What Is 4 To The Power Of 5
listenit
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
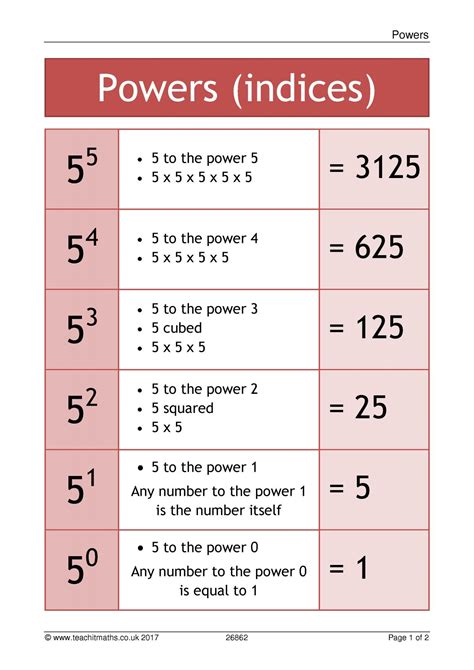
Table of Contents
What is 4 to the Power of 5? A Deep Dive into Exponentiation
The seemingly simple question, "What is 4 to the power of 5?" opens a door to a fascinating world of mathematics, specifically exponentiation. While the answer itself is straightforward—1024—the journey to understanding how we arrive at this answer, and the broader implications of exponentiation, is far more enriching. This article will explore this calculation in detail, examining its underlying principles and exploring its applications in various fields.
Understanding Exponentiation: The Basics
Exponentiation, at its core, represents repeated multiplication. The expression 4 to the power of 5, written as 4⁵, signifies multiplying the base number (4) by itself five times. In mathematical notation:
4⁵ = 4 × 4 × 4 × 4 × 4
This concept might seem elementary, but it forms the foundation for numerous complex mathematical operations and applications in diverse fields.
The Components of Exponentiation
Before diving deeper, let's define the key components of an exponential expression:
- Base: This is the number being multiplied repeatedly. In 4⁵, the base is 4.
- Exponent: This is the number indicating how many times the base is multiplied by itself. In 4⁵, the exponent is 5. It's also known as the power.
- Result: This is the outcome of the repeated multiplication. In this case, the result is 1024.
Calculating 4 to the Power of 5
The simplest way to calculate 4⁵ is through direct multiplication:
- 4 × 4 = 16
- 16 × 4 = 64
- 64 × 4 = 256
- 256 × 4 = 1024
Therefore, 4 to the power of 5 equals 1024.
Alternative Calculation Methods
While direct multiplication is straightforward, particularly for smaller exponents, other methods become more efficient for larger exponents. These include:
-
Using a calculator: Most calculators have an exponentiation function (usually denoted as x^y or ^). Simply input 4 as the base, 5 as the exponent, and the calculator will compute the result (1024).
-
Logarithms: Logarithms provide the inverse operation of exponentiation. While calculating 4⁵ directly using logarithms isn't necessarily more efficient, it illustrates the relationship between these crucial mathematical functions.
Beyond the Calculation: Applications of Exponentiation
The seemingly simple calculation of 4⁵ has profound implications across numerous fields:
1. Computer Science and Data Storage
Exponentiation is fundamental to understanding data storage capacity. Computers work in binary (base-2) systems, and powers of 2 are frequently used to describe memory size (kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes, etc.). Understanding exponentiation is crucial for comprehending the exponential growth of data storage needs.
2. Compound Interest and Financial Growth
In finance, compound interest calculations rely heavily on exponentiation. The formula for compound interest includes an exponential term that reflects the compounding effect of interest over time. Understanding how quickly money can grow with compound interest is crucial for financial planning.
3. Population Growth and Biology
Population growth often follows an exponential pattern. If a population grows at a constant rate, its size can be modeled using an exponential equation. Understanding exponential growth is crucial in biology, ecology, and epidemiology.
4. Physics and Engineering
Exponentiation plays a significant role in numerous physics and engineering applications, including radioactive decay, signal processing, and the study of complex systems. Exponential functions are used to model a wide variety of natural phenomena.
5. Mathematics and Number Theory
Exponentiation is a foundational concept in number theory, playing a key role in concepts like modular arithmetic, cryptography, and Fermat's Last Theorem.
Expanding the Concept: Properties of Exponents
Understanding the properties of exponents further clarifies the nature of exponentiation and allows for efficient manipulation of exponential expressions. These properties include:
-
Product of Powers: When multiplying two powers with the same base, you add the exponents: aᵐ × aⁿ = aᵐ⁺ⁿ
-
Quotient of Powers: When dividing two powers with the same base, you subtract the exponents: aᵐ ÷ aⁿ = aᵐ⁻ⁿ
-
Power of a Power: When raising a power to another power, you multiply the exponents: (aᵐ)ⁿ = aᵐⁿ
-
Power of a Product: When raising a product to a power, you raise each factor to that power: (ab)ⁿ = aⁿbⁿ
-
Power of a Quotient: When raising a quotient to a power, you raise both the numerator and the denominator to that power: (a/b)ⁿ = aⁿ/bⁿ
These properties are essential for simplifying and solving complex exponential equations.
Error Handling and Considerations
While calculating 4⁵ is straightforward, it's crucial to be mindful of potential errors, especially when dealing with larger numbers or more complex exponential expressions:
-
Order of Operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS): Remember to follow the order of operations (Parentheses/Brackets, Exponents/Orders, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction) to ensure accurate calculations.
-
Rounding Errors: When dealing with very large or very small numbers, rounding errors can accumulate and impact the accuracy of the result. Using high-precision calculators or software can mitigate this issue.
-
Negative Exponents: A negative exponent indicates the reciprocal of the positive exponent. For example, 4⁻⁵ = 1/4⁵ = 1/1024.
-
Zero and Fractional Exponents: Understanding the meaning of 0 as an exponent (any number raised to the power of 0 is 1) and fractional exponents (which represent roots) is important for a comprehensive understanding of exponentiation.
Conclusion: The Significance of 4 to the Power of 5
The answer to "What is 4 to the power of 5?" is 1024. While this specific calculation might seem inconsequential in isolation, it represents a fundamental concept within mathematics and has far-reaching implications across various fields. Understanding exponentiation is not merely about calculating a specific numerical result; it's about grasping a fundamental principle that underpins numerous processes and phenomena in the world around us. From the growth of populations to the storage of digital information, the power of exponentiation continues to shape our understanding and interaction with the world. This detailed exploration should equip you with a stronger grasp of exponentiation and its practical applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Molecules Are Formed By The Bonding Together Of
Mar 18, 2025
-
Limit Of Ln X As X Approaches 0
Mar 18, 2025
-
How To Find Valence Electrons For Transition Metals
Mar 18, 2025
-
8 8 8 8 8 8
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Does Meiosis Generate Genetic Diversity
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 4 To The Power Of 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
