Vapor Pressure Of Water At 20c
listenit
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
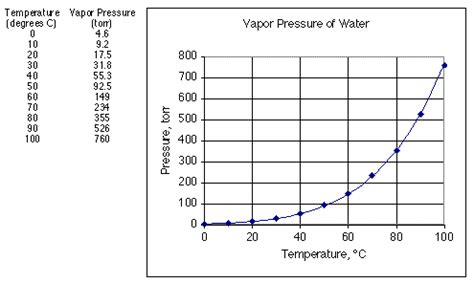
Table of Contents
Vapor Pressure of Water at 20°C: A Deep Dive
The vapor pressure of water at 20°C, a seemingly simple concept, holds significant importance across various scientific disciplines and everyday life. Understanding this fundamental property unlocks insights into weather patterns, industrial processes, and even the human body's functioning. This article delves into the intricacies of water's vapor pressure at this specific temperature, exploring its definition, measurement, applications, and influencing factors.
What is Vapor Pressure?
Vapor pressure, in its simplest definition, is the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (liquid or solid) at a given temperature in a closed system. For water at 20°C, this means the pressure exerted by water molecules that have transitioned from the liquid phase to the gaseous phase (water vapor) within a sealed container. Crucially, this pressure is dynamic; molecules constantly escape the liquid phase and return to it, achieving an equilibrium where the rate of evaporation equals the rate of condensation. This equilibrium pressure is what we measure as the vapor pressure.
Understanding Equilibrium
The concept of equilibrium is critical. Imagine a sealed container containing liquid water at 20°C. Initially, water molecules with sufficient kinetic energy overcome intermolecular forces and escape into the gaseous phase above the liquid. As more water vapor accumulates, some molecules collide with the liquid surface and return to the liquid phase. Eventually, a dynamic equilibrium is reached where the rate of evaporation equals the rate of condensation. At this point, the vapor pressure remains constant.
Measuring Vapor Pressure of Water at 20°C
Precise measurement of vapor pressure is essential for various scientific and engineering applications. Several methods exist, each with varying degrees of accuracy and complexity:
1. Manometric Methods
These methods directly measure the pressure exerted by the water vapor. A common technique involves enclosing a sample of water in a closed vessel connected to a manometer (a device for measuring pressure). The pressure difference between the water vapor and the surrounding atmosphere is then measured. However, ensuring complete saturation (equilibrium) within the system is crucial for accurate readings.
2. Isoteniscope Method
The isoteniscope is a specialized device designed to measure vapor pressure with high precision. It utilizes the principle of balancing the vapor pressure against an external pressure, typically atmospheric pressure. By adjusting the external pressure until the liquid level in the isoteniscope is balanced, the vapor pressure can be determined accurately.
3. Static Methods
Static methods involve measuring the pressure in a closed system containing liquid water and its vapor at equilibrium. This generally requires highly sensitive pressure gauges and careful control of temperature to ensure accurate and stable readings.
The Value at 20°C
The accepted value for the vapor pressure of water at 20°C is approximately 2.34 kPa (kilopascals) or 17.5 mmHg (millimeters of mercury). It's important to note that this value can slightly vary depending on the purity of the water and the precision of the measurement method.
Factors Affecting Vapor Pressure
Several factors influence the vapor pressure of water, particularly temperature and the presence of dissolved substances.
1. Temperature Dependence
Temperature significantly impacts vapor pressure. As temperature increases, the kinetic energy of water molecules increases, allowing more molecules to overcome intermolecular forces and escape into the gaseous phase. Consequently, the vapor pressure increases with rising temperature. This relationship is often described by the Clausius-Clapeyron equation, a powerful tool for predicting vapor pressure changes with temperature.
2. Dissolved Substances
The presence of dissolved substances in water affects its vapor pressure. This phenomenon, known as Raoult's Law, states that the vapor pressure of a solvent above a solution is proportional to the mole fraction of the solvent. In simpler terms, adding solutes to water reduces the number of water molecules available to escape into the gaseous phase, thereby lowering the vapor pressure. The extent of this reduction depends on the concentration of the dissolved substance.
3. Atmospheric Pressure
While not a direct factor influencing the equilibrium vapor pressure itself within a closed system, atmospheric pressure influences the boiling point of water. At lower atmospheric pressures (higher altitudes), water boils at a lower temperature. This seemingly unrelated phenomenon is directly related; the vapor pressure of water needs to equal the external atmospheric pressure for boiling to occur.
Applications of Vapor Pressure Knowledge
Understanding the vapor pressure of water at 20°C and its variation with other factors has widespread practical applications:
1. Meteorology and Climate Science
Vapor pressure is a critical parameter in meteorology. It's a key component in determining relative humidity, a measure of how much water vapor is present in the air compared to the maximum amount the air can hold at a given temperature. This information is crucial for weather forecasting and understanding climate patterns. High vapor pressures contribute to atmospheric moisture content and precipitation.
2. Industrial Processes
Many industrial processes rely on controlling water vapor pressure. For instance, in drying processes, understanding and managing the vapor pressure allows for efficient removal of water from materials. Similarly, in humidification systems, controlling vapor pressure maintains optimal humidity levels in various industrial settings. Desalination plants also rely on understanding vapor pressure to separate salt from water.
3. Biology and Physiology
Vapor pressure plays a role in biological systems. For instance, transpiration in plants involves the evaporation of water from leaves, driven by the difference in vapor pressure between the leaf and the surrounding air. In the human body, maintaining proper hydration is partially dependent on understanding vapor pressure and its implications for water loss through respiration and perspiration.
4. Chemical Engineering
Vapor-liquid equilibrium (VLE) calculations, essential in chemical engineering, rely heavily on accurate vapor pressure data. These calculations are used in the design and operation of distillation columns, reactors, and other process equipment.
5. Food Science
Understanding vapor pressure is vital in food preservation and processing. Water activity, a measure related to vapor pressure, significantly affects microbial growth and the shelf life of food products. Controlling water activity through methods such as drying or freezing influences the growth and survival of microorganisms.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple concept of the vapor pressure of water at 20°C is far-reaching in its implications. Its value, approximately 2.34 kPa, serves as a fundamental parameter in a wide range of applications, from predicting weather patterns to designing industrial processes. Understanding the factors influencing vapor pressure, particularly temperature and dissolved substances, provides a deeper appreciation for this important thermodynamic property and its significance in various fields. The continued study and refinement of vapor pressure measurements contribute to advancements in meteorology, engineering, biology, and countless other disciplines. As our understanding grows, so too will our ability to harness the power of this fundamental property for innovation and problem-solving.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
7 8 Divided By 1 4
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Is 0 55 As A Fraction
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Is The Antiderivative Of X 2
Mar 22, 2025
-
X 3 2x 2 3x 6
Mar 22, 2025
-
How To Find Equation Of Secant Line
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Vapor Pressure Of Water At 20c . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
