What Is The Difference Between Interstellar And Intergalactic
listenit
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
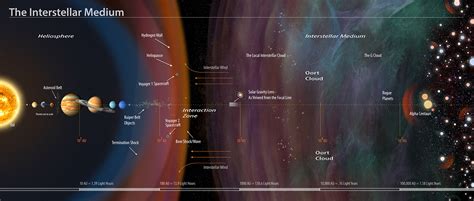
Table of Contents
What's the Difference Between Interstellar and Intergalactic? A Deep Dive into Cosmic Scales
The vastness of space is a concept that constantly challenges our comprehension. Terms like "interstellar" and "intergalactic" are often thrown around, sometimes interchangeably, leading to confusion. However, understanding the distinction between these two terms is crucial to grasping the true scale of the universe and the incredible distances involved. This article will delve deep into the difference between interstellar and intergalactic space, exploring the environments, distances, and phenomena unique to each.
Understanding the Cosmic Neighborhood: Stars and Galaxies
Before diving into the differences, let's establish a firm foundation. Our understanding hinges on the fundamental building blocks of the cosmos: stars and galaxies.
-
Stars: These are massive, luminous spheres of plasma held together by their own gravity. They are the powerhouses of the universe, generating energy through nuclear fusion. Our Sun is a star, a relatively average one in the grand scheme of things.
-
Galaxies: These are colossal systems containing billions, even trillions, of stars, bound together by gravity. They also contain vast amounts of gas, dust, and dark matter. Our own galaxy, the Milky Way, is a spiral galaxy, home to our solar system.
Interstellar Space: Between the Stars
Interstellar space refers to the space between stars within a galaxy. It's not a completely empty void. Instead, it's a relatively sparse region containing:
1. Interstellar Medium (ISM): The Stuff Between Stars
The ISM is a mixture of gas and dust, primarily hydrogen and helium, with trace amounts of heavier elements. This material is incredibly diffuse, with densities far lower than the best vacuum we can create on Earth. However, even this low density can have significant effects.
2. Nebulae: Cosmic Nurseries and Remnants
Nebulae are vast clouds of gas and dust, often visible as luminous or dark patches in the sky. Some nebulae are stellar nurseries, where new stars are born from the gravitational collapse of the ISM. Others are remnants of supernovae, the explosive deaths of massive stars, which enrich the ISM with heavy elements.
3. Cosmic Rays: High-Energy Particles
Interstellar space is also crisscrossed by cosmic rays, high-energy particles traveling at near-light speeds. These particles originate from various sources, including supernovae and active galactic nuclei, and can have significant effects on the ISM.
4. Distances in Interstellar Space: Light-Years and Beyond
Distances in interstellar space are measured in light-years, the distance light travels in one year (approximately 9.46 trillion kilometers). While seemingly vast, interstellar distances are dwarfed by intergalactic distances. The nearest star to our Sun, Proxima Centauri, is about 4.24 light-years away. This seemingly close proximity is still an immense distance, emphasizing the emptiness of interstellar space.
Intergalactic Space: Beyond the Galaxies
Intergalactic space is the vast expanse between galaxies. It represents the true emptiness of the universe, with densities far lower than even interstellar space. This void isn't completely empty, however.
1. Intergalactic Medium (IGM): A tenuous web
The IGM is a tenuous plasma of gas, mainly hydrogen and helium, spread throughout the intergalactic space. It's incredibly diffuse, with far lower densities than the ISM. However, the IGM plays a crucial role in the large-scale structure of the universe.
2. Galaxy Clusters and Superclusters: Islands in the Void
Galaxies aren't uniformly distributed throughout the universe. They tend to cluster together, forming groups and clusters, which in turn can form larger superclusters. These structures are connected by filaments of the IGM, forming a vast cosmic web.
3. Voids: The Emptiest Regions of the Universe
Between the filaments of the cosmic web are vast voids, regions where galaxies are extremely sparse. These voids are truly enormous, spanning hundreds of millions of light-years. They represent the most empty regions of the known universe.
4. Distances in Intergalactic Space: Megaparsecs and Beyond
Distances in intergalactic space are measured in megaparsecs (Mpc), where 1 Mpc is equal to 3.26 million light-years. The distances between galaxies can range from a few Mpc to hundreds or even thousands of Mpc. The sheer scale is almost incomprehensible, highlighting the immense vastness of the universe.
Key Differences Summarized: Interstellar vs. Intergalactic
The table below summarizes the key differences between interstellar and intergalactic space:
| Feature | Interstellar Space | Intergalactic Space |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Within a galaxy, between stars | Between galaxies |
| Density | Relatively higher, though still very low | Extremely low, approaching a perfect vacuum |
| Contents | ISM (gas, dust, cosmic rays), nebulae | IGM (tenuous plasma), galaxy clusters and superclusters, voids |
| Distances | Light-years | Megaparsecs (millions of light-years) |
| Environment | More dynamic, with star formation and supernovae | Relatively static, dominated by the large-scale structure of the universe |
Exploring the Mysteries: Ongoing Research
Both interstellar and intergalactic space hold many unsolved mysteries. Scientists are constantly working to unravel the complexities of these vast regions:
-
The nature of dark matter and dark energy: These enigmatic substances make up the vast majority of the universe's mass-energy content, yet their nature remains elusive. Understanding their influence on the distribution of galaxies and the expansion of the universe is crucial.
-
The formation and evolution of galaxies: How galaxies formed from the initial conditions of the early universe is still being researched. Understanding the role of the IGM in galaxy formation is crucial.
-
The composition and distribution of the IGM: The IGM is incredibly difficult to observe, yet understanding its composition and dynamics is crucial to understanding the large-scale structure of the universe.
-
The search for extraterrestrial life: Interstellar space, while vast and challenging, is still the most likely location to find other life forms within our galaxy. Detecting signals or evidence of life from other star systems is a major goal of ongoing research.
Conclusion: A Universe of Scale
The difference between interstellar and intergalactic space is one of scale and emptiness. While interstellar space is relatively dense compared to intergalactic space, both are incredibly vast and represent regions of the universe that still hold many mysteries. Understanding the differences between these two regions is essential to appreciating the true scale of the cosmos and the ongoing quest to understand our place within it. The ongoing research into these vast regions promises to reveal even more stunning insights into the universe in the years to come, continually reshaping our understanding of the cosmos.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
1 1 X 2 Power Series
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Percent Of 75 Is 40
Mar 17, 2025
-
Translating Graph Up By 4 Units
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 3 2
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Derivative Of Ln 1 X
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Difference Between Interstellar And Intergalactic . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
