What Is A Advantage Of Asexual Reproduction
listenit
Mar 12, 2025 · 5 min read
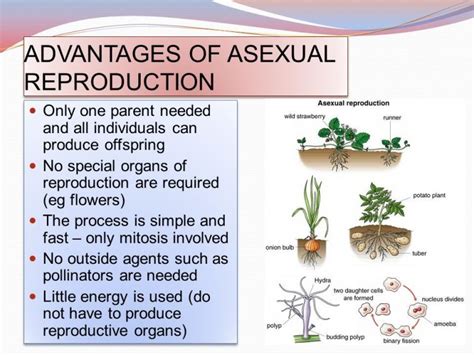
Table of Contents
The Undeniable Advantages of Asexual Reproduction: A Deep Dive
Asexual reproduction, the creation of offspring from a single parent without the fusion of gametes, often gets overshadowed by its more glamorous counterpart, sexual reproduction. However, a closer examination reveals a suite of significant advantages that have ensured its prevalence throughout the biological world. While sexual reproduction offers genetic diversity, asexual reproduction boasts a speed, efficiency, and stability that are undeniably compelling in specific ecological contexts. This article will delve into the myriad benefits of asexual reproduction, exploring its ecological significance and evolutionary implications.
Speed and Efficiency: The Quick Route to Population Growth
One of the most striking advantages of asexual reproduction is its sheer speed and efficiency. Unlike sexual reproduction, which requires the energetically costly processes of mate searching, courtship, and fertilization, asexual reproduction can be remarkably swift. A single parent can rapidly produce numerous offspring, a trait particularly advantageous in environments with abundant resources or unpredictable conditions.
Exploiting Transient Resources: A Prime Example
Imagine a pond suddenly enriched with nutrients. Organisms capable of rapid asexual reproduction, such as certain algae or bacteria, can quickly exploit this ephemeral resource surge. They multiply exponentially, outcompeting slower-reproducing sexual species and dominating the available niche before the resource depletion occurs. This rapid proliferation allows them to maximize their reproductive output in a short window of opportunity.
Colonization and Dispersion: A Tale of Two Strategies
Asexual reproduction also facilitates rapid colonization of new habitats. A single individual can initiate a new population, a feat impossible for sexual reproducers requiring at least two individuals. This is crucial for species dispersing to new islands, colonizing disturbed areas, or spreading rapidly across vast territories. Imagine a plant fragment carried by a river; if it's capable of asexual reproduction, it could potentially establish a new colony in a new location, without needing another plant for pollination.
Genetic Stability: Maintaining the Winning Formula
A second major advantage of asexual reproduction lies in its ability to maintain genetic stability. Offspring inherit an exact copy of their parent's genome, replicating successful genetic combinations. In stable, predictable environments where the existing genotype is well-adapted, this consistency can be highly beneficial.
Environmental Consistency: A Stable Advantage
In unchanging environments, there's little evolutionary pressure to diversify genetic makeup. Asexual reproduction guarantees that successful adaptations are faithfully transmitted across generations, ensuring the continued success of the lineage in a predictable habitat. This is particularly true for organisms living in environments with limited environmental fluctuation.
Eliminating the Risk of Harmful Combinations: A Calculated Gamble
Sexual reproduction involves the recombination of genes, which can lead to the creation of both beneficial and detrimental genetic combinations. Asexual reproduction avoids this risk by ensuring that offspring maintain the advantageous genetic configuration of the parent. This is particularly important in stable environments where the risk of producing poorly adapted offspring through sexual recombination outweighs the potential benefits of genetic diversity.
Reduced Energetic Costs: A Resource-Efficient Strategy
Asexual reproduction is significantly less energetically demanding compared to sexual reproduction. The absence of mate searching, courtship rituals, and the production of gametes conserves considerable resources. This energy efficiency translates into a higher reproductive output for a given amount of energy expenditure.
Energy Allocation: Prioritizing Reproduction
In resource-limited environments, energy conservation is crucial. Asexual reproduction allows organisms to allocate more energy towards growth, survival, and the production of offspring, increasing overall reproductive success. This reduced energetic burden can be particularly beneficial in harsh environments where resources are scarce.
Investing in Growth: A Strategy for Success
The energy saved by not engaging in the elaborate processes of sexual reproduction can be redirected towards other crucial life functions, such as growth, development, and maintenance. This increased energy allocation can result in larger, more robust individuals that are better equipped to survive and reproduce successfully.
Rapid Adaptation to Specific Niches: Specialized Success
While often associated with limited genetic diversity, asexual reproduction can surprisingly facilitate rapid adaptation to highly specific niches. Clonal lineages can specialize to thrive in particular microhabitats or resource conditions.
Niche Specialization: A Unique Advantage
Consider a bacterial colony colonizing a specific type of substrate. Through mutations and selection within the asexually reproducing population, some clones might develop adaptations better suited to the specific chemical composition of that substrate. These specialized clones can then outcompete both the original clone and sexually reproducing species, demonstrating a surprising capacity for niche adaptation.
Exploiting Local Resources: Efficiency of the Extreme
Asexual reproduction can facilitate the exploitation of localized resources with little genetic alteration. A small mutation providing a slight advantage in utilizing a particular nutrient can quickly spread throughout the asexual population, resulting in a rapid shift in the population’s adaptation to that specific resource.
The Trade-offs: Understanding the Limitations
It's important to acknowledge that asexual reproduction also presents certain limitations. The lack of genetic recombination results in limited genetic diversity, making populations vulnerable to environmental changes or pathogens. A single detrimental mutation can potentially wipe out an entire population, highlighting a significant drawback of this reproductive strategy.
Evolutionary Bottlenecks: A Precarious Position
Asexually reproducing populations are more vulnerable to extinction due to this lack of genetic diversity. A sudden environmental shift or the emergence of a new pathogen can severely impact a homogeneous population, leading to a population crash or even extinction. This makes asexual reproduction a risky strategy in dynamic environments.
Muller's Ratchet: A Slow Accumulation of Deleterious Mutations
The accumulation of deleterious mutations within an asexual lineage over time, a process known as Muller's ratchet, is another significant constraint. Sexual reproduction provides a mechanism to purge these harmful mutations through recombination, but asexual lineages have no such mechanism, potentially leading to a gradual decline in fitness over generations.
Conclusion: The Power of Context
Ultimately, the success of asexual reproduction depends heavily on the specific ecological context. In stable, resource-rich environments where rapid population growth and maintenance of successful genotypes are paramount, asexual reproduction offers undeniable advantages. However, in dynamic environments characterized by frequent environmental changes or high pathogen pressure, the lack of genetic diversity poses a significant risk. The widespread presence of asexual reproduction across the tree of life underscores its profound adaptive significance, showcasing its power as a successful and effective reproductive strategy in specific, suitable environments. Understanding these advantages and limitations is crucial to fully appreciating the diverse reproductive strategies found in nature and their evolutionary significance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Highest Common Factor Of 8 And 16
May 09, 2025
-
Calculate The Concentration Of Each Solution In Mass Percent
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Atoms Are In Calcium
May 09, 2025
-
9 Minus The Quotient Of 2 And X
May 09, 2025
-
Write 3 3 4 As A Decimal
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Advantage Of Asexual Reproduction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.