What Are The Products Of Combustion Of A Hydrocarbon
listenit
Apr 08, 2025 · 5 min read
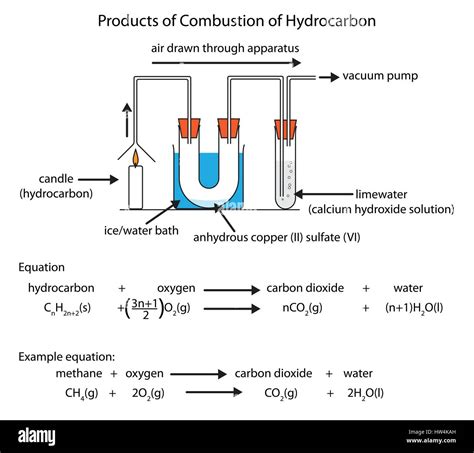
Table of Contents
What Are the Products of Combustion of a Hydrocarbon? A Comprehensive Guide
The combustion of hydrocarbons, a fundamental process in various industries and even our daily lives, forms the basis for energy generation, transportation, and countless industrial processes. Understanding the products of this reaction is crucial for various applications, from optimizing engine efficiency to minimizing environmental impact. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the intricacies of hydrocarbon combustion, exploring the primary and secondary products, influencing factors, and their environmental implications.
Understanding Hydrocarbon Combustion
Hydrocarbons, organic compounds consisting solely of carbon and hydrogen atoms, are the primary fuel source in many combustion processes. When hydrocarbons react with oxygen (O2), they undergo a rapid oxidation reaction, releasing significant energy in the form of heat and light. This exothermic reaction is what we commonly know as burning or combustion. The completeness of this combustion process, however, significantly impacts the resulting products.
Primary Products of Complete Combustion
Under ideal conditions, with sufficient oxygen supply and appropriate temperature, the complete combustion of a hydrocarbon yields only two primary products:
1. Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
This is the most significant product of complete hydrocarbon combustion. For every carbon atom in the hydrocarbon molecule, one molecule of carbon dioxide is produced. CO2 is a colorless, odorless gas that is a major contributor to the greenhouse effect. Its role in climate change is a topic of significant global concern.
2. Water (H2O)
For every two hydrogen atoms in the hydrocarbon molecule, one molecule of water is produced. This water is usually released as vapor, although it can condense into liquid water depending on the ambient temperature and humidity.
Example: The complete combustion of methane (CH4) can be represented by the following balanced chemical equation:
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
This equation demonstrates that one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen to produce one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water.
Incomplete Combustion and its Products
When the oxygen supply is insufficient or the combustion temperature is too low, incomplete combustion occurs. This leads to the formation of several byproducts in addition to CO2 and H2O. These byproducts are often harmful pollutants with significant environmental and health consequences.
1. Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Carbon monoxide is a highly toxic and colorless, odorless gas. It's a significant product of incomplete combustion and arises when there isn't enough oxygen to fully oxidize the carbon atoms to CO2. CO binds to hemoglobin in the blood, preventing the transport of oxygen, potentially leading to death. CO is a major air pollutant and a serious health hazard.
2. Soot (Elemental Carbon, C)
Soot is a black, fine particulate matter composed primarily of elemental carbon. It's formed when the fuel-rich environment doesn't allow complete oxidation of carbon atoms. Soot contributes to air pollution, respiratory problems, and can have a negative impact on climate. It also reduces the efficiency of combustion engines by reducing heat transfer.
3. Unburnt Hydrocarbons (HC)
Unburnt hydrocarbons are the original fuel molecules that haven't undergone complete oxidation during combustion. These can include a range of different hydrocarbons depending on the original fuel source. Unburnt hydrocarbons contribute to smog formation and are also greenhouse gases.
4. Other Products of Incomplete Combustion
Depending on the specific hydrocarbon and the conditions of combustion, other products can also form during incomplete combustion. These may include:
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx): These are formed when nitrogen in the air reacts with oxygen at high temperatures. NOx gases are precursors to acid rain and smog.
- Particulate matter (PM): This includes soot, but can also encompass other fine particles formed during combustion. PM contributes to respiratory problems and cardiovascular disease.
- Aldehydes: These are organic compounds formed from incomplete oxidation of hydrocarbons. Some aldehydes are irritants and can contribute to smog formation.
- Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs): These are complex hydrocarbons formed during incomplete combustion. Many PAHs are known carcinogens.
Factors Affecting Combustion Products
Several factors influence the products of hydrocarbon combustion, including:
- Oxygen availability: Sufficient oxygen is crucial for complete combustion. A deficiency in oxygen leads to incomplete combustion and the formation of harmful byproducts.
- Temperature: High temperatures generally favor complete combustion. Lower temperatures can result in incomplete combustion.
- Fuel type: The chemical structure of the hydrocarbon influences the combustion process and the products formed. Different hydrocarbons have different combustion characteristics.
- Mixing of fuel and air: Efficient mixing of fuel and air ensures complete combustion. Poor mixing can lead to local fuel-rich regions where incomplete combustion occurs.
- Presence of catalysts: Catalysts can accelerate the rate of combustion and promote complete oxidation, minimizing the formation of pollutants.
Environmental Implications
The products of hydrocarbon combustion have significant environmental implications. The emission of greenhouse gases like CO2 contributes to climate change. Incomplete combustion leads to the release of harmful pollutants that affect air quality, human health, and ecosystems. Acid rain, smog, and respiratory problems are all linked to pollutants from incomplete combustion.
Minimizing Harmful Emissions
Various strategies are employed to minimize the harmful effects of hydrocarbon combustion:
- Improved combustion technologies: Designing more efficient combustion systems that ensure complete combustion and minimize pollutant formation.
- Use of catalysts: Catalytic converters are commonly used in vehicles to convert harmful pollutants like CO and NOx into less harmful substances.
- Fuel modification: Using cleaner fuels with lower sulfur content reduces the formation of sulfur dioxide (SO2), a contributor to acid rain.
- Emission control regulations: Implementing strict emission standards for vehicles and industrial processes helps reduce the release of harmful pollutants.
- Alternative energy sources: Shifting towards renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydro power, reduces reliance on fossil fuels and their associated emissions.
Conclusion
The products of hydrocarbon combustion are diverse, ranging from the relatively harmless CO2 and H2O in complete combustion to a range of harmful pollutants in incomplete combustion. Understanding these products, the factors that influence them, and their environmental impact is critical for developing cleaner combustion technologies, reducing pollution, and mitigating the effects of climate change. Continuous research and technological advancements are vital in minimizing the environmental footprint associated with hydrocarbon combustion and transitioning toward sustainable energy alternatives. The focus should always remain on maximizing complete combustion while simultaneously developing effective strategies for capturing and mitigating any remaining harmful byproducts. This will be vital in ensuring a healthier planet for future generations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
5 Abiotic Factors In The Savanna
Apr 08, 2025
-
What Is 20 In Decimal Form
Apr 08, 2025
-
1 Sqrt X 2 1 Integral
Apr 08, 2025
-
What Are The Rungs Of The Ladder Made Of
Apr 08, 2025
-
The Mass Of A Mole Of Nacl Is The
Apr 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Products Of Combustion Of A Hydrocarbon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.