What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 10 And 12
listenit
Mar 17, 2025 · 4 min read
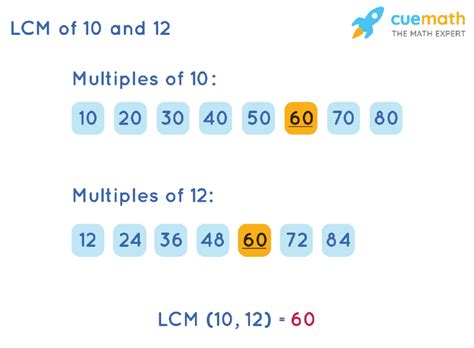
Table of Contents
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 10 and 12? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic problem, but understanding the underlying concepts unlocks a world of mathematical beauty and practical applications. This article explores the LCM of 10 and 12 in detail, delving into various methods of calculation, explaining the theoretical underpinnings, and showcasing its relevance in diverse fields.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. It's a fundamental concept in number theory with significant applications in areas like scheduling, music theory, and even computer science.
Think of it like this: imagine you have two gears with 10 and 12 teeth respectively. The LCM represents the number of rotations after which both gears will simultaneously return to their starting positions. Finding this "synchronization point" is precisely what calculating the LCM achieves.
Methods for Calculating the LCM of 10 and 12
There are several ways to determine the LCM of 10 and 12. Let's explore the most common approaches:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward method, especially suitable for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest multiple common to both.
- Multiples of 10: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80...
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84...
Notice that 60 is the smallest number present in both lists. Therefore, the LCM of 10 and 12 is 60.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides deeper insight into the structure of the numbers. We first find the prime factorization of each number.
- Prime factorization of 10: 2 x 5
- Prime factorization of 12: 2 x 2 x 3 = 2² x 3
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization and multiply them together.
- Highest power of 2: 2² = 4
- Highest power of 3: 3¹ = 3
- Highest power of 5: 5¹ = 5
LCM(10, 12) = 2² x 3 x 5 = 4 x 3 x 5 = 60
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) are closely related. The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is equal to the product of the two numbers. That is:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
First, we find the GCD of 10 and 12 using the Euclidean algorithm or prime factorization.
- Prime factorization method for GCD: The common prime factor is 2. Therefore, GCD(10, 12) = 2.
Now, we can calculate the LCM:
LCM(10, 12) = (10 x 12) / GCD(10, 12) = 120 / 2 = 60
Real-World Applications of LCM
The LCM isn't just a theoretical concept; it has practical applications in numerous fields:
1. Scheduling and Time Management
Imagine you have two events that occur at regular intervals. The LCM helps determine when both events will coincide. For example:
- Bus A arrives every 10 minutes.
- Bus B arrives every 12 minutes.
The LCM(10, 12) = 60 minutes, meaning both buses will arrive at the same time every hour.
2. Music Theory
In music, the LCM is crucial for understanding harmony and rhythm. The LCM helps determine when two musical phrases with different durations will synchronize.
3. Construction and Engineering
LCM is used to calculate the lengths of materials needed for projects where repetitive patterns are involved. For instance, in tiling a floor with tiles of two different sizes, the LCM determines the smallest size of a square area that can be tiled perfectly using both tile types.
4. Computer Science
LCM finds applications in algorithms related to process synchronization, scheduling tasks, and managing resources. In computer graphics, the LCM might be used to synchronize frame rates between different components.
Further Exploration: Extending the Concept
The concept of LCM extends beyond two numbers. You can find the LCM of three or more numbers using similar methods. For instance, the prime factorization method remains effective; you simply include all prime factors raised to their highest powers across all numbers.
Furthermore, the concept of LCM is intrinsically linked to other number theory concepts like GCD, prime factorization, and modular arithmetic. Understanding these connections enriches your mathematical comprehension and expands your problem-solving skills.
Conclusion: The Significance of LCM(10, 12) = 60
We've explored various methods to calculate the least common multiple of 10 and 12, consistently arriving at the answer: 60. This seemingly simple calculation reveals the elegance and practical utility of fundamental number theory concepts. The LCM's applications extend far beyond basic arithmetic, showcasing its importance in scheduling, music, engineering, and computer science. By understanding the LCM, we gain a deeper appreciation of the mathematical structure that underlies many aspects of our world. Further exploration of related concepts will only deepen this understanding and reveal more about the interconnectedness of mathematical ideas. The seemingly simple problem of finding the LCM of 10 and 12 provides a gateway to a richer and more profound understanding of mathematics and its widespread applicability.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Does It Mean For A Solution To Be Saturated
May 09, 2025
-
Derivative Of Log Base 2 Of X
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Minutes Are In 1 4 Of An Hour
May 09, 2025
-
A Parallelogram Is A Square Always Sometimes Never
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Percentage Of 0 3
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 10 And 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.