What Is The Conjugate Base Of Ammonia
listenit
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
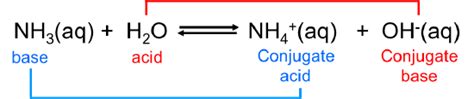
Table of Contents
What is the Conjugate Base of Ammonia? A Deep Dive into Acid-Base Chemistry
Understanding conjugate acid-base pairs is fundamental to grasping acid-base chemistry. This article delves deep into the concept, focusing specifically on ammonia (NH₃) and its conjugate base. We'll explore its properties, reactions, and significance in various chemical processes. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of this crucial aspect of chemistry.
Understanding Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
The Brønsted-Lowry theory defines an acid as a proton (H⁺) donor and a base as a proton acceptor. A conjugate acid-base pair consists of two species that differ by only a single proton (H⁺). When an acid donates a proton, it forms its conjugate base. Conversely, when a base accepts a proton, it forms its conjugate acid.
This relationship is crucial for understanding acid-base reactions and predicting their equilibrium. The stronger the acid, the weaker its conjugate base, and vice-versa. This inverse relationship is a key principle in acid-base chemistry.
Ammonia (NH₃): A Weak Base
Ammonia, NH₃, is a weak base. This means it only partially ionizes in water, accepting a proton from water molecules to form ammonium ions (NH₄⁺) and hydroxide ions (OH⁻). This is represented by the following equilibrium reaction:
NH₃(aq) + H₂O(l) ⇌ NH₄⁺(aq) + OH⁻(aq)
The equilibrium lies to the left, indicating that most of the ammonia remains un-ionized in solution. The presence of hydroxide ions (OH⁻) is what makes the solution basic, increasing its pH.
Identifying the Conjugate Base of Ammonia
According to the Brønsted-Lowry theory, the conjugate base of ammonia is formed when ammonia accepts a proton. This is counter-intuitive since ammonia acts as a base, donating electrons. However, to find the conjugate base, we need to consider what happens if ammonia were to act as an acid.
If ammonia were to act as an acid, it would donate a proton (H⁺). In this hypothetical scenario, it would lose one proton, leaving behind the amide ion (NH₂⁻). Therefore, the amide ion (NH₂⁻) is the conjugate base of ammonia.
This is a crucial distinction. While ammonia usually acts as a base, its conjugate base is formed by considering the hypothetical scenario where it acts as an acid and loses a proton.
Properties of the Amide Ion (NH₂⁻)
The amide ion (NH₂⁻) is a strong base. It readily reacts with water, completely accepting a proton from water molecules:
NH₂⁻(aq) + H₂O(l) → NH₃(aq) + OH⁻(aq)
This reaction goes to completion, unlike the partial ionization of ammonia. The complete ionization leads to a high concentration of hydroxide ions (OH⁻), resulting in a highly alkaline solution.
Comparison: Ammonia vs. Amide Ion
| Feature | Ammonia (NH₃) | Amide Ion (NH₂⁻) |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Weak base | Strong base |
| Protonation | Accepts a proton | Accepts a proton (completely) |
| Ionization | Partial ionization in water | Complete ionization in water |
| pH of solution | Slightly basic | Highly basic |
| Stability | Relatively stable | Highly reactive |
Reactions Involving Ammonia and its Conjugate Base
Ammonia participates in numerous reactions, both as a base and as a ligand in coordination complexes. The amide ion, being a strong base, is involved in reactions that require strong basicity. Some examples include:
-
Reaction with water: As mentioned earlier, the amide ion reacts completely with water to form ammonia and hydroxide ions.
-
Formation of amides: The amide ion is a key intermediate in the formation of amides, which are organic compounds containing the -CONH₂ group.
-
Deprotonation reactions: Due to its strong basicity, the amide ion can readily deprotonate weaker acids.
-
Use in organic synthesis: The strong basicity of the amide ion makes it a valuable reagent in organic synthesis, particularly in reactions involving deprotonation and nucleophilic attack.
Significance in Different Fields
Both ammonia and its conjugate base, the amide ion, have significant applications across various fields:
-
Agriculture: Ammonia is a vital component of fertilizers, providing nitrogen essential for plant growth.
-
Industrial Chemistry: Ammonia is used in the production of numerous chemicals, including nitric acid, urea, and various fertilizers. The amide ion plays a role in some specialized industrial processes.
-
Pharmaceutical Industry: Ammonia and its derivatives are used in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals.
-
Analytical Chemistry: Ammonia is used as a solvent and a reagent in various analytical techniques.
Safety Precautions
Both ammonia and the amide ion are corrosive and should be handled with appropriate safety precautions:
-
Ammonia: Ammonia gas is toxic and irritating to the respiratory system. It should be handled in a well-ventilated area, and appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) should be used.
-
Amide Ion: The amide ion is highly reactive and corrosive. Direct contact should be avoided, and appropriate safety measures should be in place when handling it.
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding of Conjugate Bases
Understanding the concept of conjugate acid-base pairs is crucial for mastering acid-base chemistry. While ammonia is widely known as a weak base, its conjugate base, the amide ion, is a significantly stronger base. This difference in basicity highlights the importance of considering the hypothetical scenario of an acid donating a proton to determine the conjugate base. The properties, reactions, and applications of both ammonia and the amide ion emphasize their significance across various scientific and industrial domains. By understanding their respective properties and roles, we gain a more comprehensive understanding of the broader landscape of acid-base chemistry. Always remember to prioritize safety when handling these chemicals.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Does Pitch Relate To Frequency
May 09, 2025
-
How Does A Buffer Help A Solution Maintain Ph
May 09, 2025
-
Non Living Things In A Grassland
May 09, 2025
-
How To Find Rel Max And Min
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Electrons Does Carbon 14 Have
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Conjugate Base Of Ammonia . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.