What Is The Formula For Calcium Fluoride
listenit
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
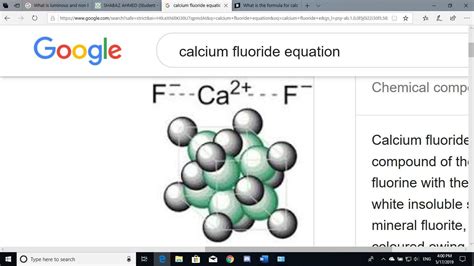
Table of Contents
What is the Formula for Calcium Fluoride? A Deep Dive into its Chemistry, Properties, and Applications
Calcium fluoride, a compound found in nature and utilized extensively in various applications, is a fascinating substance with a rich history and multifaceted properties. Understanding its chemical formula is the cornerstone to appreciating its significance in science and industry. This article will thoroughly explore the formula for calcium fluoride, delving into its chemical makeup, crystal structure, physical and chemical properties, and diverse applications. We'll also touch upon its safety considerations and environmental impact.
Understanding the Chemical Formula: CaF₂
The chemical formula for calcium fluoride is CaF₂. This simple yet powerful formula tells us much about the compound's composition:
-
Ca: Represents one calcium atom (Ca). Calcium is an alkaline earth metal, belonging to Group 2 of the periodic table. It readily loses two electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
-
F₂: Represents two fluorine atoms (F). Fluorine is a halogen, a highly reactive non-metal in Group 17 of the periodic table. It readily gains one electron to achieve a stable electron configuration.
The formula CaF₂ indicates that in one unit of calcium fluoride, there is one calcium cation (Ca²⁺) and two fluoride anions (F⁻). This 1:2 ratio is crucial for maintaining electrical neutrality within the compound. The positive charge of the calcium ion (+2) is balanced by the combined negative charges of the two fluoride ions (-1 each). This ionic bonding is a key factor driving the properties of calcium fluoride.
Ionic Bonding and Crystal Structure
The strong electrostatic attraction between the positively charged calcium ion and the negatively charged fluoride ions forms an ionic bond. This type of bonding results in a highly ordered, crystalline structure. Calcium fluoride adopts the fluorite structure, a cubic crystal system where each calcium ion is surrounded by eight fluoride ions, and each fluoride ion is surrounded by four calcium ions. This arrangement leads to its characteristic physical properties.
Physical Properties of Calcium Fluoride
The unique crystal structure and ionic bonding of CaF₂ dictate its physical properties:
-
Color and Appearance: Pure calcium fluoride is colorless and transparent, though impurities can introduce variations in color. It can appear white, yellow, brown, or even purple depending on the presence of trace elements.
-
Hardness: It possesses a relatively high hardness (Mohs hardness of 4), meaning it's resistant to scratching.
-
Density: Calcium fluoride has a moderate density (approximately 3.18 g/cm³).
-
Melting Point: It has a high melting point (around 1418 °C), reflecting the strong ionic bonds within its structure. This high melting point makes it suitable for high-temperature applications.
-
Solubility: Calcium fluoride exhibits low solubility in water, making it relatively inert in aqueous environments. However, its solubility increases in acidic solutions.
-
Optical Properties: Calcium fluoride's transparency across a wide range of the electromagnetic spectrum, from ultraviolet to infrared, is a crucial characteristic for its applications in optical systems. Its high refractive index and low dispersion make it an ideal material for lenses and windows in various spectroscopic and optical instruments.
-
Thermal Properties: Calcium fluoride displays excellent thermal conductivity and stability at high temperatures, further enhancing its suitability for various industrial applications.
Chemical Properties of Calcium Fluoride
Calcium fluoride's chemical behavior is largely influenced by its ionic nature and the relatively high electronegativity of fluorine:
-
Reactivity: It is relatively chemically inert under normal conditions. It is resistant to oxidation and reduction reactions.
-
Acid Reactivity: Although generally insoluble in water, calcium fluoride reacts with strong acids, such as sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid, to produce the corresponding calcium salts and hydrogen fluoride (HF). This reaction should be handled with caution due to the highly corrosive and toxic nature of hydrogen fluoride. The equation for the reaction with sulfuric acid is:
CaF₂ + H₂SO₄ → CaSO₄ + 2HF
-
Thermal Stability: Calcium fluoride exhibits remarkable thermal stability, meaning it resists decomposition even at elevated temperatures.
-
Fluoride Ion Release: While minimally soluble in water, calcium fluoride can release fluoride ions under specific conditions, such as in acidic environments or when exposed to certain chelating agents. This characteristic has implications for its applications and potential environmental impact.
Applications of Calcium Fluoride
The unique combination of physical and chemical properties makes calcium fluoride a versatile material with widespread applications across various fields:
1. Optics and Photonics:
-
Optical Lenses and Windows: Its transparency across a broad spectral range, low dispersion, and high refractive index make it ideal for manufacturing lenses and windows used in various optical instruments, including microscopes, telescopes, and spectrometers. It is particularly useful in applications requiring high transmission in the ultraviolet and infrared regions.
-
Laser Optics: Calcium fluoride crystals are used in the production of various lasers, both as optical elements and as laser host materials.
-
Fiber Optics: While not as common as other materials, calcium fluoride is used in specialized fiber optic applications.
2. Metallurgy and Materials Science:
-
Fluxing Agent: In metallurgy, it acts as a fluxing agent, which helps in removing impurities from molten metals during smelting and refining processes.
-
Ceramic Materials: It's used as an additive in the production of certain ceramics to enhance their properties.
3. Dentistry and Medicine:
-
Dental Applications: Calcium fluoride has been used in some dental products to help strengthen tooth enamel and prevent dental caries (tooth decay).
-
Medical Imaging: While not a primary material, calcium fluoride has shown promise in certain medical imaging applications.
4. Nuclear Applications:
- Nuclear Reactor Components: Due to its high thermal conductivity and resistance to radiation damage, calcium fluoride finds some limited application in nuclear reactor components.
5. Chemical Industry:
- Fluoride Source: Calcium fluoride is a source of fluoride ion for various chemical processes.
Safety Considerations and Environmental Impact
While generally considered non-toxic in its solid form, certain considerations regarding safety and environmental impact should be addressed:
-
Hydrogen Fluoride Production: The reaction of calcium fluoride with strong acids produces hydrogen fluoride (HF), a highly corrosive and toxic substance. Handling this reaction requires appropriate safety precautions, including protective gear and proper ventilation.
-
Fluoride Ion Release: The release of fluoride ions from calcium fluoride under specific conditions can have environmental implications. Excessive fluoride in water sources can be detrimental to human health and the environment.
-
Waste Disposal: Proper disposal of calcium fluoride waste is important to prevent environmental contamination.
Conclusion: A Versatile and Essential Compound
The simple formula CaF₂ belies the rich complexity and diverse applications of calcium fluoride. Its unique combination of physical and chemical properties, including its optical transparency, thermal stability, and low reactivity, make it a valuable material across numerous scientific and industrial sectors. While precautions regarding handling and environmental considerations are necessary, calcium fluoride continues to play a significant role in modern technology and remains a subject of ongoing research and development. Understanding its chemical formula is the first step in appreciating its multifaceted significance in our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate And Sodium Hydroxide
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Proper Name For Hbr Aq
May 09, 2025
-
Sodium Chloride And Lead Ii Acetate
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Percentage Of 20 Out Of 50
May 09, 2025
-
What Are The Factors Of 196
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Formula For Calcium Fluoride . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.