What Is The Difference Between Natural Selection And Artificial Selection
listenit
Apr 06, 2025 · 6 min read
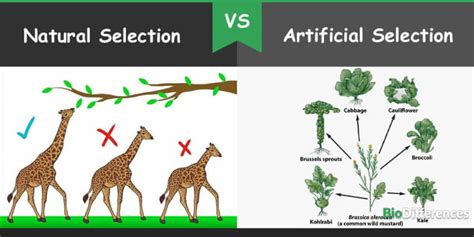
Table of Contents
What's the Difference Between Natural Selection and Artificial Selection?
The processes of natural and artificial selection are both powerful forces shaping the characteristics of living organisms, yet they differ significantly in their driving mechanisms and outcomes. Understanding these differences is crucial for grasping the intricacies of evolution and the impact humans have had on the biodiversity of our planet. This article will delve into the core distinctions between natural and artificial selection, exploring their mechanisms, examples, and broader implications.
Understanding Natural Selection: Nature's Editing Hand
Natural selection, the cornerstone of Darwin's theory of evolution, is a process where organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring. This "survival of the fittest" isn't about brute strength alone, but encompasses a broader range of traits enhancing an organism's ability to thrive within its specific ecological niche. These advantageous traits, termed adaptations, can be physical (e.g., camouflage, speed), physiological (e.g., disease resistance, metabolic efficiency), or behavioral (e.g., foraging strategies, mating rituals).
The Mechanisms of Natural Selection:
Natural selection operates through several key mechanisms:
-
Variation: Individuals within a population exhibit variation in their traits. This variation arises from genetic mutations, gene flow, and sexual reproduction. Without variation, there's nothing for selection to act upon.
-
Inheritance: These variations are heritable; they can be passed down from parents to offspring through genetic material (DNA). Only heritable traits can be subject to natural selection.
-
Differential Survival and Reproduction: Individuals with traits better suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on those advantageous traits to their offspring. This leads to a gradual shift in the genetic makeup of the population over time.
-
Adaptation: Over generations, the frequency of advantageous traits increases within the population, leading to adaptation – the evolution of traits that enhance survival and reproduction in a particular environment.
Examples of Natural Selection in Action:
The evidence for natural selection is abundant and diverse. Consider these examples:
-
Peppered Moths: During the Industrial Revolution in England, the peppered moth population shifted dramatically. Initially, lighter-colored moths were more common, blending well with lichen-covered trees. However, industrial pollution darkened the tree bark, making darker moths better camouflaged from predators. Over time, the frequency of darker moths increased significantly, showcasing natural selection favoring a trait that provided better survival in a changed environment.
-
Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria: The widespread use of antibiotics has driven the evolution of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Bacteria with mutations conferring resistance to antibiotics survive and reproduce, passing on the resistance genes to their offspring. This has created a significant challenge in treating bacterial infections.
-
Darwin's Finches: The various beak shapes of Darwin's finches on the Galapagos Islands are a classic example of adaptive radiation through natural selection. Different beak shapes are adaptations to exploit different food sources on the islands.
Understanding Artificial Selection: Human Intervention
Artificial selection, also known as selective breeding, is the process by which humans select and breed organisms for desirable traits. Unlike natural selection, where environmental pressures drive the selection process, artificial selection is consciously directed by human intervention. Humans choose which individuals will reproduce based on specific criteria, shaping the characteristics of future generations.
The Mechanisms of Artificial Selection:
Artificial selection operates through:
-
Human Choice: Humans identify desirable traits and select individuals possessing those traits for breeding. This is a conscious decision, unlike the random nature of environmental pressures in natural selection.
-
Controlled Breeding: Humans control mating patterns, ensuring that individuals with the desired traits are paired to produce offspring with a higher probability of inheriting those traits.
-
Genetic Modification (a subset of Artificial Selection): While not strictly breeding, genetic modification allows for even more targeted alterations to an organism's genome, resulting in significant changes in traits faster than traditional selective breeding.
Examples of Artificial Selection:
Artificial selection has been employed for millennia to improve crops, livestock, and companion animals. Examples include:
-
Domesticated Dogs: The astonishing diversity of dog breeds is a testament to the power of artificial selection. From tiny Chihuahuas to giant Great Danes, humans have selectively bred dogs for specific traits such as size, coat type, temperament, and hunting abilities.
-
Agricultural Crops: Modern agricultural crops bear little resemblance to their wild ancestors. Through artificial selection, humans have cultivated plants with higher yields, improved nutritional content, increased disease resistance, and desirable characteristics like size, color, and taste. Think of the difference between wild tomatoes and the large, uniformly shaped tomatoes found in supermarkets.
-
Livestock: Livestock animals such as cattle, pigs, and sheep have undergone extensive artificial selection to enhance meat production, milk yield, wool quality, and other economically valuable traits.
Key Differences Between Natural and Artificial Selection:
| Feature | Natural Selection | Artificial Selection |
|---|---|---|
| Driving Force | Environmental pressures (e.g., predation, competition, climate) | Human intervention and choice |
| Selection Criteria | Survival and reproductive success | Desirable traits determined by humans |
| Time Scale | Generally occurs over long periods | Can be much faster, especially with genetic modification |
| Predictability | Less predictable; dependent on environmental changes | More predictable; controlled by human choices |
| Outcome | Adaptation to the environment; increased fitness | Improvement of traits based on human preferences; may not always improve overall fitness |
| Potential Negative Consequences | Can lead to reduced genetic diversity and vulnerability to environmental changes | Can lead to reduced genetic diversity, inbreeding depression, and ethical concerns |
The Implications of Both Processes:
Both natural and artificial selection are powerful evolutionary forces with significant implications:
-
Biodiversity: Natural selection maintains biodiversity by driving adaptation to diverse environments. Artificial selection, while benefiting humanity in many ways, can reduce biodiversity by focusing on a limited set of desirable traits.
-
Human Health: Natural selection plays a role in the evolution of diseases and the development of resistance to treatments. Artificial selection is used in developing new medicines and treatments.
-
Food Security: Artificial selection is vital for food production, ensuring sufficient food supplies for a growing human population. However, overuse of artificial selection can lead to environmental problems and health concerns related to monocultures.
-
Ethical Considerations: Artificial selection raises ethical questions regarding genetic manipulation, animal welfare, and the potential unforeseen consequences of altering natural systems.
Conclusion: Two Sides of the Same Coin
Natural and artificial selection, while distinct processes, are both fundamental aspects of evolution. Natural selection shapes life in response to environmental pressures, leading to adaptation and biodiversity. Artificial selection demonstrates the profound power of human intervention in shaping the characteristics of living organisms. Understanding the differences and implications of these two processes is crucial for appreciating the complexity of life on Earth and making informed decisions about our impact on the planet's biodiversity and future. Continued research in both areas will be vital for tackling challenges such as food security, disease resistance, and the preservation of biodiversity in a rapidly changing world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 65 In Decimal Form
Apr 06, 2025
-
X 3 X 2 X 1 0
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 54 And 36
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Many 6 Are In A Deck Of Cards
Apr 06, 2025
-
4 Divided By 1 3 5
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Difference Between Natural Selection And Artificial Selection . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
