What Is The Electron Configuration For Argon
listenit
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
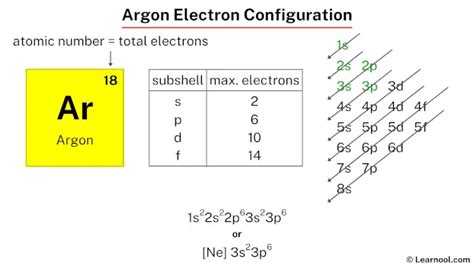
Table of Contents
What is the Electron Configuration for Argon? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Argon, a noble gas residing quietly in Group 18 of the periodic table, holds a fascinating place in the world of chemistry. Its unique properties, stemming directly from its electron configuration, make it a crucial element in various industrial applications. Understanding Argon's electron configuration is key to unlocking the secrets behind its inertness and its remarkable applications. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of Argon's electron configuration, delving into the underlying principles of atomic structure and the implications of its electronic arrangement.
Understanding Electron Configuration
Before diving into Argon's specific configuration, let's establish a solid foundation in understanding the concept of electron configuration itself. Electron configuration describes the arrangement of electrons within the various energy levels and sublevels of an atom. This arrangement dictates an atom's chemical behavior, its reactivity, and its physical properties. It follows specific rules based on the principles of quantum mechanics.
The Aufbau Principle
The Aufbau principle, which translates to "building-up" principle, guides the filling of electrons into atomic orbitals. Electrons initially occupy the lowest energy levels available, progressing systematically to higher energy levels as the number of electrons increases. This principle forms the basis for predicting the electron configuration of any element.
Hund's Rule
Hund's rule dictates that electrons will individually occupy each orbital within a subshell before pairing up in any one orbital. This minimizes electron-electron repulsion and contributes to the overall stability of the atom.
Pauli Exclusion Principle
The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons within an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers. This means that each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons, with opposite spins.
Argon's Electron Configuration: A Step-by-Step Explanation
Argon (Ar) has an atomic number of 18, meaning it possesses 18 protons and, in its neutral state, 18 electrons. To determine its electron configuration, we follow the Aufbau principle and fill the orbitals in order of increasing energy.
Energy Levels and Sublevels
Electrons reside in energy levels (principal quantum numbers, n), which are further divided into sublevels (s, p, d, and f). Each sublevel has a specific number of orbitals and can accommodate a certain number of electrons.
- n=1 (Principal Energy Level 1): Contains only the 1s sublevel, which can hold a maximum of 2 electrons.
- n=2 (Principal Energy Level 2): Contains the 2s and 2p sublevels. The 2s sublevel holds 2 electrons, while the 2p sublevel, with three orbitals, can hold up to 6 electrons.
- n=3 (Principal Energy Level 3): Contains the 3s, 3p, and 3d sublevels. The 3s sublevel holds 2 electrons, the 3p sublevel holds 6 electrons, and the 3d sublevel (which is higher in energy than the 4s) holds 10 electrons.
- n=4 (Principal Energy Level 4): Contains the 4s, 4p, 4d, and 4f sublevels (and so on for higher energy levels).
Filling the Orbitals for Argon
Following the Aufbau principle, we fill the orbitals for Argon (18 electrons) as follows:
- 1s²: Two electrons fill the 1s orbital.
- 2s²: Two electrons fill the 2s orbital.
- 2p⁶: Six electrons fill the three 2p orbitals.
- 3s²: Two electrons fill the 3s orbital.
- 3p⁶: Six electrons fill the three 3p orbitals.
Therefore, the complete electron configuration for Argon is 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶. This configuration represents a stable arrangement of electrons.
The Significance of Argon's Full Valence Shell
Argon's electron configuration showcases a complete valence shell. The valence shell is the outermost energy level containing electrons that participate in chemical bonding. For Argon, the valence shell is the third energy level (n=3), and it is completely filled with eight electrons (two in the 3s sublevel and six in the 3p sublevel). This full valence shell is responsible for Argon's inertness and lack of reactivity. It doesn't readily gain, lose, or share electrons because it is already in a very stable state.
Noble Gases and the Octet Rule
Argon belongs to the noble gases, a group of elements characterized by their exceptional stability and non-reactivity. This stability arises from their complete valence electron shells. The octet rule, while not universally applicable, suggests that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable configuration of eight valence electrons (like that of the noble gases). Argon, with its already complete octet, perfectly exemplifies this rule.
Argon's Applications: Leveraging its Inertness
Argon's unique chemical properties, a direct consequence of its electron configuration, lead to its widespread use in various industrial and scientific applications. Because it's non-reactive, it can be used in environments where reactivity would be detrimental.
Welding and Metallurgy
Argon's inertness is crucial in welding applications, particularly in Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) and Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW). It acts as a shielding gas, preventing oxidation and contamination of the weld pool, resulting in a cleaner, stronger weld. It also finds use in other metallurgical processes where an inert atmosphere is required.
Lighting
Argon is used in various types of lighting, including fluorescent lights and incandescent light bulbs. Its inertness prevents the filament from oxidizing and prolongs the bulb's lifespan. In fluorescent lights, Argon helps to conduct electricity and excite the mercury vapor, which then emits ultraviolet light that is converted to visible light by the phosphor coating.
Healthcare
Argon's inertness finds applications in cryosurgery, a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses extremely low temperatures to destroy abnormal tissues. Argon gas is used in combination with other elements to produce extremely low temperatures. Additionally, Argon can be found in other medical tools and procedures.
Scientific Research
Argon's inertness is advantageous in various scientific research applications, including chromatography, where it acts as a carrier gas, and in the creation of controlled atmospheres for sensitive experiments.
Isotopes of Argon and their Electron Configurations
Naturally occurring Argon is composed of three stable isotopes: ³⁶Ar, ³⁸Ar, and ⁴⁰Ar. Although these isotopes have different numbers of neutrons, their electron configurations remain the same (1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶). The number of neutrons affects the atomic mass but not the electron arrangement, which is determined by the number of protons. This consistency in electron configuration highlights the importance of protons in defining an element's chemical behavior.
Conclusion: Argon's Electron Configuration and its Impact
The electron configuration of Argon, 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶, is not merely a collection of numbers and letters; it's the fundamental blueprint that governs Argon's chemical and physical properties. This seemingly simple arrangement dictates its inertness, its stability, and its vast array of applications. By understanding Argon's electron configuration, we gain valuable insight into the behavior of atoms, the principles of quantum mechanics, and the practical applications of fundamental scientific knowledge. From welding to medical procedures to scientific research, the seemingly unremarkable Argon plays a vital role, a role directly shaped by its unique electronic structure. The exploration of electron configuration continues to be an important area of study in chemistry and physics, furthering our understanding of the material world around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Percent Of 90 Is 25
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Molar Mass Of Ammonium Sulfate
Mar 19, 2025
-
1 Square Foot Is How Many Square Inches
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Ounces In A Pt
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Ml In 2 Litres
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Electron Configuration For Argon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
