What Is The Low Point Of A Wave Called
listenit
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
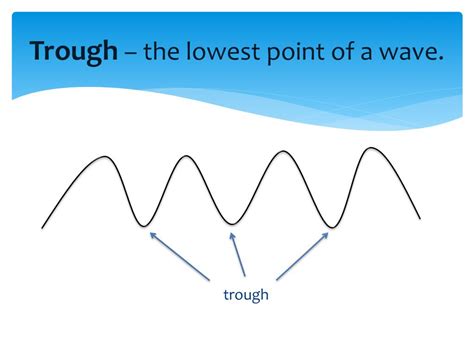
Table of Contents
What is the Low Point of a Wave Called? Understanding Wave Anatomy and Terminology
The ocean's rhythmic pulse, its ceaseless ebb and flow, is a mesmerizing spectacle. Understanding the mechanics of waves is crucial for surfers, sailors, coastal engineers, and anyone fascinated by the power and beauty of the sea. One fundamental aspect of wave structure is identifying its different parts. This article delves into the specifics of wave anatomy, focusing on the low point of a wave, often referred to as the trough. We'll explore its significance, its relation to other wave characteristics, and its role in various oceanic phenomena.
Understanding Wave Terminology: Crest vs. Trough
Before we delve into the details of the trough, let's establish a clear understanding of basic wave terminology. Waves, whether in the ocean, a lake, or even a ripple in a cup of tea, have distinct features:
-
Crest: This is the highest point of a wave. It represents the peak of the wave's elevation above the mean water level.
-
Trough: This is the lowest point of a wave, the opposite of the crest. It signifies the valley between successive wave crests. This is the focal point of our exploration.
-
Wavelength: This is the horizontal distance between two successive crests (or troughs). It dictates the size and energy of the wave.
-
Wave Height: This is the vertical distance between the crest and the trough. It's a key indicator of wave intensity.
-
Wave Period: This measures the time it takes for two successive crests (or troughs) to pass a fixed point. This is a crucial parameter in understanding wave frequency.
The Trough: A Deeper Dive into the Low Point of a Wave
The trough, as the lowest point of a wave, isn't merely a negative counterpart to the crest. It plays a significant role in the overall dynamics of wave propagation and interaction. Think of it as the 'valley' between two hills (crests). Its depth relative to the mean water level is a critical factor in determining the wave's height and, consequently, its energy. A deeper trough indicates a higher wave, and therefore, a more powerful wave.
The Trough's Role in Wave Formation and Propagation
The formation of a wave begins with a disturbance, often wind blowing across the water's surface. The wind imparts energy to the water, creating ripples that gradually develop into larger waves. The interplay between the crests and troughs is fundamental to wave propagation. As the wave travels, the water particles don't actually move forward with the wave but rather move in circular orbits. This movement is most pronounced near the surface and diminishes with depth. In the trough, the downward movement of water particles is at its maximum, contributing to the overall energy transfer of the wave.
Trough Depth and Wave Characteristics
The depth of the trough is intrinsically linked to several key wave characteristics:
-
Wave Height: As previously mentioned, a greater difference between the crest and trough translates to a higher wave height. This is directly related to the wave's energy – higher waves possess greater energy.
-
Wave Steepness: The ratio of wave height to wavelength determines the wave's steepness. A very steep wave is likely to break, with the trough playing a role in this process. When the wave steepness exceeds a critical limit, the wave becomes unstable and collapses, transferring its energy to the surrounding water.
-
Wave Breaking: The breaking of a wave is a complex process involving the interaction of the crest and trough. As a wave approaches the shore, the bottom of the wave interacts with the seabed, causing it to slow down. The upper part of the wave continues at its original speed, leading to an increase in wave steepness. Ultimately, the crest overtakes the trough, resulting in the wave breaking. The shape and depth of the trough significantly influence this breaking process.
Troughs and Their Impact on Coastal Processes
The trough's influence extends far beyond the open ocean. It plays a vital role in shaping coastal environments:
-
Erosion: The forceful backwash associated with the trough in breaking waves is a major contributor to coastal erosion. The constant pounding of water against the shoreline, particularly during storm surges, can significantly alter the coastline. The energy concentrated in the trough during breaking contributes to the removal of sediment and the shaping of cliffs and beaches.
-
Sediment Transport: Troughs are not only involved in erosion but also in the transport of sediment. The backwash from breaking waves, which is strongest in the trough area, carries sediment away from the shoreline. This transported sediment can be deposited elsewhere, forming new landforms.
-
Beach Morphology: The continuous interaction between the crests and troughs of waves significantly shapes beach morphology. The size and distribution of sediment on a beach are influenced by the wave's energy, which is partially determined by the trough's depth. The variations in the trough's depth over time can lead to changes in the beach's profile.
Troughs in Different Wave Types
The characteristics of a trough can vary depending on the type of wave:
-
Wind Waves: These are the most common type of waves, generated by wind blowing over the water's surface. The troughs in wind waves are generally relatively shallow and their depth depends on wind speed, fetch (distance over which the wind blows), and duration.
-
Swell Waves: These are long-period waves that have traveled a considerable distance from their origin. Their troughs tend to be more regular and predictable than those in wind waves.
-
Tsunamis: These are destructive waves caused by underwater earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or landslides. Tsunamis have extremely long wavelengths and travel at high speeds. While the trough's depth might not be as visually pronounced in the open ocean, the immense energy concentrated in the trough is what makes tsunamis so devastating when they reach the coast. The trough can pull enormous amounts of water away from the shoreline before the devastating crest arrives.
Measuring Trough Depth: Instruments and Techniques
Accurately measuring the depth of a trough, especially in the open ocean, presents challenges. Several methods are used, each with its limitations:
-
Wave Buoys: These are floating instruments equipped with sensors that measure various wave parameters, including wave height and period. From this data, the trough depth can be indirectly calculated.
-
Radar Altimeters: These satellite-based instruments use radar pulses to measure the distance to the ocean surface. They can provide data on wave height, enabling the calculation of trough depth.
-
Acoustic Doppler Current Profilers (ADCPs): These instruments use sound waves to measure water currents and wave characteristics. They can provide detailed information about the vertical structure of waves, including trough depth.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Wave Dynamics
The trough, though often overlooked, is an essential element in understanding wave dynamics. Its depth, in conjunction with crest height and wavelength, defines the wave's overall energy and its impact on coastal processes. From shaping beaches and contributing to erosion to playing a crucial role in wave breaking and tsunami formation, the trough’s significance is undeniable. By studying the trough, scientists can gain a better understanding of wave behavior, predict extreme events, and improve coastal management strategies. The next time you witness the ocean’s power, remember to appreciate not only the majestic crest but also the equally important, and often hidden, depth of the trough. Further research into the complexities of trough dynamics promises a deeper understanding of this fundamental aspect of our planet's oceans.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Four Nitrogenous Bases Found In Dna Are
Apr 06, 2025
-
Why Is Water Liquid At Room Temp
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 6 And 16
Apr 06, 2025
-
A Gardener Is Mowing A 20 By 40 Yard
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is The Name For Nh4
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Low Point Of A Wave Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
