What Is The Number Of Valence Electrons For Nitrogen
listenit
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
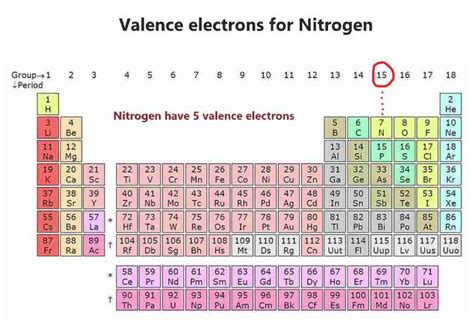
Table of Contents
What is the Number of Valence Electrons for Nitrogen? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding
Understanding the number of valence electrons an atom possesses is crucial in predicting its chemical behavior and reactivity. This article will delve deep into the concept of valence electrons, focusing specifically on nitrogen and its role in chemical bonding. We'll explore its atomic structure, electron configuration, and how its valence electrons determine its participation in various chemical reactions.
Understanding Valence Electrons
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons of an atom. They are the electrons most involved in chemical reactions and bond formation. These electrons are located in the highest energy level (also known as the outermost shell or valence shell) of an atom. The number of valence electrons determines an element's reactivity and the types of chemical bonds it can form. Elements with a full valence shell (typically 8 electrons, following the octet rule) are generally unreactive, while those with incomplete valence shells readily react to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Nitrogen's Atomic Structure and Electron Configuration
Nitrogen (N), atomic number 7, resides in Group 15 (also known as Group VA or the pnictogens) of the periodic table. Its atomic number signifies that it possesses 7 protons and 7 electrons in a neutral atom. To understand its valence electron count, we need to explore its electron configuration.
Electron Configuration: 1s²2s²2p³
The electron configuration of nitrogen is 1s²2s²2p³. This tells us how the electrons are distributed among the different energy levels and sublevels within the atom.
- 1s²: Two electrons occupy the first energy level (n=1) in the 's' sublevel. This is the innermost shell and is considered a core shell, not directly involved in bonding.
- 2s²: Two electrons occupy the second energy level (n=2) in the 's' sublevel.
- 2p³: Three electrons occupy the second energy level (n=2) in the 'p' sublevel. The 'p' sublevel can hold a maximum of six electrons.
Determining the Number of Valence Electrons for Nitrogen
The valence electrons are those in the outermost energy level. In nitrogen's case, the outermost energy level is n=2. This level contains both the 2s and 2p electrons. Therefore, nitrogen has a total of five valence electrons (two from the 2s sublevel and three from the 2p sublevel).
The Significance of Five Valence Electrons
The presence of five valence electrons significantly influences nitrogen's chemical behavior. To achieve a stable octet (eight electrons in its outermost shell), nitrogen readily forms covalent bonds, sharing electrons with other atoms. This explains why nitrogen is rarely found as a single atom but rather exists as a diatomic molecule (N₂) or forms various compounds.
Nitrogen's Role in Chemical Bonding
Nitrogen's five valence electrons allow it to participate in a variety of chemical bonding scenarios:
1. Covalent Bonding: The Formation of N₂
Nitrogen's most common form is the diatomic molecule, N₂. In this molecule, each nitrogen atom shares three electrons with the other, forming a triple covalent bond. This triple bond is exceptionally strong, contributing to the relatively inert nature of nitrogen gas in its elemental form. The sharing of electrons allows each nitrogen atom to achieve a stable octet configuration.
2. Covalent Bonding: Formation of Ammonia (NH₃)
Nitrogen readily forms covalent bonds with other elements. A prime example is ammonia (NH₃). In ammonia, nitrogen shares three electrons with three hydrogen atoms, forming three single covalent bonds. This allows nitrogen to achieve a stable octet, while each hydrogen atom achieves a stable duet (two electrons).
3. Covalent Bonding: Formation of Nitric Oxide (NO)
Nitrogen can form covalent bonds with other elements where the octet rule isn't fully satisfied. Nitric oxide (NO) is a good example. In NO, the nitrogen atom has only seven electrons in its valence shell. This is due to the odd number of electrons involved in the bonding process.
4. Ionic Bonding (Less Common)
While less common than covalent bonding, nitrogen can participate in ionic bonding under specific circumstances. However, it generally requires highly electronegative elements. Even in these cases, the core idea of achieving a stable octet remains influential.
The Importance of Valence Electrons in Predicting Chemical Behavior
The number of valence electrons is paramount in predicting an element's reactivity and the types of chemical bonds it will form. Nitrogen's five valence electrons lead to its propensity to form covalent bonds, often leading to molecules and compounds with diverse properties and functionalities.
Nitrogen's Importance in Biological Systems
Nitrogen's crucial role extends to biological systems. It's a key component of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, and nucleic acids, the fundamental components of DNA and RNA. The ability of nitrogen to form strong covalent bonds is vital for the structural integrity and functionality of these essential biomolecules.
Applications of Nitrogen and its Compounds
The unique properties stemming from nitrogen's valence electron count make it essential in various applications:
-
Fertilizers: Nitrogen is a critical component of fertilizers, fueling plant growth and agricultural productivity. Compounds like ammonia and nitrates provide essential nitrogen sources for plants.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Nitrogen is integral to the synthesis of many pharmaceutical compounds. Its presence in numerous drug molecules is critical for their therapeutic effects.
-
Explosives: Some nitrogen compounds, like nitrates and nitroglycerin, are utilized in explosives due to their ability to undergo rapid decomposition reactions that release significant energy.
-
Food Packaging: Nitrogen gas is often used in food packaging to extend shelf life by preventing oxidation and spoilage.
-
Industrial Processes: Nitrogen plays a significant role in diverse industrial processes, including the production of ammonia, nitric acid, and other crucial chemicals.
Conclusion: The Significance of Nitrogen's Five Valence Electrons
The seemingly simple number of five valence electrons in nitrogen significantly impacts its chemical behavior and numerous applications. This number dictates its bonding preferences, reactivity, and the properties of the compounds it forms. Understanding nitrogen's valence electron structure is critical to comprehending its significance in various fields, ranging from agriculture to medicine and industrial manufacturing. The strong covalent bonds it forms are responsible for its presence in the building blocks of life, while its reactivity allows for the production of a wide range of crucial compounds. Nitrogen's five valence electrons truly are the foundation of its remarkable chemical versatility.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 1 6 Of A Pizza
Mar 17, 2025
-
How To Write 50 As A Fraction
Mar 17, 2025
-
The Si Unit Of Charge Is The
Mar 17, 2025
-
How To Take Gradient Of A Function
Mar 17, 2025
-
Jerry Walked A Dog From 640 To 730 Asvab
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Number Of Valence Electrons For Nitrogen . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
