What Is The Si For Volume
listenit
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
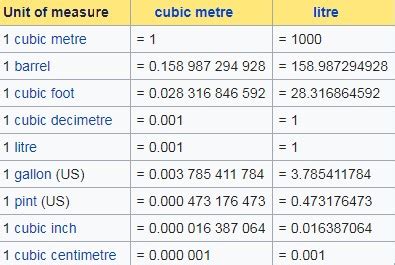
Table of Contents
What is the SI Unit for Volume? Exploring Cubic Meters and Liters
The question, "What is the SI unit for volume?" might seem straightforward, but delving deeper reveals a nuanced understanding of measurement systems and their practical applications. While the answer is definitively the cubic meter (m³), the story doesn't end there. Understanding the SI system, its relationship to other units like liters, and the practical implications for various applications is crucial for anyone working with measurements. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of volume measurement, clarifying the role of the cubic meter and its connections to other commonly used units.
Understanding the International System of Units (SI)
The International System of Units (SI), also known as the metric system, is the modern form of the metric system and is the most widely used system of measurement internationally. It's built upon seven base units, from which all other units are derived. These base units include:
- Meter (m): The base unit of length.
- Kilogram (kg): The base unit of mass.
- Second (s): The base unit of time.
- Ampere (A): The base unit of electric current.
- Kelvin (K): The base unit of thermodynamic temperature.
- Mole (mol): The base unit of amount of substance.
- Candela (cd): The base unit of luminous intensity.
Volume, as a measure of three-dimensional space, isn't a base unit. Instead, it's a derived unit, meaning it's derived from the base unit of length – the meter.
The Cubic Meter: The SI Unit of Volume
Because volume is three-dimensional, the SI unit for volume is the cubic meter (m³). This represents a cube with sides measuring one meter in length. It's a fundamental unit for expressing the capacity or space occupied by an object or substance. The cubic meter is essential in numerous fields, including:
- Engineering: Calculating the volume of materials for construction projects, determining the capacity of tanks and reservoirs, and assessing the displacement of fluids.
- Physics: Defining the volume of gases in thermodynamic calculations and understanding fluid dynamics.
- Chemistry: Measuring the volume of reactants and products in chemical reactions.
- Environmental Science: Estimating the volume of pollutants in the environment, measuring water flow in rivers, and analyzing soil volume.
Advantages of Using Cubic Meters
The cubic meter offers several significant advantages:
- Consistency: It aligns perfectly with the SI system, ensuring a coherent and consistent measurement framework.
- Scalability: It's easily scalable. Larger volumes can be expressed using prefixes like kilocubic meters (km³), megacubic meters (Mm³), and so on, while smaller volumes can use prefixes like cubic centimeters (cm³) or cubic millimeters (mm³).
- Universality: Its widespread acceptance internationally facilitates seamless communication and collaboration across various scientific and engineering disciplines.
The Liter: A Commonly Used Unit of Volume
While the cubic meter is the official SI unit, the liter (L) is frequently used, particularly in everyday life and for measuring liquids. One liter is exactly equal to one cubic decimeter (dm³), which in turn is equivalent to 1000 cubic centimeters (cm³) or 0.001 cubic meters (m³). The liter's popularity stems from its convenient scale for common volumes.
Liter vs. Cubic Meter: When to Use Each
The choice between liters and cubic meters depends largely on the context and the magnitude of the volume being measured:
- Large volumes: Cubic meters are more appropriate for large-scale applications like calculating the volume of a building, a reservoir, or a large container.
- Small volumes: Liters are better suited for measuring smaller volumes such as liquids in bottles, containers, or everyday measurements in cooking or baking.
- Scientific precision: In scientific contexts demanding high precision, the cubic meter, aligned with the SI system, is generally preferred.
Converting Between Cubic Meters and Liters
Converting between cubic meters and liters is straightforward because of the established equivalence:
- Cubic meters to liters: Multiply the value in cubic meters by 1000. For example, 2 m³ = 2000 L.
- Liters to cubic meters: Divide the value in liters by 1000. For example, 5000 L = 5 m³.
Other Units of Volume and Their Relationship to the SI System
While the cubic meter and liter are dominant, several other units are used in various contexts:
- Cubic centimeters (cm³): Commonly used for smaller volumes, often interchangeable with milliliters (mL).
- Cubic millimeters (mm³): Suitable for extremely small volumes.
- Cubic kilometers (km³): Used for very large volumes, such as the volume of a large body of water or a geological formation.
- Gallons (gal), quarts (qt), pints (pt), ounces (oz): These are part of the imperial system and require conversion factors to relate them to the SI system. Converting these units to cubic meters requires using specific conversion factors.
Practical Applications Across Various Fields
The SI unit for volume, the cubic meter, and its related unit, the liter, play crucial roles across a multitude of fields:
1. Construction and Engineering
Accurate volume calculations are essential for determining material quantities, designing foundations, and estimating the capacity of structures. Engineers use cubic meters to calculate the volume of concrete needed for a building, the amount of earth to be excavated for a foundation, or the capacity of a water tank.
2. Environmental Science
In environmental studies, volume calculations are critical for assessing water resources, measuring pollution levels, and understanding ecological processes. Scientists use cubic meters to measure the volume of water in rivers, lakes, and reservoirs, helping manage water resources effectively and accurately monitoring pollution levels.
3. Medicine and Healthcare
The precise measurement of volumes is essential in medical applications, particularly in administering medication, performing blood tests, and managing fluid intake and output. Accurate dosage calculations depend on the precise measurement of liquid volumes, typically using milliliters or cubic centimeters.
4. Chemistry and Physics
Volume measurements are paramount in chemical reactions and physical experiments. Scientists carefully measure the volume of reactants and products in chemical reactions, enabling the accurate determination of reaction rates, yields, and other critical parameters. In physics, precise volume measurements are vital in studies of fluid dynamics, thermodynamics, and other areas.
5. Meteorology
Meteorologists frequently use cubic meters to measure the volume of clouds, enabling them to estimate rainfall potential and better understand atmospheric processes. This plays a crucial role in weather forecasting and understanding climatic patterns.
Conclusion: The Importance of Consistent Volume Measurement
The choice of the SI unit for volume, the cubic meter, provides a foundation for consistent and universally understood measurements. While the liter offers convenience in many practical applications, understanding its relationship to the cubic meter is crucial for maintaining accuracy and facilitating seamless communication across diverse scientific and engineering disciplines. From large-scale engineering projects to the precise measurements in medical applications, the consistent application of volume units within the SI framework remains essential for accurate calculations, clear communication, and progress in various fields. Mastering the nuances of volume measurement ensures accuracy and precision across a multitude of scientific and practical applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Find Area Of Parallelogram With Vectors
Apr 05, 2025
-
Why Do Contour Lines Never Cross
Apr 05, 2025
-
Is Boron A Gas Solid Or Liquid
Apr 05, 2025
-
How Do You Factor 2x 2 7x 3
Apr 05, 2025
-
Which Group Of Metals Are The Most Reactive
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Si For Volume . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
