What Is The Gram Formula Mass Of Ca Oh 2
listenit
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
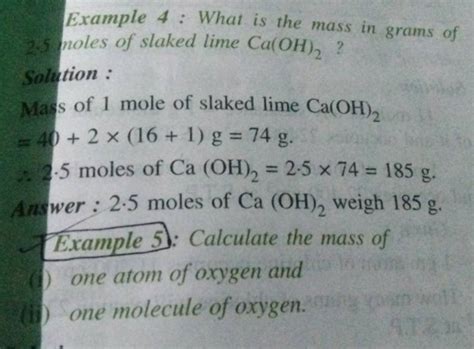
Table of Contents
What is the Gram Formula Mass of Ca(OH)₂? A Comprehensive Guide
Determining the gram formula mass (also known as molar mass or molecular weight) of a compound is a fundamental skill in chemistry. This guide will comprehensively explain how to calculate the gram formula mass of calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)₂, and delve into related concepts to provide a thorough understanding.
Understanding Gram Formula Mass
The gram formula mass represents the mass of one mole of a substance. A mole is a fundamental unit in chemistry, defined as 6.022 x 10²³ particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.). The gram formula mass is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). Knowing the gram formula mass is crucial for various stoichiometric calculations, including determining the amount of reactants needed for a reaction or the amount of product formed.
Calculating the Gram Formula Mass of Ca(OH)₂
To calculate the gram formula mass of Ca(OH)₂, we need to consider the atomic masses of each element present in the compound: calcium (Ca), oxygen (O), and hydrogen (H). These atomic masses are typically found on the periodic table.
Step 1: Identify the elements and their atomic masses.
- Calcium (Ca): The atomic mass of calcium is approximately 40.08 g/mol.
- Oxygen (O): The atomic mass of oxygen is approximately 16.00 g/mol.
- Hydrogen (H): The atomic mass of hydrogen is approximately 1.01 g/mol.
Step 2: Determine the number of atoms of each element in the compound.
The chemical formula Ca(OH)₂ indicates that one molecule of calcium hydroxide contains:
- 1 calcium (Ca) atom
- 2 oxygen (O) atoms
- 2 hydrogen (H) atoms
Step 3: Calculate the total mass contribution of each element.
- Calcium (Ca): 1 atom × 40.08 g/mol = 40.08 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 2 atoms × 16.00 g/mol = 32.00 g/mol
- Hydrogen (H): 2 atoms × 1.01 g/mol = 2.02 g/mol
Step 4: Sum the mass contributions of all elements.
Adding the mass contributions of each element gives us the gram formula mass of Ca(OH)₂:
40.08 g/mol (Ca) + 32.00 g/mol (O) + 2.02 g/mol (H) = 74.10 g/mol
Therefore, the gram formula mass of Ca(OH)₂ is approximately 74.10 g/mol.
Importance of Accurate Atomic Mass Values
It's crucial to use accurate atomic mass values from a reliable source, such as a modern periodic table. Slight variations in atomic mass values can lead to discrepancies in the calculated gram formula mass. Most periodic tables provide atomic masses with several decimal places to ensure greater accuracy.
Applications of Gram Formula Mass
Understanding and calculating the gram formula mass has numerous applications in various chemical calculations:
-
Stoichiometry: Gram formula mass is essential for converting between moles and grams of a substance. This is critical in stoichiometric calculations, allowing us to determine the amount of reactants needed or products formed in a chemical reaction.
-
Concentration Calculations: Gram formula mass is used to calculate the molarity (moles per liter) or molality (moles per kilogram) of a solution. Knowing the concentration of a solution is important for many chemical processes and experiments.
-
Titration Calculations: In titration experiments, the gram formula mass is used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution by reacting it with a solution of known concentration.
-
Gas Laws: Gram formula mass is involved in calculations related to the ideal gas law (PV = nRT), where 'n' represents the number of moles of a gas.
Beyond the Basics: Understanding Isotopes and Average Atomic Mass
The atomic masses listed on the periodic table are actually weighted averages of the atomic masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. This means they have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. The weighted average accounts for the relative abundance of each isotope. For example, chlorine has two common isotopes, ³⁵Cl and ³⁷Cl, with different abundances. The atomic mass of chlorine reported on the periodic table reflects this weighted average. While this average is sufficient for most calculations, it's important to be aware that individual atoms will have a specific mass number based on their isotopic composition.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When calculating gram formula mass, several common mistakes can occur:
-
Incorrectly identifying the number of atoms: Carefully examine the chemical formula to ensure you correctly count the number of atoms of each element.
-
Using outdated or inaccurate atomic masses: Always use the most current atomic masses from a reliable source, like a modern periodic table.
-
Incorrect unit conversions: Pay close attention to units and make sure you're using consistent units throughout your calculations.
-
Mathematical errors: Double-check your calculations to avoid simple mathematical errors.
Advanced Applications: Working with Hydrates and Complex Ions
The concepts of gram formula mass extend beyond simple ionic compounds like Ca(OH)₂. For example, many ionic compounds exist as hydrates, meaning they incorporate water molecules within their crystal structure. In these cases, the mass of the water molecules must also be included in the gram formula mass calculation. Similarly, when dealing with complex ions, the total mass of all atoms within the complex ion needs to be considered.
Conclusion: Mastering Gram Formula Mass Calculations
Calculating the gram formula mass of a compound is a fundamental skill in chemistry. Understanding the underlying principles, including the use of accurate atomic masses and the concept of moles, is essential for tackling various stoichiometric and analytical calculations. By following the steps outlined in this guide and practicing regularly, you can confidently determine the gram formula mass of any compound and successfully apply this knowledge in your chemical studies. Remember to always double-check your work and utilize updated atomic mass values for accurate results. The accurate calculation of the gram formula mass of Ca(OH)₂ (and other compounds) is paramount for accurate work in chemistry and related fields. Mastering this concept opens doors to a deeper understanding of chemical reactions and quantitative analysis.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Oxidation Number Of O In Oh
Mar 16, 2025
-
70 Degrees Is What In Celsius
Mar 16, 2025
-
How Many Square Feet Are In 100 Square Meters
Mar 16, 2025
-
Power Series Representation Of Ln 1 X
Mar 16, 2025
-
How Many Nm In One M
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Gram Formula Mass Of Ca Oh 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
