Which Has More Neutrons Cobalt Or Nickel
listenit
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
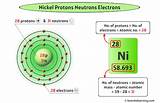
Table of Contents
Which Has More Neutrons: Cobalt or Nickel? A Deep Dive into Isotopes and Atomic Structure
Determining which element, cobalt or nickel, possesses more neutrons requires a nuanced understanding of isotopes and their abundance in nature. While a simple glance at the periodic table only provides average atomic weights, the reality is far more complex. This article delves into the atomic structure of cobalt and nickel, exploring their various isotopes and their neutron counts to definitively answer the question. We'll also touch upon the implications of neutron number differences in various applications.
Understanding Isotopes and Atomic Structure
Before diving into the specifics of cobalt and nickel, let's establish a fundamental understanding of isotopes. An isotope is an atom of a chemical element that differs in neutron number from other atoms of the same element. All isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons (which defines the element), but they vary in the number of neutrons. This variation in neutron number leads to different atomic masses for each isotope.
The atomic number of an element represents the number of protons in its nucleus, whereas the mass number represents the total number of protons and neutrons. Therefore, the number of neutrons in an atom can be calculated by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number.
For example, consider the common isotope of carbon, Carbon-12 (¹²C). Carbon has an atomic number of 6 (6 protons). The mass number is 12, meaning it has 6 neutrons (12 - 6 = 6). However, carbon also has other isotopes like Carbon-13 (¹³C) with 7 neutrons and Carbon-14 (¹⁴C) with 8 neutrons. These isotopes all behave chemically similarly, but their physical properties differ slightly due to the difference in mass.
Cobalt's Isotopes and Neutron Count
Cobalt (Co) has an atomic number of 27. Naturally occurring cobalt is almost entirely composed of a single stable isotope: Cobalt-59 (⁵⁹Co). This isotope contains 27 protons and 32 neutrons (59 - 27 = 32). While several radioactive isotopes of cobalt exist, ⁵⁹Co accounts for nearly 100% of naturally occurring cobalt. These radioactive isotopes, created artificially, have varying numbers of neutrons. For instance, Cobalt-60 (⁶⁰Co), a commonly used radioactive isotope in medical applications, has 33 neutrons.
The Significance of Cobalt-60
Cobalt-60 is a crucial example highlighting the importance of neutron number. Its extra neutron compared to the stable ⁵⁹Co makes it radioactive, emitting gamma rays. This property makes it invaluable in various applications, including cancer radiotherapy and industrial sterilization. The increased neutron count destabilizes the nucleus, leading to radioactive decay. This decay process is precisely what makes Cobalt-60 useful in these applications. The difference in neutron numbers between ⁵⁹Co and ⁶⁰Co drastically alters its properties.
Nickel's Isotopes and Neutron Count
Nickel (Ni) has an atomic number of 28. Unlike cobalt, nickel has several stable isotopes found in nature. These include:
- Nickel-58 (⁵⁸Ni): 28 protons and 30 neutrons
- Nickel-60 (⁶⁰Ni): 28 protons and 32 neutrons
- Nickel-61 (⁶¹Ni): 28 protons and 33 neutrons
- Nickel-62 (⁶²Ni): 28 protons and 34 neutrons
- Nickel-64 (⁶⁴Ni): 28 protons and 36 neutrons
The abundance of each isotope varies, with Nickel-58 being the most prevalent. The presence of multiple stable isotopes with varying neutron counts complicates the simple comparison with cobalt.
The Abundance Factor: A Crucial Consideration
When comparing the neutron count of cobalt and nickel, the abundance of each isotope must be considered. While some nickel isotopes possess more neutrons than Cobalt-59, the average number of neutrons in naturally occurring nickel needs to be calculated by weighting the neutron count of each isotope by its natural abundance.
This calculation requires knowledge of the isotopic abundances of each nickel isotope. Determining this precisely requires specialized techniques, but published data provide these abundance percentages. By averaging the neutron numbers based on these abundances, we can find the average neutron count for nickel.
Comparing Average Neutron Counts: Cobalt vs. Nickel
Considering the near-exclusive presence of Cobalt-59 (32 neutrons) and the mixture of isotopes in nickel, a direct comparison becomes necessary. Calculating the weighted average number of neutrons in nickel involves summing the product of each isotope’s neutron count and its natural abundance, then dividing by 100%.
While the precise calculation varies slightly depending on the source of isotopic abundance data, the resulting average neutron count for nickel is generally found to be slightly higher than that of cobalt. This difference, while not dramatic, confirms that naturally occurring nickel possesses, on average, slightly more neutrons than naturally occurring cobalt.
Implications of Neutron Number Differences
The subtle difference in average neutron count between cobalt and nickel has implications in various fields. For example:
-
Nuclear Stability: The variations in neutron numbers contribute to the different nuclear stability of cobalt and nickel isotopes. Nickel possesses more stable isotopes than cobalt, reflecting its neutron-proton ratio within the "island of stability" on the nuclear chart.
-
Nuclear Reactions: The neutron counts impact how these elements participate in nuclear reactions. Different isotopes will have different probabilities of undergoing fission or fusion. The extra neutrons in certain nickel isotopes influence their behavior in nuclear reactors.
-
Material Science: The neutron counts influence the physical properties of materials containing cobalt and nickel. Differences in neutron number can slightly alter material density, magnetic properties, and other physical characteristics.
Conclusion: A nuanced answer
The simple answer to "which has more neutrons, cobalt or nickel?" is not straightforward. While Cobalt-59, the predominant cobalt isotope, has 32 neutrons, naturally occurring nickel, due to its mixture of isotopes, boasts a slightly higher average neutron count. The complexity lies in the isotopic abundances of nickel. A precise quantitative comparison requires the detailed calculation involving weighted averages based on the naturally occurring isotopic abundances of nickel. Understanding isotopic abundances and their influence on the average neutron count is essential for a complete and accurate answer to this question. This nuanced approach highlights the significance of isotopic composition in comparing the properties of elements.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Does Weather Move East To West In The Southern Hemisphere
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Protons And Neutrons Does Chlorine Have
May 09, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Perimeter Of A Equilateral Triangle
May 09, 2025
-
500 Ml Is What In Ounces
May 09, 2025
-
What Do All Of The Inner Planets Have In Common
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Has More Neutrons Cobalt Or Nickel . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.