What Happens To Volume When Temperature Increases
listenit
Apr 08, 2025 · 6 min read
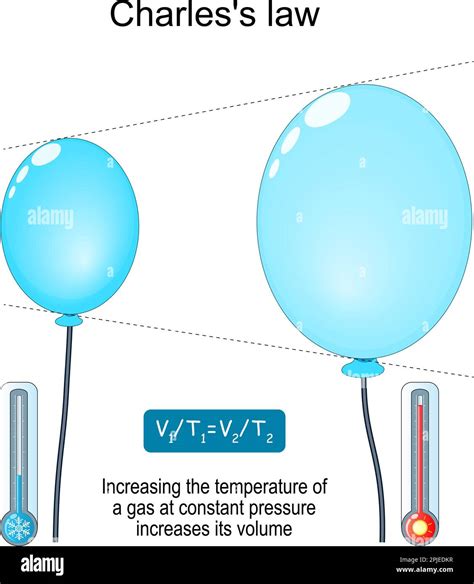
Table of Contents
What Happens to Volume When Temperature Increases? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the relationship between temperature and volume is fundamental to various scientific fields, from everyday cooking to advanced engineering projects. This comprehensive guide explores the effects of temperature increases on volume, focusing on different states of matter – solids, liquids, and gases – and delving into the underlying principles governing these changes. We'll examine the concepts of thermal expansion, its applications, and exceptions to the general rules.
The Basics: Thermal Expansion
Thermal expansion refers to the tendency of matter to change its volume in response to changes in temperature. Generally, an increase in temperature leads to an increase in volume, while a decrease in temperature results in a decrease in volume. This phenomenon is caused by the increased kinetic energy of atoms and molecules at higher temperatures. As temperature rises, these particles move more vigorously, increasing the average distance between them and, consequently, expanding the material's volume.
The extent of thermal expansion varies significantly depending on the material's properties, specifically its coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE). The CTE is a material-specific constant that quantifies the fractional change in size per degree Celsius (or Fahrenheit) change in temperature. Materials with high CTEs expand significantly with temperature changes, while those with low CTEs exhibit minimal expansion.
Different States of Matter: Unique Responses to Temperature Changes
The relationship between temperature and volume manifests differently across the three fundamental states of matter:
1. Solids:
- Expansion: Solid materials generally expand in all three dimensions (length, width, and height) when heated. This is known as volumetric thermal expansion. However, the expansion is typically relatively small compared to liquids and gases. Think of the expansion of a metal bridge on a hot summer day – the expansion might be small but significant enough to require expansion joints to prevent damage.
- Factors Affecting Expansion: The crystalline structure and bonding strength of the solid significantly influence its CTE. Metals, for example, generally have higher CTEs than ceramics. Anisotropic materials (materials with directional-dependent properties) can expand differently along different axes.
- Applications: Understanding thermal expansion in solids is crucial in engineering design. Consider the design of bridges, railways, and even microchips; thermal expansion must be accounted for to prevent structural failures or malfunctions.
2. Liquids:
- Expansion: Liquids exhibit significantly greater thermal expansion than solids. The weaker intermolecular forces in liquids allow for greater freedom of movement for the molecules, resulting in a larger increase in volume with increasing temperature. This is why you might observe liquids overflowing from a container when heated significantly.
- Anomalous Expansion of Water: Water exhibits an anomalous behavior. It expands when heated above 4°C, but it contracts when cooled below 4°C. This unusual behavior is critical for aquatic life, as it prevents bodies of water from freezing solid from the bottom up, allowing aquatic life to survive even in freezing temperatures.
- Applications: Liquid thermal expansion is exploited in various applications, such as liquid-in-glass thermometers. The expansion of the liquid (usually mercury or alcohol) is directly proportional to the temperature change, providing a means for accurate temperature measurement.
3. Gases:
- Expansion: Gases exhibit the most significant thermal expansion among the three states of matter. The weak intermolecular forces in gases allow for extensive molecular movement, making them highly susceptible to volume changes with temperature fluctuations. The ideal gas law (PV = nRT) elegantly describes this relationship, where pressure (P), volume (V), number of moles (n), and temperature (T) are related through the ideal gas constant (R).
- Charles's Law: A specific case of the ideal gas law, Charles's Law, states that at constant pressure, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. This means that if you double the absolute temperature of a gas while keeping the pressure constant, its volume will also double.
- Applications: The thermal expansion of gases finds application in numerous technologies, including hot air balloons, where heated air expands, reducing its density and enabling buoyancy. It's also crucial in internal combustion engines, where the expansion of gases produced by combustion drives the pistons.
Factors Influencing Thermal Expansion: Beyond Temperature
While temperature is the primary driver of thermal expansion, several other factors can influence the extent of volume change:
- Pressure: Increasing pressure generally reduces the volume of a substance, counteracting the effect of temperature increase. This effect is particularly important in liquids and solids, where compressibility is lower than in gases.
- Material Composition: The type of material significantly impacts its thermal expansion. Different materials have different atomic structures and intermolecular forces, leading to varying CTEs. Alloys, for example, can be designed to have specific CTEs by carefully choosing their composition.
- Phase Transitions: Phase transitions (such as melting or boiling) involve dramatic changes in volume. For instance, when ice melts into water, the volume decreases because the water molecules are more closely packed in the liquid phase than in the solid phase.
Exceptions and Anomalies
While the general rule is that volume increases with temperature, several exceptions exist:
- Water's Anomalous Behavior: As mentioned before, water exhibits anomalous expansion behavior below 4°C.
- Negative Thermal Expansion: Some materials exhibit negative thermal expansion, meaning their volume decreases with increasing temperature over certain temperature ranges. This unusual behavior is associated with specific crystal structures and bonding arrangements.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
The principles of thermal expansion are crucial in various aspects of everyday life and engineering:
- Thermometers: Liquid-in-glass thermometers rely on the thermal expansion of liquids to measure temperature.
- Bimetallic Strips: These strips, made of two metals with different CTEs, bend when heated due to differential expansion, used in thermostats and other temperature-sensitive devices.
- Bridges and Rail Tracks: Expansion joints are incorporated into bridges and rail tracks to accommodate thermal expansion and prevent structural damage.
- Engine Design: The thermal expansion of gases plays a crucial role in the operation of internal combustion engines.
- Precision Manufacturing: Thermal expansion is considered in precision manufacturing to ensure the accuracy of dimensions in components.
Conclusion: Understanding the Interplay of Temperature and Volume
The relationship between temperature and volume is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering. While the general principle of thermal expansion holds true for most substances, understanding the nuances and exceptions, like water's anomalous behavior and negative thermal expansion, is vital for accurately predicting and controlling the behavior of materials under varying temperature conditions. This knowledge is essential for designing safe and functional structures, machines, and devices across numerous industries. Further research and exploration into the specific CTEs of different materials and their responses under various conditions remain crucial for advancements in diverse fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Factors For 32
Apr 08, 2025
-
Number Of Valence Electrons For Boron
Apr 08, 2025
-
What Holds Two Strands Of Dna Together
Apr 08, 2025
-
What Happens To Atoms After A Chemical Change
Apr 08, 2025
-
What Decimal Is Equivalent To 1 3
Apr 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Happens To Volume When Temperature Increases . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.