What Is The Formula For Magnesium Sulfide
listenit
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
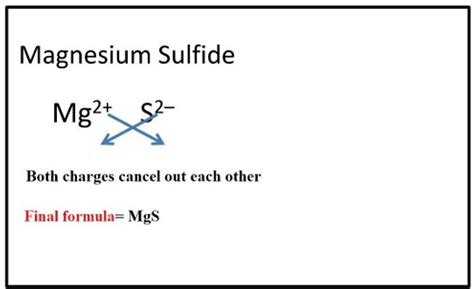
Table of Contents
What is the Formula for Magnesium Sulfide? A Deep Dive into Chemical Composition and Properties
Magnesium sulfide, a fascinating inorganic compound, holds a significant place in various scientific and industrial applications. Understanding its chemical formula, properties, and synthesis methods is crucial for anyone working with this material. This comprehensive article will delve into the intricacies of magnesium sulfide, exploring its formula, structure, synthesis, properties, and uses. We’ll also touch upon its safety considerations and environmental impact.
Unveiling the Formula: MgS
The chemical formula for magnesium sulfide is simply MgS. This concise notation tells us that one molecule of magnesium sulfide consists of one magnesium (Mg) atom and one sulfur (S) atom, bonded ionically. This ionic bond arises from the transfer of two electrons from the magnesium atom to the sulfur atom. Magnesium, an alkaline earth metal, readily loses two electrons to achieve a stable octet, while sulfur, a chalcogen, readily gains two electrons to also achieve a stable octet. This electron transfer results in the formation of Mg²⁺ (magnesium cation) and S²⁻ (sulfide anion), which are strongly attracted to each other through electrostatic forces.
Understanding the Ionic Bond
The ionic bond in MgS is a key determinant of its properties. The strong electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions leads to a high melting point and boiling point, and contributes to its crystalline structure. Unlike covalent compounds, MgS doesn't exist as discrete molecules; instead, it forms a three-dimensional lattice structure where each magnesium ion is surrounded by six sulfide ions, and vice versa. This lattice structure contributes to its hardness and brittleness.
Synthesis of Magnesium Sulfide: Methods and Considerations
Magnesium sulfide can be synthesized through various methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common methods include:
1. Direct Combination of Magnesium and Sulfur:
This is the simplest method, involving the direct reaction of elemental magnesium and sulfur under controlled conditions. The reaction is highly exothermic (releases heat) and requires careful control to prevent uncontrolled combustion. The reaction is represented by the following equation:
Mg(s) + S(s) → MgS(s)
The reaction usually requires heating the mixture to initiate the reaction and maintain a controlled temperature to ensure complete conversion. Excess sulfur should be avoided as it can lead to the formation of magnesium polysulfides.
2. Reaction of Magnesium Oxide with Hydrogen Sulfide:
Magnesium oxide (MgO) can react with hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) at high temperatures to produce magnesium sulfide and water. This method offers better control over the reaction conditions compared to direct combination. The reaction equation is:
MgO(s) + H₂S(g) → MgS(s) + H₂O(g)
This method requires a high-temperature furnace and careful handling of the toxic hydrogen sulfide gas.
3. Reduction of Magnesium Sulfate with Carbon:
Magnesium sulfate (MgSO₄) can be reduced with carbon at high temperatures to produce magnesium sulfide, carbon dioxide, and sulfur dioxide. This method is less common due to the generation of polluting gases. The reaction is represented by:
MgSO₄(s) + 4C(s) → MgS(s) + 4CO(g)
The resulting MgS often needs further purification to remove impurities.
Properties of Magnesium Sulfide: A Detailed Examination
Magnesium sulfide possesses several distinctive physical and chemical properties that make it suitable for various applications.
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: MgS is typically a white to pale yellow crystalline solid. The color can vary depending on the purity and presence of impurities.
- Melting Point: MgS has a relatively high melting point, around 2000 °C (3632 °F). This high melting point reflects the strong ionic bonds within its crystal lattice.
- Solubility: MgS is insoluble in water, but it reacts slowly with water to form magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen sulfide:
MgS(s) + 2H₂O(l) → Mg(OH)₂(s) + H₂S(g)
- Crystal Structure: MgS crystallizes in a rock salt (NaCl) structure, characterized by a face-centered cubic lattice.
- Hardness: MgS is relatively hard, reflecting the strong ionic bonds in its structure.
- Density: Magnesium sulfide has a density of approximately 2.68 g/cm³.
Chemical Properties:
- Reactivity with Water: As mentioned above, MgS reacts slowly with water to produce magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen sulfide. This reaction is accelerated by the presence of acids.
- Reactivity with Acids: MgS readily reacts with acids to form magnesium salts and hydrogen sulfide:
MgS(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl₂(aq) + H₂S(g)
- Oxidation: MgS is susceptible to oxidation in the presence of air, forming magnesium oxide and sulfur dioxide. This oxidation can lead to a change in color and a reduction in its purity.
Applications of Magnesium Sulfide: Diverse Uses
Magnesium sulfide's unique properties make it valuable in several applications:
- Phosphors: MgS is a crucial component in certain phosphors used in electroluminescent devices and cathode ray tubes. It can be doped with various activators to alter its luminescence properties.
- High-Temperature Lubricants: Due to its high melting point and stability, MgS is being explored for applications in high-temperature lubricants.
- Catalyst: In some catalytic reactions, MgS can act as a catalyst or catalyst support.
- Chemical Precursor: MgS serves as a precursor for the synthesis of other magnesium compounds.
- Inorganic Pigments: Magnesium sulfide's pale yellow color has potential uses in the production of certain inorganic pigments.
- Research Applications: MgS is frequently used in various scientific research studies related to materials science, chemistry, and physics.
Safety and Environmental Considerations: Handling Magnesium Sulfide
While magnesium sulfide itself isn't inherently highly toxic, several safety precautions should be taken when handling it:
- Hydrogen Sulfide Generation: The reaction of MgS with water or acids produces hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), a highly toxic and flammable gas. Adequate ventilation is crucial to prevent H₂S buildup.
- Dust Inhalation: Inhalation of MgS dust can cause respiratory irritation. Appropriate respiratory protection should be used when handling MgS powder.
- Skin Contact: Skin contact with MgS may cause mild irritation. Gloves and protective clothing should be worn.
- Environmental Impact: While MgS itself is not considered a major environmental pollutant, the generation of hydrogen sulfide during its reactions poses environmental concerns. Appropriate disposal methods should be followed to prevent environmental contamination.
Conclusion: A Versatile Compound with Diverse Applications
Magnesium sulfide, with its simple formula MgS, exhibits a complex interplay of chemical and physical properties. Its synthesis, through various methods, allows for controlled production tailored to specific applications. From its use in phosphors to its potential applications in high-temperature lubricants, MgS plays a significant role in various fields. However, understanding its reactivity and potential for generating toxic hydrogen sulfide gas is crucial for ensuring safe handling and minimizing environmental impact. Future research will undoubtedly uncover further applications of this versatile compound, expanding its influence across multiple scientific and industrial domains. Further study and exploration are needed to fully understand and harness the potential of this intriguing material.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Average Of Integers From 25 To 41
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is Half Of 1 2 A Teaspoon
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Atmospheric Layer Does Weather Occur
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Decimal For 13 16
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Do You Write 9 26 Repeating As A Fraction
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Formula For Magnesium Sulfide . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
