What Is The Mass Number Of Potassium
listenit
Apr 04, 2025 · 5 min read
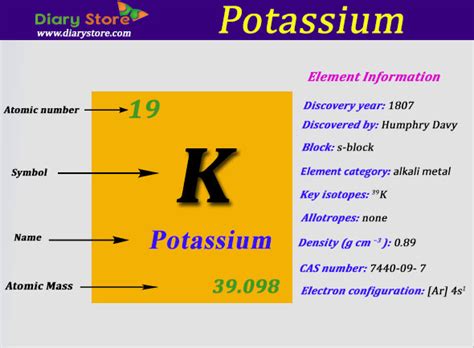
Table of Contents
What is the Mass Number of Potassium? Understanding Isotopes and Atomic Mass
Potassium, a vital element for human life and a common component in fertilizers, is represented by the symbol K (from the Latin word kalium). But understanding potassium goes beyond its simple symbol. To truly grasp its properties and behavior, we need to delve into the concept of mass number and its relationship to isotopes. This comprehensive guide will explore what the mass number of potassium is, how it's determined, and the significance of its different isotopes.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before we tackle the mass number of potassium, let's review the fundamental components of an atom:
- Protons: Positively charged particles found in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element; all potassium atoms have 19 protons. This is also known as the atomic number.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles also residing in the nucleus. Unlike protons, the number of neutrons can vary within the same element, leading to different isotopes.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus. The number of electrons usually equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
Isotopes: The Key to Understanding Mass Number Variation
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons. This difference in neutron count affects the atom's mass but not its chemical properties significantly. Potassium has several naturally occurring isotopes, each with a different mass number.
What is Mass Number?
The mass number (A) represents the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus. It's an integer value and is a crucial characteristic used to identify specific isotopes. It's important to distinguish the mass number from the atomic mass, which is the weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element.
Potassium Isotopes and Their Mass Numbers
Potassium possesses three naturally occurring isotopes:
-
Potassium-39 (³⁹K): This is the most abundant isotope, making up approximately 93.3% of naturally occurring potassium. Its mass number is 39, meaning it contains 19 protons and 20 neutrons (39 - 19 = 20).
-
Potassium-40 (⁴⁰K): A radioactive isotope, ⁴⁰K constitutes about 0.0117% of natural potassium. Its mass number is 40, indicating 19 protons and 21 neutrons (40 - 19 = 21). This isotope is of particular interest because of its role in radioactive dating techniques and its contribution to the Earth's internal heat. The radioactive decay of ⁴⁰K is crucial in geochronology, providing insights into the age of rocks and minerals.
-
Potassium-41 (⁴¹K): The third naturally occurring isotope, ⁴¹K, comprises roughly 6.7% of natural potassium. Its mass number is 41, meaning it possesses 19 protons and 22 neutrons (41 - 19 = 22).
Calculating Atomic Mass: A Weighted Average
The atomic mass of potassium listed on the periodic table is not simply the average of the mass numbers of its isotopes. Instead, it's a weighted average, taking into account the relative abundance of each isotope. The atomic mass reflects the average mass of a large number of potassium atoms, considering the prevalence of each isotope.
The calculation involves multiplying the mass number of each isotope by its relative abundance (expressed as a decimal), summing these products, and obtaining the weighted average. For potassium, the atomic mass is approximately 39.10 amu (atomic mass units). This value reflects the higher abundance of ³⁹K, which significantly influences the average.
Significance of Potassium Isotopes in Various Fields
The different isotopes of potassium have diverse applications across multiple scientific disciplines:
1. Geology and Geochronology:
The radioactive decay of ⁴⁰K is fundamental to radiometric dating, allowing geologists to determine the age of rocks and minerals. By analyzing the ratio of ⁴⁰K to its decay products (⁴⁰Ar and ⁴⁰Ca), scientists can estimate the time elapsed since the rock's formation. This technique is vital for understanding geological processes and the Earth's history.
2. Biology and Medicine:
Potassium plays a critical role in various biological processes, including nerve impulse transmission, muscle contraction, and maintaining fluid balance within cells. The different isotopes have been used in tracer studies to investigate potassium transport and metabolism within living organisms. Radioactive ⁴⁰K, while present in trace amounts in the body, contributes to our natural background radiation exposure.
3. Nuclear Physics and Research:
The properties of potassium isotopes, including their radioactive decay characteristics, are valuable in nuclear physics research. Studies on potassium isotopes contribute to a broader understanding of nuclear reactions, decay processes, and nuclear structure.
Distinguishing Mass Number and Atomic Mass: A Crucial Point
It's essential to clarify the difference between mass number and atomic mass. The mass number is a whole number representing the total number of nucleons (protons and neutrons) in a specific isotope. The atomic mass is a weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes, reflecting their relative abundances. While related, they are distinct concepts crucial for understanding the properties and behavior of elements.
The Importance of Precision in Scientific Measurement
Accurate determination of mass numbers and atomic masses is critical in various scientific applications. Mass spectrometry, a highly precise technique, allows scientists to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions, providing highly accurate data on isotope abundances and atomic masses. This precision is essential for accurate dating techniques, medical applications, and fundamental research in nuclear physics.
Conclusion: Understanding Potassium's Mass Numbers and Isotopes
The mass number of potassium isn't a single value, but rather a range of values reflecting the existence of multiple isotopes. Understanding these isotopes, their mass numbers, and their relative abundances is crucial to grasping potassium's properties and its applications in various fields. From geological dating to biological processes, the different potassium isotopes play important roles, highlighting the complexity and fascinating nature of this essential element. The distinction between mass number and atomic mass is critical, reflecting the importance of precise measurement in scientific research. The information presented provides a comprehensive overview of the mass numbers of potassium isotopes and their significance in numerous scientific disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What The Square Root Of 30
Apr 04, 2025
-
Monomer For Nucleic Acids Is Called
Apr 04, 2025
-
16 And 2 3 As A Fraction
Apr 04, 2025
-
Iron Rusting Is A Chemical Change
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Many Unpaired Electrons Does Phosphorus Have
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Mass Number Of Potassium . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
