Use Distributive Property To Remove The Parentheses
listenit
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
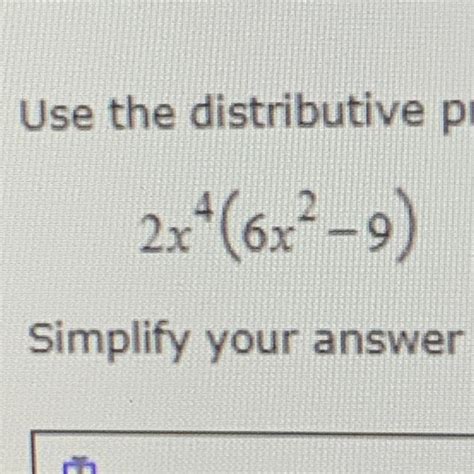
Table of Contents
Mastering the Distributive Property: Removing Parentheses with Ease
The distributive property is a fundamental concept in algebra that allows us to simplify expressions containing parentheses. Understanding and applying this property effectively is crucial for success in mathematics, paving the way for more complex algebraic manipulations. This comprehensive guide will explore the distributive property in detail, providing numerous examples and practical applications to solidify your understanding. We'll delve into different scenarios, tackling both simple and complex expressions to build your confidence and proficiency.
Understanding the Distributive Property
The distributive property states that multiplying a sum (or difference) by a number is the same as multiplying each addend (or subtrahend) by that number and then adding (or subtracting) the products. This can be represented mathematically as:
a(b + c) = ab + ac
and
a(b - c) = ab - ac
Where 'a', 'b', and 'c' can represent numbers, variables, or expressions. The key takeaway is that the term outside the parentheses is distributed to each term inside the parentheses.
Visualizing the Distributive Property
Imagine you have 3 bags, each containing 2 apples and 3 oranges. To find the total number of fruits, you can either add the contents of each bag (2 + 3 = 5 fruits per bag) and then multiply by the number of bags (5 fruits/bag * 3 bags = 15 fruits), or you can distribute the number of bags to each type of fruit: (3 bags * 2 apples/bag) + (3 bags * 3 oranges/bag) = 6 apples + 9 oranges = 15 fruits. Both methods yield the same result, illustrating the distributive property visually.
Applying the Distributive Property: Step-by-Step Examples
Let's explore various examples to demonstrate the practical application of the distributive property.
Example 1: Simple Numerical Expressions
3(4 + 5)
Applying the distributive property:
3(4) + 3(5) = 12 + 15 = 27
Alternatively, simplifying within the parenthesis first:
3(9) = 27
Both methods provide the same answer, highlighting the validity of the distributive property.
Example 2: Combining Variables and Numbers
2x(3 + y)
Distributing 2x to both terms within the parentheses:
2x(3) + 2x(y) = 6x + 2xy
This example demonstrates the distributive property's application with variables, a common scenario in algebra.
Example 3: Dealing with Subtraction
-5(2a - 4b)
Remember to distribute the negative sign along with the 5:
-5(2a) - (-5)(4b) = -10a + 20b
This example emphasizes the importance of carefully handling negative signs when applying the distributive property. A common mistake is forgetting to distribute the negative sign correctly.
Example 4: More Complex Expressions
2x(3x² + 4x - 6)
Distribute 2x to each term:
2x(3x²) + 2x(4x) + 2x(-6) = 6x³ + 8x² - 12x
This example showcases the distributive property's application with higher-order polynomial expressions.
Example 5: Expressions with Fractions
(1/2)(4x + 6y - 8)
Distribute 1/2 to each term:
(1/2)(4x) + (1/2)(6y) + (1/2)(-8) = 2x + 3y - 4
This example illustrates that the distributive property functions seamlessly with fractions.
Distributing Negative Numbers and Variables
Special attention should be paid to scenarios involving negative numbers and variables outside the parentheses.
Negative Numbers
Distributing a negative number requires careful attention to signs. Remember that multiplying a positive number by a negative number results in a negative number, and multiplying two negative numbers results in a positive number.
Example: -2(x - 3) = -2x + 6
Variables
Variables outside the parentheses behave the same way as numbers during distribution.
Example: x(y + z) = xy + xz
Combining the Distributive Property with Other Algebraic Operations
Often, you'll encounter expressions requiring a combination of the distributive property and other algebraic operations like combining like terms and simplifying fractions.
Example: 3(2x + 4) - 2(x - 1)
First, apply the distributive property:
6x + 12 - 2x + 2
Then, combine like terms:
(6x - 2x) + (12 + 2) = 4x + 14
This example demonstrates the importance of applying the distributive property before simplifying further.
Advanced Applications of the Distributive Property
The distributive property extends beyond simple algebraic expressions and finds application in more advanced mathematical concepts.
Factoring Polynomials
The distributive property is instrumental in factoring polynomials. Factoring is the reverse process of distributing. By identifying a common factor amongst terms, you can factor it out, effectively using the distributive property in reverse.
Example: 6x² + 3x = 3x(2x + 1)
Here, 3x is the common factor, and it's factored out leaving (2x + 1) in the parentheses.
Solving Equations
The distributive property plays a crucial role in solving equations involving parentheses.
Example: 2(x + 3) = 10
Distributing the 2:
2x + 6 = 10
Subtracting 6 from both sides:
2x = 4
Dividing both sides by 2:
x = 2
Working with Complex Numbers
The distributive property extends to complex numbers as well, adhering to the same principles.
Example: i(2 + 3i) = 2i + 3i² = 2i - 3
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While seemingly straightforward, the distributive property often leads to mistakes if not applied carefully. Here are some common errors to watch out for:
- Forgetting to distribute to all terms: Remember to distribute the term outside the parentheses to every term inside the parentheses.
- Incorrectly handling negative signs: Pay close attention to the signs when distributing a negative number. Remember that a negative times a negative is positive.
- Combining like terms prematurely: Apply the distributive property first, before combining like terms.
- Making careless arithmetic errors: Double-check your arithmetic to avoid simple calculation mistakes.
Practice Makes Perfect
The best way to master the distributive property is through consistent practice. Work through numerous problems, varying the complexity and including different types of numbers and variables. Start with simpler examples and gradually move towards more challenging ones. Utilize online resources, textbooks, and practice worksheets to hone your skills. Regular practice will build your confidence and fluency in applying the distributive property.
Conclusion: The Distributive Property: Your Algebraic Ally
The distributive property is an indispensable tool in algebra and beyond. Mastering its application will significantly enhance your ability to simplify expressions, solve equations, and tackle more advanced mathematical concepts. By understanding its principles, practicing regularly, and avoiding common pitfalls, you can confidently use the distributive property to remove parentheses and simplify algebraic expressions with ease. Remember, consistent practice is key to success.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Mass Number Of Magnesium
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Symmetrical Lines Does A Rectangle Have
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Percent Of 0 125
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 7 And 14
Mar 28, 2025
-
Why Are Phylogenetic Trees Considered Hypotheses
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Use Distributive Property To Remove The Parentheses . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
