What Is The Formula For Dinitrogen Pentoxide
listenit
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
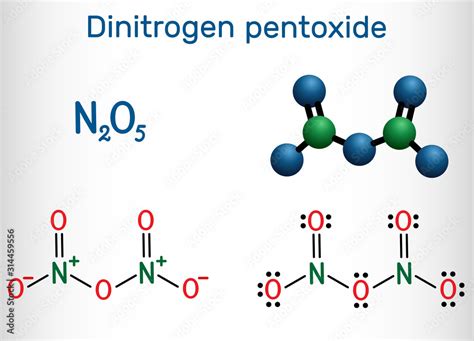
Table of Contents
What is the Formula for Dinitrogen Pentoxide? A Deep Dive into its Properties and Applications
Dinitrogen pentoxide, a fascinating and potent compound, holds a significant place in chemistry. Understanding its formula is the key to unlocking its properties and appreciating its diverse applications. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the world of dinitrogen pentoxide, exploring its formula, structure, synthesis, properties, and applications, all while optimizing for search engines to ensure maximum visibility and understanding.
Understanding the Chemical Formula: N₂O₅
The chemical formula for dinitrogen pentoxide is N₂O₅. This simple formula reveals the elemental composition: two nitrogen atoms (N) and five oxygen atoms (O). However, this formula alone doesn't fully encapsulate the complexity of this compound. The structure and bonding are equally crucial to understanding its behavior.
The Importance of Chemical Formulae in Chemistry
Understanding chemical formulae is foundational to chemistry. They provide a concise representation of the composition of a substance, allowing chemists to:
- Predict properties: The formula offers clues about the compound's likely properties, including reactivity, polarity, and physical state.
- Balance chemical equations: Accurate formulae are essential for writing balanced chemical equations, which are crucial for stoichiometric calculations and understanding chemical reactions.
- Determine molar mass: The formula is used to calculate the molar mass, a vital property in many chemical calculations.
- Understand bonding: The formula can provide insights into the types of bonds present in the molecule, impacting its properties and reactivity.
Delving into the Structure of Dinitrogen Pentoxide
Dinitrogen pentoxide exists in two forms: a colorless, crystalline solid (the more common form) and a colorless gas. The solid form exists as the ionic compound nitronium nitrate, with the formula [NO₂⁺][NO₃⁻]. This structure reveals a crucial aspect: dinitrogen pentoxide isn't a simple molecule with a single covalent structure, but rather an ionic compound composed of nitronium cations (NO₂⁺) and nitrate anions (NO₃⁻).
The Ionic Nature of Solid Dinitrogen Pentoxide
The ionic nature profoundly influences the properties of dinitrogen pentoxide. The strong electrostatic forces between the nitronium and nitrate ions lead to its relatively high melting point and its solubility in polar solvents.
The Gaseous Form: Covalent Structure
In the gaseous phase, dinitrogen pentoxide exists as a covalent molecule with a more complex structure. While still containing two nitrogen atoms and five oxygen atoms, the arrangement differs from the solid-state ionic structure.
Visualizing the Structure: Imagine a central nitrogen atom double-bonded to one oxygen atom and single-bonded to two other oxygen atoms. Each of these singly-bonded oxygen atoms is further bonded to another oxygen atom via a single bond. This forms a rather asymmetrical structure.
Synthesis of Dinitrogen Pentoxide: Methods and Considerations
The synthesis of dinitrogen pentoxide involves several different pathways, often requiring careful control of reaction conditions. The commonly used methods include:
Dehydration of Nitric Acid
One of the most common methods involves the careful dehydration of nitric acid (HNO₃) using a dehydrating agent such as phosphorus(V) oxide (P₄O₁₀). This reaction yields dinitrogen pentoxide and phosphoric acid (H₃PO₄) as a byproduct. The reaction proceeds as follows:
2HNO₃ + P₄O₁₀ → N₂O₅ + 2H₃PO₄
Careful control of temperature and humidity is critical for success, as dinitrogen pentoxide is readily susceptible to hydrolysis.
Reaction of Nitric Acid with Ozone
Another method involves reacting nitric acid with ozone (O₃). This reaction produces dinitrogen pentoxide and oxygen (O₂). This method offers a potentially cleaner synthesis path, avoiding some of the byproducts associated with the dehydration route.
Other less common synthesis routes exist, but these two are most prominent in laboratory settings.**
Properties of Dinitrogen Pentoxide: A Detailed Exploration
Dinitrogen pentoxide exhibits a range of properties that stem directly from its unique structure and bonding. Understanding these properties is vital for safe handling and effective application.
Physical Properties
- Appearance: Colorless crystalline solid or colorless gas.
- Melting Point: Approximately 41°C (This indicates relatively weak intermolecular forces compared to many ionic compounds).
- Boiling Point: Decomposes before reaching its boiling point, typically around 47°C.
- Solubility: Soluble in certain non-polar solvents and dissolves readily in water to form nitric acid.
Chemical Properties
- Reactivity: Highly reactive and acts as a powerful oxidizing agent.
- Hydrolysis: Readily reacts with water to form nitric acid (HNO₃). This reaction is highly exothermic.
- Decomposition: Decomposes upon heating to form nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) and oxygen (O₂).
- Acidity: In aqueous solutions, it forms a strong acid, nitric acid.
Applications of Dinitrogen Pentoxide: From Industrial to Research Settings
Dinitrogen pentoxide, despite its reactivity, finds several significant applications across various fields:
Nitration Reactions
One of its most important uses lies in its role as a nitrating agent in organic chemistry. Dinitrogen pentoxide is often employed in nitration reactions, where a nitro group (-NO₂) is introduced into an organic molecule. This process is vital in producing various nitro compounds, used extensively in the manufacture of explosives, dyes, and pharmaceuticals.
Rocket Propellant Oxidizer
Due to its high oxygen content and strong oxidizing capabilities, dinitrogen pentoxide has been explored for use as an oxidizer in rocket propellants. Although its corrosive nature poses challenges, its high energy density makes it an attractive candidate for future propellant formulations.
Laboratory Reagent
In laboratory settings, dinitrogen pentoxide serves as a valuable reagent in various chemical syntheses. Its ability to act as a potent nitrating agent and oxidizing agent makes it useful in specialized reactions requiring controlled oxidation or nitration processes.
Safety Precautions: Handling Dinitrogen Pentoxide
Dinitrogen pentoxide is a dangerous chemical requiring strict adherence to safety protocols:
- Avoid contact with skin and eyes: It is highly corrosive and can cause severe burns.
- Handle in a well-ventilated area: The decomposition products of dinitrogen pentoxide, particularly nitrogen dioxide, are toxic.
- Store in a cool, dry place: Avoid exposure to moisture, which can lead to hydrolysis and the formation of corrosive nitric acid.
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment: This includes gloves, safety glasses, and a laboratory coat.
Conclusion: A Powerful Compound with Varied Uses
Dinitrogen pentoxide, with its formula N₂O₅, is a fascinating compound with a rich chemistry. Its dual nature – ionic in the solid state and covalent in the gaseous state – profoundly influences its properties and applications. From its role as a potent nitrating agent to its potential use as a rocket propellant oxidizer, dinitrogen pentoxide demonstrates the diverse roles of seemingly simple chemical compounds. However, its inherent reactivity and potential hazards demand strict adherence to safety protocols during its handling and use. Continued research into its properties and applications will undoubtedly lead to further advancements in various fields. Understanding its formula is only the starting point of a deeper exploration of this powerful and versatile compound.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 25 And 30
Mar 31, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 576
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Is 1 And 4 5 As A Decimal
Mar 31, 2025
-
4 5 To The Power Of 2
Mar 31, 2025
-
Can You Determine The Activation Energy Of The Reverse Reaction
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Formula For Dinitrogen Pentoxide . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
