What Is A Shaft In Mining
listenit
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
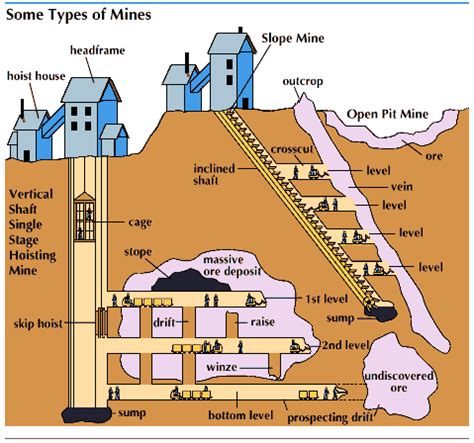
Table of Contents
What is a Shaft in Mining? A Comprehensive Guide
A mine shaft is a crucial element in underground mining operations, serving as a vital passageway for accessing and extracting valuable resources from beneath the earth's surface. Understanding its function, construction, and safety aspects is essential for anyone involved in or interested in the mining industry. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of mine shafts, exploring their various types, construction methods, safety protocols, and their overall importance in the mining process.
Defining a Mine Shaft: More Than Just a Hole in the Ground
A mine shaft, in its simplest definition, is a vertical or steeply inclined passageway excavated from the surface down to the ore body or the mining level. Unlike tunnels or adits, which often follow the contours of the ore body or existing geological formations, shafts are predominantly vertical, providing direct access to deep underground workings. They are far more than just holes in the ground; they are engineered structures designed to withstand immense pressures, facilitate the movement of personnel, equipment, and extracted materials, and ensure the overall safety of the mining operation.
Types of Mine Shafts: Tailored to Specific Needs
The design and construction of a mine shaft are highly dependent on several factors, including the depth of the ore body, the geological characteristics of the surrounding rock, and the anticipated volume of material to be extracted. Several types of mine shafts exist, each tailored to meet specific requirements:
1. Vertical Shafts: The Classic Design
Vertical shafts are the most common type, extending straight down from the surface to the desired mining level. Their straightforward design facilitates the efficient movement of materials using hoisting systems. Their simplicity, however, can be offset by challenges related to ventilation and water management at greater depths.
2. Inclined Shafts: Navigating Challenging Terrain
Inclined shafts, also known as ramps or inclines, are excavated at an angle, typically less than 90 degrees. This design can be advantageous in situations where the ore body is located on a slope or where the geological conditions make a vertical shaft impractical. Inclined shafts allow for easier access using vehicles and equipment, but they require more extensive support systems due to the lateral forces involved.
3. Combination Shafts: Blending Advantages
Some mines utilize combination shafts, combining vertical and inclined sections to optimize access and material handling. This approach often balances the efficiency of vertical shafts for deep access with the easier transportation facilitated by inclined sections closer to the surface.
4. Shafts Based on Purpose: Beyond Material Extraction
While shafts primarily serve for ore extraction, they also serve other functions:
- Ventilation Shafts: These shafts are crucial for maintaining adequate airflow within the mine, preventing the buildup of hazardous gases and ensuring the safety and well-being of miners.
- Escape Shafts: Safety regulations often mandate the construction of separate escape shafts, providing alternative escape routes in case of emergencies.
- Service Shafts: These shafts accommodate various services like pipelines, electrical cables, and communication lines, supporting the overall mining operation.
Construction of a Mine Shaft: A Complex Engineering Endeavor
Building a mine shaft is a complex and meticulously planned engineering undertaking, requiring a multi-disciplinary team of experts. The construction process involves several key stages:
1. Site Preparation and Exploration: Laying the Foundation
Before excavation begins, extensive geological surveys and site investigations are conducted to assess the ground conditions and identify potential hazards. This stage includes detailed mapping of the ore body, analysis of rock strength, and identification of any underground water sources.
2. Shaft Sinking: Excavating the Passageway
The actual excavation of the shaft is a challenging task, often employing specialized techniques depending on the geological conditions and the depth of the shaft. Methods include:
- Drilling and Blasting: This traditional method uses explosives to break up the rock, followed by removal of the debris. This approach is commonly used in harder rock formations.
- Raise Boring: This technique utilizes a large-diameter drill to bore up from the bottom level, creating a shaft from below. This is a more efficient method in softer rock formations and is useful for creating ventilation or escape shafts.
- Shaft Lining: Once excavated, the shaft walls are often reinforced with a lining made of concrete, steel, or timber to prevent collapse and ensure stability. The type of lining depends on the geological conditions and the depth of the shaft.
3. Equipment Installation: Providing the Infrastructure
After the shaft sinking is complete, various equipment is installed to support the mining operations. These include:
- Hoisting Systems: Powerful hoisting systems are installed to lift and lower personnel, equipment, and extracted ore. These can range from simple winches to complex multi-rope systems for deep shafts.
- Ventilation Systems: Sophisticated ventilation systems are incorporated to maintain proper airflow within the mine, preventing the accumulation of harmful gases and ensuring safe working conditions.
- Drainage Systems: Pumping systems are installed to remove groundwater that may accumulate in the shaft and mining levels, preventing flooding and maintaining a safe working environment.
Safety in Mine Shafts: Prioritizing Human Life
Safety is paramount in mine shaft operations. The confined environment, deep depths, and the potential for hazards necessitate rigorous safety protocols and preventative measures. These include:
- Rigorous Inspections: Regular inspections are essential to detect any signs of structural weakness or potential hazards.
- Emergency Systems: Emergency escape systems, including emergency exits, rescue equipment, and communication systems, are crucial for ensuring the safety of miners in case of accidents or emergencies.
- Ventilation Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of air quality within the shaft and mining levels ensures adequate ventilation and prevents the buildup of hazardous gases.
- Training and Education: Miners receive comprehensive training on safe working practices and emergency procedures to minimize the risk of accidents.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Miners wear appropriate PPE, including hard hats, safety glasses, and respirators, to protect them from potential hazards.
The Importance of Mine Shafts in Modern Mining
Mine shafts are not merely passageways; they are the backbone of many underground mining operations, impacting various aspects of mining:
- Accessibility: They provide essential access to deep ore bodies that would otherwise be inaccessible.
- Efficiency: They facilitate the efficient transportation of materials and personnel, reducing operational costs and improving productivity.
- Safety: They facilitate the implementation of safety measures, minimizing risks and protecting workers.
- Environmental Impact: Their design and construction influence the environmental impact of mining operations, including issues related to water management and ground stability.
- Economic Viability: The efficiency and safety of shaft operations directly impact the economic viability of mining projects.
Conclusion: An Enduring Element of Underground Mining
Mine shafts are fundamental to underground mining, representing a complex interplay of engineering, geology, and safety. Their design, construction, and ongoing maintenance are crucial for the successful and safe extraction of valuable resources. The ongoing advancements in mining technology and safety standards continue to refine shaft designs and improve the overall safety and efficiency of these vital elements in the mining industry. From the initial planning stages to the final stages of decommissioning, understanding the nuances of mine shafts is essential for anyone involved in or interested in the world of underground mining.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Write 60 As A Fraction
Mar 26, 2025
-
Does Constant Velocity Mean No Acceleration
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Are 3 Fractions Equivalent To 3 8
Mar 26, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 68
Mar 26, 2025
-
12 Is What Percent Of 200
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Shaft In Mining . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
