What Is 9 10 As A Decimal
listenit
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
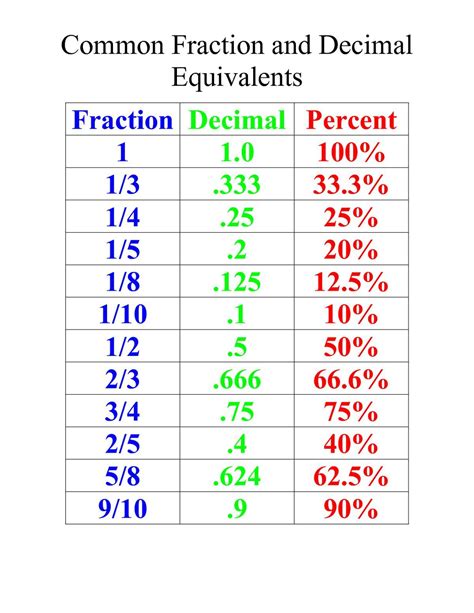
Table of Contents
What is 9/10 as a Decimal? A Comprehensive Guide
The question, "What is 9/10 as a decimal?" might seem deceptively simple, but it opens the door to understanding fundamental concepts in mathematics, particularly the relationship between fractions and decimals. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question directly but also delve into the broader context of fraction-to-decimal conversion, offering practical examples and explaining the underlying principles.
Understanding Fractions and Decimals
Before we tackle the specific conversion of 9/10, let's establish a firm understanding of what fractions and decimals represent.
Fractions: A fraction represents a part of a whole. It's expressed as a ratio of two numbers – the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number). The denominator indicates the number of equal parts the whole is divided into, and the numerator indicates how many of those parts are being considered. For example, in the fraction 9/10, the denominator 10 means the whole is divided into 10 equal parts, and the numerator 9 means we are considering 9 of those parts.
Decimals: A decimal is another way of representing a part of a whole. It uses a base-10 system, with the digits to the right of the decimal point representing tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on. Each place value is ten times smaller than the place value to its left. For instance, 0.1 represents one-tenth (1/10), 0.01 represents one-hundredth (1/100), and so on.
Converting Fractions to Decimals: The Simple Method
The conversion of a fraction to a decimal is essentially a division problem. You divide the numerator by the denominator. Let's apply this to our example:
9/10 = 9 ÷ 10 = 0.9
Therefore, 9/10 as a decimal is 0.9.
This method works seamlessly for fractions with denominators that are powers of 10 (10, 100, 1000, etc.). For fractions with denominators that are not powers of 10, we need a slightly different approach, which we'll explore next.
Converting Fractions to Decimals: The Long Division Method
Consider a fraction like 3/4. The denominator is not a power of 10. To convert this to a decimal, we use long division:
- Divide the numerator (3) by the denominator (4). Since 4 doesn't go into 3, we add a decimal point and a zero to the numerator (making it 3.0).
- Perform the long division. 4 goes into 30 seven times (4 x 7 = 28). Subtract 28 from 30, leaving a remainder of 2.
- Add another zero to the remainder. This becomes 20.
- Continue the division. 4 goes into 20 five times (4 x 5 = 20). The remainder is 0, so the division is complete.
Therefore, 3/4 = 0.75.
This long division method is applicable to any fraction, regardless of its denominator. However, some fractions result in repeating decimals, which we will discuss shortly.
Dealing with Repeating Decimals
Not all fractions convert to neat, terminating decimals. Some result in repeating decimals – decimals where a digit or a sequence of digits repeats infinitely. For example, 1/3 = 0.3333... (the 3 repeats infinitely). We represent this using a bar over the repeating digit(s): 1/3 = 0.$\overline{3}$.
Similarly, 1/7 = 0.142857142857... = 0.$\overline{142857}$.
When converting fractions with repeating decimals, it's crucial to understand that the decimal representation is an approximation, as we can't write out an infinite number of digits.
Understanding Decimal Place Value
The position of each digit in a decimal number determines its value. The digit immediately to the right of the decimal point is in the tenths place (1/10), the next digit to the right is in the hundredths place (1/100), and so on. Understanding place value is crucial for interpreting and manipulating decimal numbers accurately.
For example, in the decimal 0.9, the digit 9 is in the tenths place, representing 9/10.
Practical Applications of Fraction-to-Decimal Conversion
The ability to convert fractions to decimals is essential in many areas, including:
- Science: Measurements and calculations in physics, chemistry, and other scientific fields often involve both fractions and decimals.
- Engineering: Precision engineering requires accurate calculations using both fractional and decimal representations.
- Finance: Calculating percentages, interest rates, and other financial metrics frequently involves converting fractions to decimals.
- Everyday Life: Dividing a pizza among friends, measuring ingredients for a recipe, or calculating discounts all benefit from understanding these conversions.
Advanced Concepts: Converting Fractions with Mixed Numbers
A mixed number combines a whole number and a fraction (e.g., 2 1/2). To convert a mixed number to a decimal, first convert it to an improper fraction. Then, use the division method discussed earlier.
For example, to convert 2 1/2 to a decimal:
- Convert to an improper fraction: 2 1/2 = (2 x 2 + 1)/2 = 5/2
- Divide the numerator by the denominator: 5 ÷ 2 = 2.5
Therefore, 2 1/2 = 2.5.
Beyond the Basics: Using Calculators and Software
While understanding the manual methods is important for grasping the underlying principles, calculators and computer software can efficiently handle fraction-to-decimal conversions, especially for more complex fractions. However, knowing the manual methods ensures you understand what the calculator is doing and can double-check its results.
Conclusion: Mastering Fractions and Decimals
The conversion of 9/10 to its decimal equivalent (0.9) is a straightforward example that underscores the fundamental relationship between fractions and decimals. However, this seemingly simple conversion opens the door to a deeper understanding of mathematical principles, including long division, place value, repeating decimals, and the conversion of mixed numbers. Mastering these concepts is vital for success in various academic and professional fields, ensuring that you are equipped to handle numerical calculations with accuracy and confidence. Remember to practice regularly and utilize different resources, both manual and technological, to reinforce your understanding and develop your proficiency in handling fractions and decimals. The more comfortable you are with these foundational concepts, the smoother your journey through more advanced mathematical concepts will be.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Does King Use This Allusion
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 18 And 12
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is 4 Percent Of 1000
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Fl Oz In Half Gallon
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is 4 Divided By 1 3
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 9 10 As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
