What Is The Si Unit Of Measurement For Volume
listenit
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
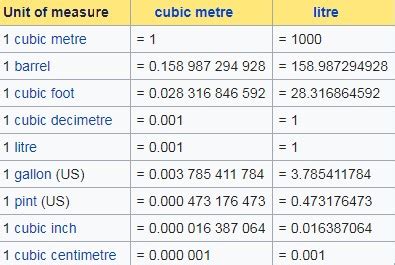
Table of Contents
What is the SI Unit of Measurement for Volume?
The SI unit of measurement for volume is the cubic meter (m³). This seemingly simple answer, however, opens the door to a fascinating exploration of volume measurement, its applications across various scientific fields, and the historical context surrounding its standardization. Understanding the cubic meter and its relationship to other common volume units is crucial for anyone working with measurements in science, engineering, or everyday life. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of volume measurement, providing you with a thorough understanding of the cubic meter and its significance.
Understanding Volume and its Measurement
Before diving into the specifics of the cubic meter, let's establish a fundamental understanding of what volume represents. Volume is a measure of the three-dimensional space occupied by a substance or object. Unlike length or mass, which are one-dimensional and one-dimensional respectively, volume considers all three dimensions – length, width, and height – to quantify the space enclosed.
This is why the SI unit is cubic: it's a measure of three dimensions. Imagine a cube; its volume is determined by multiplying its length, width, and height. If each side of the cube measures one meter, the volume is one cubic meter (1 m³).
Different Approaches to Measuring Volume
The method used to measure volume depends on the nature of the substance. For regular solids (objects with easily measurable dimensions like cubes, spheres, or cylinders), calculating volume using geometrical formulas is straightforward. However, for irregular solids or liquids, different techniques are required.
-
Regular Solids: Simple geometric formulas are used. For example:
- Cube: Volume = side³
- Cuboid (rectangular prism): Volume = length × width × height
- Sphere: Volume = (4/3)πr³ (where r is the radius)
- Cylinder: Volume = πr²h (where r is the radius and h is the height)
-
Irregular Solids: The displacement method is commonly employed. This involves submerging the object in a liquid (usually water) and measuring the volume of water displaced. The volume of the displaced water equals the volume of the object.
-
Liquids: Liquids are typically measured using graduated cylinders, beakers, or volumetric flasks, which are calibrated to indicate specific volumes.
The Cubic Meter: A Deep Dive into the SI Unit
The cubic meter (m³), as the SI unit of volume, holds a central position in the International System of Units (SI). Its significance stems from its coherence with other SI base units: it's derived directly from the meter, the base unit of length. This consistency is a hallmark of the SI system, promoting clarity and ease of conversion between different units.
Why the Cubic Meter is Important
The adoption of the cubic meter as the standard volume unit offers several advantages:
- Universality: Its use transcends geographical boundaries and ensures consistent understanding of volume measurements globally.
- Simplicity: Its derivation from the meter makes it easy to understand and apply.
- Coherence: Its integration with other SI units simplifies calculations and conversions.
- Scientific Accuracy: It forms the basis for accurate scientific measurements in fields like physics, chemistry, and engineering.
Practical Applications of the Cubic Meter
The cubic meter finds applications in a multitude of contexts:
- Engineering: Calculating volumes of materials, structures, and excavations.
- Construction: Estimating the amount of concrete, earth, or other materials needed for a project.
- Agriculture: Measuring the volume of soil, irrigation water, or harvested crops.
- Environmental Science: Determining the volume of pollutants in water bodies or the volume of greenhouse gases emitted.
- Medicine: Measuring the volume of fluids administered or analyzed in medical procedures.
Relation to Other Volume Units
While the cubic meter is the preferred SI unit, other units are commonly used depending on the context. Understanding the relationships between these units is vital for accurate conversions and effective communication.
Common Metric Units
- Cubic centimeter (cm³): One cubic centimeter is equal to one milliliter (mL). This is a convenient unit for smaller volumes, often used in chemistry and biology. 1 m³ = 1,000,000 cm³
- Cubic millimeter (mm³): Used for extremely small volumes. 1 m³ = 1,000,000,000 mm³
- Liter (L): Although not an SI unit, the liter is widely used and is equivalent to 1000 cm³ or 1 dm³. 1 m³ = 1000 L
Imperial Units
The imperial system also has its own units of volume:
- Cubic inch (in³): Used for smaller volumes in various applications.
- Cubic foot (ft³): A common unit for larger volumes, often used in construction and real estate.
- Cubic yard (yd³): Used for very large volumes, such as earthworks.
- Gallon (gal): A unit of liquid volume frequently used in the United States and some other countries.
- Fluid ounce (fl oz): A smaller unit of liquid volume.
Converting between metric and imperial units requires specific conversion factors. Online converters can be helpful for accurate conversions. It's crucial to be aware of the context and the units being used to avoid errors.
Historical Context of Volume Measurement
The standardization of volume measurement has evolved over centuries. Early civilizations relied on rudimentary methods, often using containers of arbitrary sizes. The development of standardized units, like the cubic meter within the metric system, significantly improved the accuracy and consistency of volume measurements. This process reflects a broader trend in scientific history: the development of consistent, internationally agreed-upon standards for measurement. The metric system, with its logical and interconnected units, played a pivotal role in this progress.
Advanced Concepts and Applications
The concept of volume extends beyond simple measurements. In various scientific disciplines, more nuanced understandings of volume are employed.
Density and Volume
Density, defined as mass per unit volume, is a critical concept linking mass and volume. Calculating density requires knowing both the mass and volume of a substance. The formula is: Density = Mass / Volume. Density is expressed in units like kg/m³ (kilograms per cubic meter) in the SI system.
Volume in Thermodynamics
In thermodynamics, volume is a key state variable, influencing pressure and temperature. The ideal gas law (PV = nRT) illustrates the relationship between pressure (P), volume (V), number of moles (n), gas constant (R), and temperature (T). Understanding how volume affects these parameters is essential in various thermodynamic processes.
Volume in Fluid Mechanics
Fluid mechanics extensively uses volume concepts to analyze fluid flow, pressure distribution, and buoyancy. Understanding volume and its changes is crucial for designing systems involving liquids and gases.
Volume in Medical Imaging
Medical imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans provide three-dimensional representations of internal organs and structures. The volumes of these structures can be computed from the images, providing valuable diagnostic information.
Conclusion: Mastering Volume Measurement
The cubic meter, as the SI unit of volume, represents a cornerstone of precise measurement. Its use facilitates consistent communication and calculations across diverse scientific and engineering fields. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview, from fundamental concepts to advanced applications, highlighting the significance of the cubic meter in our understanding and application of volume. Understanding the cubic meter and its relationship to other volume units is a fundamental skill for anyone involved in scientific, engineering, or technical work, ensuring accuracy and clarity in measurement and communication. Whether dealing with cubic centimeters or cubic kilometers, the foundational understanding of the cubic meter as the fundamental unit of volume remains essential.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Horizontal Columns On The Periodic Table Are Called
Apr 05, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 14 And 7
Apr 05, 2025
-
7 Cm Is How Many Inches
Apr 05, 2025
-
How Many Ounces Is A Fifth Of Liquor
Apr 05, 2025
-
Quadrilateral That Is Not A Rhombus
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Si Unit Of Measurement For Volume . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
