What's The Square Root Of 28
listenit
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
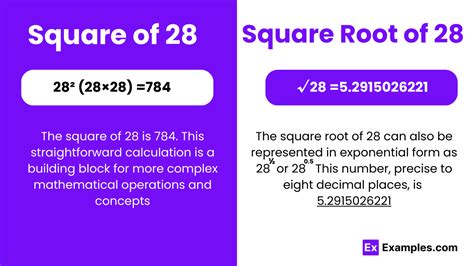
Table of Contents
What's the Square Root of 28? A Deep Dive into Square Roots and Approximations
The question, "What's the square root of 28?" seems simple enough. However, exploring this seemingly straightforward mathematical concept opens doors to a fascinating world of number theory, approximation techniques, and the history of mathematics itself. This article will delve deep into finding the square root of 28, exploring various methods and the significance of irrational numbers.
Understanding Square Roots
Before we tackle the square root of 28 specifically, let's establish a firm understanding of what a square root actually is. The square root of a number (x) is a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals x. In simpler terms, it's the inverse operation of squaring a number. For example:
- The square root of 9 (√9) is 3, because 3 * 3 = 9.
- The square root of 16 (√16) is 4, because 4 * 4 = 16.
This concept is easy enough for perfect squares – numbers that result from squaring an integer. But what about numbers like 28, which aren't perfect squares? This is where things get interesting.
The Irrationality of √28
The square root of 28 is an irrational number. This means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction (a ratio of two integers). Its decimal representation goes on forever without repeating. This characteristic is a fundamental aspect of number theory and has significant implications in various fields of mathematics and science. Understanding this irrationality is key to grasping the methods used to approximate its value.
Methods for Approximating √28
Since we can't express √28 exactly as a decimal or a fraction, we must rely on approximation techniques. Several methods exist, each with varying degrees of accuracy and complexity:
1. Prime Factorization and Simplification
The first step in approximating √28 is to simplify it using prime factorization. We break down 28 into its prime factors:
28 = 2 x 2 x 7
This can be rewritten as:
√28 = √(2 x 2 x 7) = √(2² x 7) = 2√7
This simplification doesn't give us the exact value, but it reduces the calculation to finding the square root of 7, a smaller number, and then multiplying by 2.
2. The Babylonian Method (or Heron's Method)
This iterative method provides increasingly accurate approximations. It's based on an initial guess and refining it through successive calculations. Here's how it works for √28:
-
Make an initial guess: Let's start with 5 (since 5² = 25, which is close to 28).
-
Refine the guess: Divide 28 by our initial guess (28/5 = 5.6).
-
Average the guess and the result: Average 5 and 5.6: (5 + 5.6) / 2 = 5.3
-
Repeat: Now use 5.3 as the new guess and repeat steps 2 and 3. (28/5.3 ≈ 5.283, (5.3 + 5.283)/2 ≈ 5.2915)
We can continue this process to achieve a higher degree of accuracy. The more iterations we perform, the closer we get to the true value of √28.
3. Using a Calculator
Modern calculators provide a straightforward way to obtain an approximation of √28. Simply enter 28 and press the square root button (√). You'll obtain a decimal approximation, typically accurate to several decimal places (e.g., 5.2915026221).
Understanding the Decimal Approximation
The decimal representation of √28 is approximately 5.2915026221... The ellipsis (...) indicates that the digits continue infinitely without repeating, further reinforcing its irrational nature. The level of precision needed depends on the application. For many purposes, a few decimal places (e.g., 5.29) are sufficient. However, in highly precise calculations (like engineering or scientific computations), more decimal places might be required.
Visualizing √28
While we can't visualize an irrational number directly, we can use geometric representations to understand its value. Consider a square with an area of 28 square units. The length of each side of this square represents √28. This visual representation helps connect the abstract concept of the square root to a tangible geometric reality.
The Significance of Irrational Numbers
The existence of irrational numbers like √28 significantly impacted the development of mathematics. The discovery of irrational numbers challenged the Pythagorean belief that all numbers could be expressed as ratios of integers, fundamentally altering our understanding of the number system. Irrational numbers are crucial in various mathematical fields, including calculus, geometry, and number theory.
Applications of Square Roots
Square roots, and consequently the approximation of irrational square roots like √28, have numerous applications across various fields:
- Physics: Calculating distances, velocities, and accelerations frequently involves square roots.
- Engineering: Designing structures, calculating forces, and analyzing electrical circuits often require square root calculations.
- Computer Graphics: Generating images and animations relies heavily on mathematical calculations, including square roots.
- Finance: Calculating investment returns and risk assessments can involve square root operations.
Conclusion: The Enduring Mystery of √28
While we can't express √28 as a neat fraction or a finite decimal, its approximation is readily attainable through various methods. The journey to finding its value provides a window into the fascinating world of irrational numbers, their mathematical significance, and their diverse applications across numerous fields. Understanding the concept of square roots, including those of irrational numbers, lays a crucial foundation for exploring more advanced mathematical concepts and solving real-world problems. The seemingly simple question, "What's the square root of 28?" thus unveils a wealth of mathematical knowledge and intrigue. From simple approximations to intricate iterative methods, the quest for precision continues to drive the evolution of mathematical understanding. So, the next time you encounter a question about the square root of a non-perfect square, remember the elegant simplicity and deep complexity it represents.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Two Airplanes Leave An Airport At The Same Time
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is One Sixth Of 24
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Do Solids And Liquids Have In Common
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is 8 Percent Of 40
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 24 And 28
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What's The Square Root Of 28 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
