What's The Square Root Of 25
listenit
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
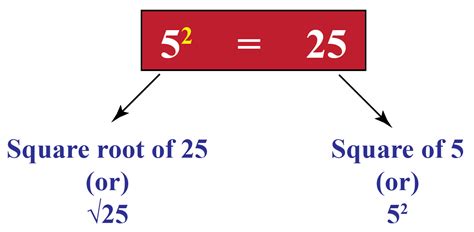
Table of Contents
What's the Square Root of 25? A Deep Dive into Square Roots and Their Applications
The seemingly simple question, "What's the square root of 25?" opens a door to a fascinating world of mathematics. While the answer itself is straightforward – 5 – understanding the concept of square roots and their broader implications extends far beyond this single calculation. This article will explore the square root of 25, delve into the fundamental principles of square roots, examine their properties, and illustrate their significance across various fields.
Understanding Square Roots: The Basics
Before we delve deeper into the specifics of the square root of 25, let's establish a firm understanding of what a square root actually is. In essence, the square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals the original number. We represent this mathematically as √x, where 'x' is the number for which we are finding the square root.
For example:
- √9 = 3 (because 3 x 3 = 9)
- √16 = 4 (because 4 x 4 = 16)
- And, as we already know, √25 = 5 (because 5 x 5 = 25)
This concept is fundamentally linked to the notion of squaring a number. Squaring a number means multiplying it by itself. Therefore, finding the square root is essentially the reverse operation of squaring.
The Square Root of 25: A Simple Solution
The square root of 25 is simply 5. This is because 5 multiplied by itself (5 x 5) equals 25. This is a relatively straightforward calculation, especially for smaller, perfect square numbers like 25. However, the simplicity of this particular example shouldn't overshadow the broader mathematical significance of square roots.
Beyond the Basics: Properties of Square Roots
Understanding the properties of square roots is crucial for more advanced mathematical operations. Some key properties include:
-
Product Property: The square root of a product is equal to the product of the square roots. For example, √(4 x 9) = √4 x √9 = 2 x 3 = 6.
-
Quotient Property: The square root of a quotient is equal to the quotient of the square roots. For example, √(16/4) = √16 / √4 = 4 / 2 = 2.
-
Non-negative Property: The principal square root of a non-negative number is always non-negative. This means that √25 is 5, not -5, although (-5) x (-5) also equals 25. We will explore this further when discussing negative square roots.
-
Square Root of Zero: The square root of zero is zero (√0 = 0).
Dealing with Negative Numbers and Imaginary Numbers
When dealing with the square roots of negative numbers, we enter the realm of imaginary numbers. The square root of a negative number is not a real number; it's an imaginary number represented by the letter 'i', where i² = -1. For instance, √(-1) = i, and √(-25) = 5i. These imaginary numbers are essential in advanced mathematics and physics, particularly in areas like electrical engineering and quantum mechanics.
Understanding the distinction between real and imaginary numbers is important because it clarifies the limitations of finding the square root of certain numbers within the realm of real numbers.
Practical Applications of Square Roots: Beyond the Classroom
While understanding square roots might seem like a purely academic exercise, their applications extend far beyond the mathematics classroom. They are fundamental to various fields, including:
1. Geometry and Trigonometry:
-
Calculating the sides of right-angled triangles: The Pythagorean theorem, a cornerstone of geometry, relies heavily on square roots. The theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the longest side) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides (a² + b² = c²). To find the length of a side, you often need to calculate a square root.
-
Finding distances and angles: Trigonometry, which deals with the relationships between angles and sides of triangles, also frequently utilizes square roots in its calculations.
2. Physics and Engineering:
-
Calculating velocity and acceleration: Many physics formulas involve calculating the square root of quantities like energy or displacement to determine velocity or acceleration.
-
Structural design and engineering: Square roots are crucial in calculating stresses and strains in structures to ensure stability and safety.
-
Electrical Engineering: As mentioned previously, the concept of imaginary numbers, stemming from the square root of negative numbers, is fundamental in electrical engineering, particularly in the analysis of AC circuits.
3. Computer Science and Programming:
-
Algorithm design and optimization: Square roots appear in various algorithms, such as those used in computer graphics and search engines.
-
Game development: Calculating distances, positions, and trajectory frequently involves using square roots.
4. Finance and Investment:
-
Calculating standard deviation: In finance, the standard deviation, a measure of the risk associated with an investment, involves calculating the square root of the variance.
-
Compound interest calculations: Although not directly involving the square root itself, compound interest calculations utilize exponential functions, which are closely related to square roots and other roots.
5. Statistics and Data Analysis:
- Calculating standard error: Similar to standard deviation in finance, the standard error, a measure of the variability in the sample mean, involves the use of square roots.
Square Roots and Higher-Order Roots
The concept of square roots extends to higher-order roots. A cube root (∛x) is a value that, when multiplied by itself three times, equals x. A fourth root (∜x) is a value that, when multiplied by itself four times, equals x, and so on. These higher-order roots are similarly used in various fields, extending the applications of the fundamental principle established by square roots.
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding Square Roots
While the square root of 25 might seem like a trivial calculation, its underlying principles and applications are far-reaching and impactful. From the Pythagorean theorem to advanced physics calculations and financial modeling, the concept of square roots is an indispensable tool across diverse fields. This article has aimed to provide a comprehensive overview of the concept, its properties, and its practical applications, highlighting its significance beyond a simple numerical answer. A firm grasp of square roots, and the broader concept of roots, forms a fundamental building block for further explorations in mathematics and its related disciplines. Mastering this basic concept paves the way for understanding more complex mathematical concepts and their numerous real-world applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 170 Degrees C In Fahrenheit
Mar 17, 2025
-
175 Of What Number Is 42
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Percent Is 20 Out Of 50
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Systematic Name For Mg No3 2
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is 5 12 As A Decimal
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What's The Square Root Of 25 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
