Write The Polynomial In Standard Form
listenit
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
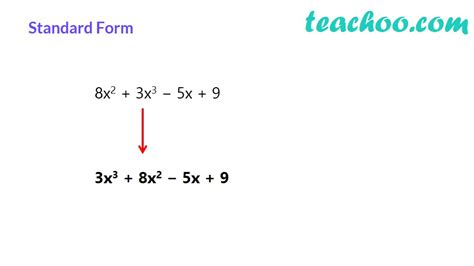
Table of Contents
Writing Polynomials in Standard Form: A Comprehensive Guide
Polynomials are fundamental algebraic expressions that appear throughout mathematics, from basic algebra to advanced calculus. Understanding how to write a polynomial in standard form is crucial for various mathematical operations, including adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing polynomials, as well as for solving polynomial equations and analyzing their graphs. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the concept of standard form for polynomials, offering numerous examples and explanations to solidify your understanding.
What is a Polynomial?
Before diving into standard form, let's revisit the definition of a polynomial. A polynomial is an expression consisting of variables and coefficients, involving only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents of variables.
Key Components of a Polynomial:
- Terms: A polynomial consists of one or more terms. Each term is a product of a coefficient and a variable raised to a non-negative integer power. For example, in the polynomial 3x² + 5x - 7, 3x², 5x, and -7 are individual terms.
- Coefficients: The numerical factors in each term are called coefficients. In 3x² + 5x - 7, the coefficients are 3, 5, and -7.
- Variables: The letters (usually x, y, z, etc.) representing unknown values are called variables.
- Exponents: The non-negative integers indicating the power of a variable are called exponents. In 3x², the exponent is 2.
- Constants: A term without a variable is called a constant term. In 3x² + 5x - 7, -7 is the constant term.
What is Standard Form of a Polynomial?
A polynomial is written in standard form when its terms are arranged in descending order of their exponents. This means the term with the highest exponent comes first, followed by the term with the next highest exponent, and so on, until the constant term (which has an exponent of 0) is at the end.
Example:
The polynomial 5x³ - 2x + 7x² + 9 can be written in standard form as:
5x³ + 7x² - 2x + 9
Steps to Write a Polynomial in Standard Form:
- Identify the terms: First, identify all the terms in the polynomial.
- Determine the degree of each term: The degree of a term is the sum of the exponents of its variables. For example, the degree of 3x²y is 3 (2 + 1).
- Arrange terms in descending order: Arrange the terms in descending order based on their degrees. The term with the highest degree comes first, followed by the term with the next highest degree, and so on. If terms have the same degree, arrange them alphabetically.
- Combine like terms (if any): If there are like terms (terms with the same variable and exponent), combine them by adding their coefficients.
Examples of Writing Polynomials in Standard Form:
Let's work through some examples to illustrate the process:
Example 1:
Write the polynomial 2x + 5x³ - 7 + x² in standard form.
- Terms: 2x, 5x³, -7, x²
- Degrees: 2x (degree 1), 5x³ (degree 3), -7 (degree 0), x² (degree 2)
- Descending Order: 5x³, x², 2x, -7
- Standard Form: 5x³ + x² + 2x - 7
Example 2:
Write the polynomial 4y² - 3y⁴ + 2y - 8y + 11 in standard form.
- Terms: 4y², -3y⁴, 2y, -8y, 11
- Degrees: 4y² (degree 2), -3y⁴ (degree 4), 2y (degree 1), -8y (degree 1), 11 (degree 0)
- Descending Order: -3y⁴, 4y², 2y, -8y, 11
- Combine Like Terms: 2y and -8y combine to -6y
- Standard Form: -3y⁴ + 4y² - 6y + 11
Example 3 (with multiple variables):
Write the polynomial 3xy² + 2x²y - 5 + x³ in standard form.
- Terms: 3xy², 2x²y, -5, x³
- Degrees: 3xy² (degree 3), 2x²y (degree 3), -5 (degree 0), x³ (degree 3)
- Descending Order (alphabetical tie-breaker): x³, 2x²y, 3xy², -5
- Standard Form: x³ + 2x²y + 3xy² - 5
The Degree of a Polynomial
The degree of a polynomial is the highest degree among its terms. When a polynomial is written in standard form, the degree is simply the exponent of the first term. This is a crucial characteristic of a polynomial that affects its properties and behavior.
Polynomials and Their Applications
Polynomials are incredibly versatile tools used in various fields:
- Computer Graphics: Polynomials are used to create curves and shapes in computer graphics and animation.
- Engineering: Engineers use polynomials to model various phenomena, such as the trajectory of a projectile or the stress on a bridge.
- Physics: Polynomials appear frequently in physics equations, describing motion, energy, and other physical quantities.
- Economics: Polynomials are employed in economic modeling to represent relationships between variables.
- Data Analysis: Polynomial regression is a powerful statistical technique used to fit curves to data.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Forgetting to arrange terms in descending order: This is the most common error. Always double-check that the terms are arranged according to their degrees.
- Incorrectly combining like terms: Be careful when combining like terms; make sure you are adding only the coefficients and not changing the variables or exponents.
- Ignoring negative signs: Pay close attention to the signs of the coefficients, especially when combining like terms.
Advanced Polynomial Concepts:
While writing polynomials in standard form is a fundamental skill, understanding more advanced concepts like polynomial factorization, finding roots (zeros), and working with polynomial functions will greatly enhance your mathematical abilities. These concepts build upon the basic understanding of standard form and are essential for solving more complex problems.
Polynomial Factorization: Breaking down a polynomial into simpler factors is a crucial technique in solving polynomial equations and simplifying expressions.
Finding Roots (Zeros): Determining the values of the variable that make a polynomial equal to zero is essential for understanding the behavior of polynomial functions.
Polynomial Functions: Understanding polynomials as functions allows you to analyze their graphs, identify key characteristics like intercepts and turning points, and apply them to real-world modeling situations.
Conclusion:
Writing a polynomial in standard form is a fundamental algebraic skill that lays the foundation for more advanced polynomial manipulation. By understanding the process of arranging terms by descending order of their exponents and combining like terms, you can confidently tackle various mathematical problems involving polynomials. Remember to practice regularly to master this skill and prepare yourself for more advanced concepts in algebra and beyond. The consistent application of these techniques will improve your proficiency and allow you to confidently solve problems involving polynomials in any context. Mastering standard form is not just about following steps; it’s about understanding the underlying structure and properties of polynomials, making you a more effective mathematician and problem-solver.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Fraction Of 1 25
Mar 18, 2025
-
Nine Is What Percent Of 25
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 9 15
Mar 18, 2025
-
Where Is Most Freshwater Located On Earth
Mar 18, 2025
-
7 Miles Is How Many Yards
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Write The Polynomial In Standard Form . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
