Which Type Of Electron Is The Highest In Energy
listenit
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
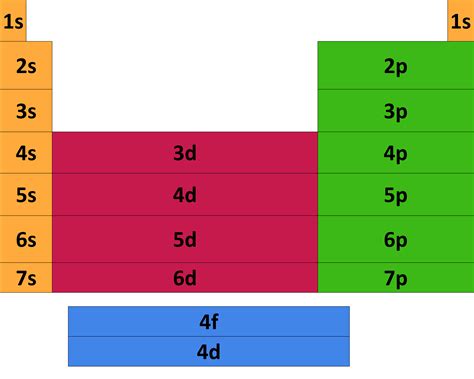
Table of Contents
Which Type of Electron is Highest in Energy? Understanding Electron Configurations and Energy Levels
Determining which type of electron possesses the highest energy requires a deep dive into atomic structure and quantum mechanics. It's not as simple as saying "the outermost electron" always holds the highest energy. The energy of an electron is complex and dependent on several factors, primarily its principal quantum number (n), azimuthal quantum number (l), and magnetic quantum number (ml), and, to a lesser extent, spin quantum number (ms). Let's explore these concepts to understand electron energy levels fully.
Understanding Quantum Numbers and Electron Orbitals
Before we delve into which electron possesses the highest energy, let's review the fundamental quantum numbers that define an electron's state within an atom:
1. Principal Quantum Number (n)
This number represents the principal energy level or shell of the electron. It's a positive integer (n = 1, 2, 3, ...). Higher values of 'n' indicate higher energy levels and greater distance from the nucleus. Electrons in shells with higher 'n' values have, generally, higher energy.
2. Azimuthal Quantum Number (l)
This number defines the subshell or orbital shape within a principal energy level. It ranges from 0 to n-1. The subshells are designated by letters:
- l = 0: s-orbital (spherical shape)
- l = 1: p-orbital (dumbbell shape)
- l = 2: d-orbital (complex shapes)
- l = 3: f-orbital (even more complex shapes)
For a given 'n', the energy levels increase with increasing 'l'. Therefore, a 3d electron generally has higher energy than a 3p electron, and a 3p electron has higher energy than a 3s electron.
3. Magnetic Quantum Number (ml)
This number specifies the orientation of the orbital in space. It ranges from -l to +l, including 0. For example, a p-orbital (l=1) has three possible orientations (ml = -1, 0, +1), corresponding to the px, py, and pz orbitals. Within a given subshell (same 'n' and 'l'), the orbitals have the same energy in the absence of external magnetic fields (this is called degeneracy).
4. Spin Quantum Number (ms)
This number describes the intrinsic angular momentum of the electron, often visualized as its spin. It can only have two values: +1/2 (spin up) or -1/2 (spin down). The spin quantum number does not significantly affect the energy level in the absence of external magnetic fields.
Electron Configuration and the Aufbau Principle
The electron configuration of an atom describes the arrangement of electrons in its various energy levels and sublevels. The Aufbau principle guides this arrangement, stating that electrons fill orbitals starting from the lowest energy levels and proceeding to higher ones. The order of filling is:
1s < 2s < 2p < 3s < 3p < 4s < 3d < 4p < 5s < 4d < 5p < 6s < 4f < 5d < 6p < 7s < 5f < 6d < 7p…
This order is not strictly followed in all cases; exceptions arise due to complex interactions between electrons.
Identifying the Highest Energy Electron
So, which electron has the highest energy? The simple answer is the electron in the highest occupied energy level. However, it's crucial to understand the nuances:
-
The outermost electron is often, but not always, the highest energy electron. Consider the transition metals. While 4s electrons are generally filled before 3d electrons according to Aufbau principle, in reality, 3d electrons are closer in energy and can be involved in bonding, making them higher in energy than the 4s electron in some situations.
-
Energy level ordering can be complex. The simple Aufbau principle is a helpful guideline, but it doesn't fully capture the subtle energy differences between orbitals. Electron-electron repulsion and relativistic effects can alter the energy ordering, especially for heavier atoms. The energy level diagrams of atoms that are more complex than hydrogen are calculated and tabulated rather than simply following the Aufbau Principle.
-
Ionization energy provides clues. The energy required to remove an electron from an atom (ionization energy) provides insights into relative electron energies. The electron with the lowest ionization energy is generally the least tightly bound and, thus, the highest in energy.
-
The valence electrons are usually the most reactive. While not always the absolute highest in energy, these outermost electrons participate directly in chemical bonding and reactions, indicating their importance in atomic interactions. They're the electrons most likely to be involved in interactions and therefore have a significant role in chemical and physical properties.
Examples
Let's consider a few examples to illustrate the concepts:
Example 1: Sodium (Na)
Sodium has an electron configuration of 1s²2s²2p⁶3s¹. The 3s¹ electron is the highest in energy because it's in the highest principal energy level (n=3) and is the outermost electron.
Example 2: Iron (Fe)
Iron has a complex electron configuration: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d⁶. While the 4s electrons are filled before the 3d electrons, the 3d and 4s electrons are close in energy. The energy ordering might shift depending on the chemical environment. In its ground state and most situations, the 3d electrons are considered higher in energy, even though they are filled after the 4s electrons. The relative energies of the 3d and 4s orbitals can change in different oxidation states.
Example 3: Heavier Atoms and Relativistic Effects
For very heavy atoms, relativistic effects become significant. These effects alter the energy levels of electrons, particularly those in s and p orbitals closest to the nucleus. This makes it challenging to definitively state which electron has the highest energy without detailed quantum mechanical calculations.
Conclusion: A nuanced perspective
In summary, identifying the highest energy electron requires careful consideration of several factors, primarily the principal, azimuthal, and magnetic quantum numbers. While the outermost electron is often the highest in energy, this isn't always the case, particularly in complex atoms with significant electron-electron interactions or relativistic effects. Understanding electron configurations, the Aufbau principle (and its limitations), and the impact of ionization energy is crucial for gaining a nuanced understanding of electron energy levels within an atom. Detailed quantum mechanical calculations are needed for an accurate determination of the highest energy electron, especially for complex atoms. This understanding is critical to various fields like chemistry, materials science, and nuclear physics where electron behavior plays a key role in atomic properties. The simple answer is therefore that it depends on the specific atom and its environment, rather than a simple rule applying to all electrons across all atoms.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 43 As A Fraction
Apr 06, 2025
-
Quotes Before Or After A Period
Apr 06, 2025
-
V 1 3pir 2h Solve For H
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Happens When An Atom Gains Or Loses An Electron
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Organelle Is The Site Of Protein Synthesis
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Type Of Electron Is The Highest In Energy . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
