Vertex Angle Of An Isosceles Triangle
listenit
Mar 14, 2025 · 7 min read
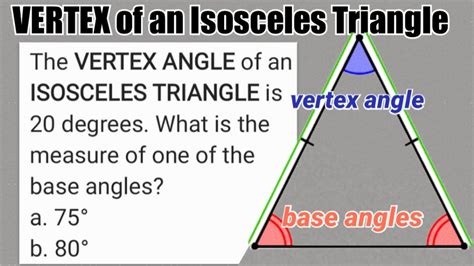
Table of Contents
Understanding the Vertex Angle of an Isosceles Triangle: A Comprehensive Guide
The isosceles triangle, a geometric shape characterized by two sides of equal length, holds a unique fascination within the world of mathematics. At the heart of its properties lies the vertex angle, a key component in understanding its characteristics and solving related problems. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the concept of the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle, exploring its definition, properties, theorems associated with it, and practical applications. We will also look at how understanding the vertex angle is crucial for various mathematical proofs and problem-solving scenarios.
Defining the Vertex Angle
Before we embark on a detailed exploration, let's precisely define the vertex angle. In an isosceles triangle, the vertex angle is the angle formed at the point where the two equal sides meet. This point is often referred to as the vertex. The other two angles, opposite the equal sides, are called the base angles. It's crucial to remember that the vertex angle is not necessarily the largest angle in the triangle. While it often is, especially in acute isosceles triangles, this is not always the case, particularly in obtuse isosceles triangles.
Visual Representation: Imagine an isosceles triangle, ABC, where AB = AC. Angle BAC is the vertex angle. Angles ABC and ACB are the base angles. A clear visual representation significantly enhances understanding. Consider sketching several examples, varying the size of the vertex angle to see how it affects the overall shape of the triangle. This hands-on approach strengthens comprehension and retention.
Properties of the Vertex Angle and Base Angles
The vertex angle of an isosceles triangle is intrinsically linked to its base angles through several key properties:
-
The Base Angles are Equal: This is a fundamental theorem of isosceles triangles. The angles opposite the two equal sides are always congruent (equal in measure). This property forms the bedrock of numerous proofs and problem-solving strategies involving isosceles triangles. Understanding and applying this property is crucial for successful problem-solving. Numerous problems rely on the equality of the base angles to find missing angles or side lengths.
-
The Sum of Angles: Like all triangles, the sum of the interior angles of an isosceles triangle is always 180 degrees. This means that the vertex angle plus the two base angles always add up to 180°. This simple yet powerful fact allows for the calculation of unknown angles when sufficient information is provided. For example, knowing the vertex angle immediately allows for the calculation of the base angles.
-
Relationship between Vertex and Base Angles: Because the base angles are equal, and the sum of all angles is 180°, there's a direct mathematical relationship between the vertex angle and each base angle. If the vertex angle is denoted as 'V' and each base angle as 'B', then the relationship is expressed as: V + 2B = 180°. This formula is extensively used to solve problems involving unknown angles.
Theorems and Proofs Related to the Vertex Angle
Several important geometric theorems are directly related to the properties of the vertex angle in an isosceles triangle:
-
Isosceles Triangle Theorem: This fundamental theorem states that if two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the angles opposite those sides are also congruent. This theorem directly underpins the equality of base angles in an isosceles triangle. Numerous proofs in geometry rely on this theorem as a fundamental premise.
-
Converse of the Isosceles Triangle Theorem: This theorem states that if two angles of a triangle are congruent, then the sides opposite those angles are also congruent. This is the converse of the Isosceles Triangle Theorem and proves useful in establishing the isosceles nature of a triangle based on angle measurements. This theorem is often employed in proofs where angle congruence is the known information.
-
The Exterior Angle Theorem: While not solely related to isosceles triangles, the exterior angle theorem plays a vital role when dealing with them. The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles. In an isosceles triangle, this means that an exterior angle at the base is equal to the sum of the vertex angle and the other base angle. This is particularly helpful when dealing with problems involving exterior angles.
Solving Problems Involving the Vertex Angle
Numerous mathematical problems involve calculating the measure of the vertex angle or base angles of an isosceles triangle. The following examples showcase typical problem-solving scenarios:
Example 1: Finding the base angles.
An isosceles triangle has a vertex angle of 70°. Find the measure of each base angle.
- Solution: Using the formula V + 2B = 180°, we have 70° + 2B = 180°. Solving for B gives B = 55°. Therefore, each base angle measures 55°.
Example 2: Finding the vertex angle.
An isosceles triangle has base angles of 45° each. Find the measure of the vertex angle.
- Solution: Using the same formula, V + 2(45°) = 180°, we solve for V to get V = 90°. Therefore, the vertex angle measures 90°. This example demonstrates an isosceles right-angled triangle.
Example 3: A more complex scenario.
An isosceles triangle ABC has AB = AC. The exterior angle at B is 110°. Find the measure of the vertex angle.
- Solution: The exterior angle at B is equal to the sum of the angles A and C (the interior angles). Since angles B and C are equal (base angles), we can represent them as x. Therefore, 110° = A + x. Also, A + x + x = 180° (sum of interior angles). This gives us A + 2x = 180°. Solving these simultaneous equations gives the value of angle A (the vertex angle).
These examples illustrate the importance of understanding the relationship between the vertex angle and base angles in solving various geometrical problems. Practice solving different types of problems using these concepts and formulas strengthens your understanding and problem-solving skills.
Applications of Isosceles Triangles and their Vertex Angles
The properties of isosceles triangles, particularly their vertex angles, find applications in numerous fields:
-
Architecture and Construction: Isosceles triangles are commonly used in architectural designs, creating aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound structures. Understanding the angles allows for precise measurements and construction.
-
Engineering: In various engineering applications, understanding the stability of structures relying on isosceles triangles is essential. This involves precise calculation of angles and stresses on the structure.
-
Computer Graphics and Game Development: Isosceles triangles are fundamental shapes in computer graphics and game development, used in creating 2D and 3D models. Precise calculations of angles are essential for accurate rendering and animation.
-
Cartography: Isosceles triangles can be used in map projections and calculations of distances and areas.
-
Physics: Isosceles triangles can appear in various physics problems, such as the analysis of forces and equilibrium. Calculating angles precisely is critical for accurate solutions.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
For those seeking a deeper understanding, exploring advanced concepts related to the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle can be highly rewarding:
-
Geometric constructions: Constructing isosceles triangles with specified vertex angles using compass and straightedge. This allows for a practical understanding of the relationship between the angles and sides.
-
Trigonometry: Applying trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent) to solve problems involving the sides and angles of isosceles triangles. This provides powerful analytical tools for more complex problems.
-
Coordinate geometry: Representing isosceles triangles on a coordinate plane and using algebraic methods to solve problems.
-
Calculus: Applying calculus to solve optimization problems involving isosceles triangles. For instance, finding the maximum area of an isosceles triangle given a fixed perimeter.
Conclusion
The vertex angle of an isosceles triangle is a fundamental concept in geometry with wide-ranging applications. Understanding its definition, properties, related theorems, and problem-solving techniques is essential for success in mathematics and numerous related fields. By mastering the concepts discussed in this comprehensive guide, you’ll build a strong foundation in geometry and enhance your problem-solving capabilities. Remember, consistent practice and exploration of different problem types are key to solidifying your understanding and gaining confidence in tackling increasingly complex geometrical challenges. Through continued learning and application, the seemingly simple isosceles triangle reveals a rich tapestry of mathematical beauty and practical utility.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Vertex Angle Of An Isosceles Triangle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
