What Is 33pi/2 In The Unit Circle
listenit
Mar 16, 2025 · 4 min read
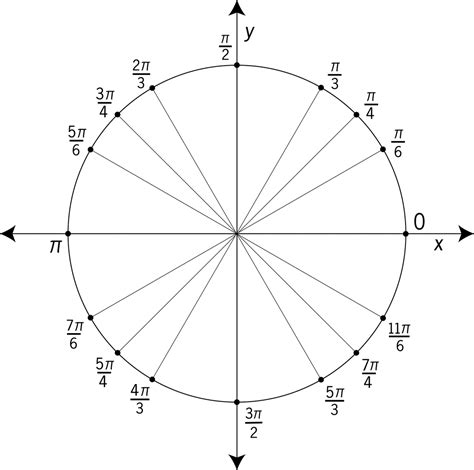
Table of Contents
What is 33π/2 in the Unit Circle? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding angles and their representation on the unit circle is fundamental to trigonometry and various applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the angle 33π/2, exploring its location on the unit circle, its equivalent angles, and its trigonometric values. We'll also touch upon the broader context of understanding angles beyond the typical 0 to 2π range.
Understanding the Unit Circle
The unit circle is a circle with a radius of 1 centered at the origin (0,0) of a coordinate plane. Its importance lies in its ability to visually represent angles and their corresponding trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, and tangent). The angle is measured counter-clockwise from the positive x-axis.
Each point on the unit circle can be represented by its coordinates (x, y), where x = cos(θ) and y = sin(θ), with θ being the angle measured from the positive x-axis. This direct relationship simplifies the calculation and understanding of trigonometric values.
Deconstructing 33π/2
The angle 33π/2 might initially seem daunting, but by breaking it down, we can easily determine its position and properties on the unit circle.
Finding Equivalent Angles
The key to understanding angles like 33π/2 lies in recognizing that angles are cyclical. A full rotation around the unit circle is 2π radians (or 360 degrees). Therefore, we can subtract multiples of 2π from 33π/2 to find an equivalent angle within the 0 to 2π range.
Let's perform the calculation:
33π/2 = 16π + π/2
Since 16π represents 8 full rotations (16π/2π = 8), we can disregard it. This leaves us with an equivalent angle of π/2.
Therefore, 33π/2 is equivalent to π/2.
Locating 33π/2 (or π/2) on the Unit Circle
The angle π/2 radians (or 90 degrees) lies on the positive y-axis of the unit circle. The coordinates of this point are (0, 1).
Visual Representation:
Imagine the unit circle. Start at the positive x-axis (0 radians). Move counter-clockwise a quarter of the way around the circle. You've reached the positive y-axis, which corresponds to π/2 radians.
Trigonometric Values of 33π/2
Since 33π/2 is equivalent to π/2, its trigonometric values are the same:
- sin(33π/2) = sin(π/2) = 1
- cos(33π/2) = cos(π/2) = 0
- tan(33π/2) = tan(π/2) = undefined (because cos(π/2) = 0, and division by zero is undefined)
Understanding Angles Beyond 2π
Many students struggle with angles larger than 2π. The concept of coterminal angles is crucial for mastering this. Coterminal angles are angles that share the same terminal side (the side that ends at the same point on the unit circle). They differ by multiples of 2π (or 360 degrees).
In our example, 33π/2, 17π/2, π/2, and even -π/2 are all coterminal angles because they all terminate at the same point on the unit circle (the positive y-axis). This concept simplifies calculations for larger angles by reducing them to their equivalent angles within the 0-2π range.
Applications of Unit Circle Understanding
The unit circle and the understanding of angles like 33π/2 are fundamental to many areas of mathematics and its applications:
-
Trigonometry: Solving trigonometric equations, evaluating trigonometric functions, and understanding trigonometric identities all rely on a strong grasp of the unit circle.
-
Calculus: Understanding radians and their relationships on the unit circle is critical for calculus concepts like derivatives and integrals of trigonometric functions.
-
Physics and Engineering: Many physical phenomena, like oscillations, waves, and rotations, are modeled using trigonometric functions. The unit circle provides a visual and conceptual tool for understanding these models.
-
Computer Graphics and Game Development: The unit circle plays a crucial role in representing rotations, transformations, and other geometric operations used extensively in creating 2D and 3D graphics.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
While we've focused on 33π/2, the principles discussed apply to any angle, no matter how large or small. Here are some advanced concepts you can explore to deepen your understanding:
-
Radians vs. Degrees: Understand the conversion between radians and degrees and when it's more appropriate to use one over the other.
-
Reference Angles: Mastering the concept of reference angles helps to simplify the calculation of trigonometric functions for angles in any quadrant.
-
Graphs of Trigonometric Functions: Visualizing the graphs of sine, cosine, and tangent functions enhances understanding of their periodicity and behavior.
Conclusion: Mastering the Unit Circle
The unit circle is a powerful tool for understanding angles and their corresponding trigonometric values. By breaking down complex angles like 33π/2 into equivalent angles within the 0 to 2π range, we can easily determine their position on the unit circle and calculate their trigonometric values. This understanding is crucial for success in trigonometry and its numerous applications across various scientific and technological fields. The more you practice working with the unit circle and visualizing angles, the more intuitive and easy it will become. Don't hesitate to explore additional resources and practice problems to solidify your understanding of this fundamental concept. Remember, mastery of the unit circle will significantly improve your ability to solve trigonometric problems and unlock deeper comprehension of related mathematical concepts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
1 4 Yd How Many Inches
Mar 16, 2025
-
Can Crawdads Live Out Of Water
Mar 16, 2025
-
How Many Kg Is 5000 G
Mar 16, 2025
-
Common Factors Of 24 And 40
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is 70 Percent Of 35
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 33pi/2 In The Unit Circle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
