare of $2 plus $1 for every 3 kilometers traveled. We can represent the total fare (x) in terms of the distance traveled (y): x = 3y + 2. This is essentially the same form as our original equation, just with different units and context.
Solving Problems Using the Equation
The equation x = 3y + 6 can be used to solve for either x or y, given the value of the other variable.
Example 1: Find x when y = 4.
Substitute y = 4 into the equation: x = 3(4) + 6 = 18. Therefore, when y = 4, x = 18.
Example 2: Find y when x = 9.
Substitute x = 9 into the equation: 9 = 3y + 6. Solving for y, we get: 3y = 3, so y = 1. Therefore, when x = 9, y = 1.
These examples demonstrate the equation's utility in finding corresponding values of x and y.
Comparing to Other Forms of Linear Equations
It's important to understand that linear relationships can be represented in several forms:
-
Slope-intercept form (y = mx + b): Most useful for graphing and identifying the slope and y-intercept.
-
Point-slope form (y - y1 = m(x - x1)): Useful when you know the slope and a point on the line.
-
Standard form (Ax + By = C): Often used in algebraic manipulations and for certain applications.
The choice of which form to use depends on the specific problem and the information available. However, being able to convert between these forms is a valuable skill.
Extending the Understanding: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
The slope of a line provides important information about its relationship to other lines:
-
Parallel Lines: Parallel lines have the same slope. Any line parallel to y = (1/3)x - 2 will also have a slope of 1/3.
-
Perpendicular Lines: Perpendicular lines have slopes that are negative reciprocals of each other. The negative reciprocal of 1/3 is -3. Therefore, any line perpendicular to y = (1/3)x - 2 will have a slope of -3.
Understanding these relationships is crucial in geometry and various applications involving lines and angles.
Conclusion: Mastering the Equation x = 3y + 6
The seemingly simple equation x = 3y + 6 offers a rich opportunity to explore fundamental concepts in algebra and linear relationships. By converting it to slope-intercept form, y = (1/3)x - 2, we gain a clear understanding of its slope, y-intercept, and the relationship between x and y. This understanding extends to graphing the line, solving for unknown variables, and analyzing its relationship to other lines. Mastering these concepts provides a solid foundation for tackling more complex mathematical problems and understanding numerous real-world applications. The ability to manipulate and interpret linear equations is a cornerstone of mathematical literacy and a valuable skill in various fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 1 2 Kilos In Pounds
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 83
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is 15 Percent Of 90
Mar 23, 2025
-
How To Find Zeros In A Polynomial Function
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is 2 5 In A Decimal
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 3y 6 In Slope Intercept Form . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
