The Triangles Are Similar. What Is The Value Of X
listenit
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
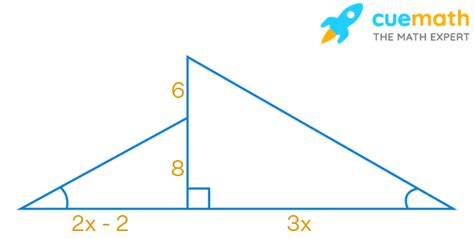
Table of Contents
The Triangles Are Similar: What is the Value of x? A Comprehensive Guide
Determining the value of 'x' when given similar triangles involves understanding the principles of similarity and applying the appropriate theorems. This comprehensive guide will delve into various methods to solve such problems, covering different triangle types and complexities. We'll explore the fundamental concepts, provide step-by-step solutions to sample problems, and equip you with the knowledge to tackle similar triangle questions with confidence.
Understanding Similar Triangles
Similar triangles are triangles that have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. This means that their corresponding angles are congruent (equal in measure), and their corresponding sides are proportional. This proportionality is key to solving for unknown values like 'x'.
Key Properties of Similar Triangles:
- Corresponding Angles are Congruent: Angle A in one triangle is equal to Angle A' in the other similar triangle, and so on for all corresponding angles.
- Corresponding Sides are Proportional: The ratio of the lengths of corresponding sides remains constant. This is often expressed as: a/a' = b/b' = c/c', where a, b, and c are the sides of one triangle, and a', b', and c' are the corresponding sides of the similar triangle.
How to Identify Similar Triangles:
Several postulates and theorems help us determine if triangles are similar. The most common are:
- AA (Angle-Angle Similarity): If two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another triangle, then the triangles are similar.
- SAS (Side-Angle-Side Similarity): If two sides of one triangle are proportional to two sides of another triangle and the included angles are congruent, then the triangles are similar.
- SSS (Side-Side-Side Similarity): If the three sides of one triangle are proportional to the three sides of another triangle, then the triangles are similar.
Solving for 'x' in Similar Triangles: Methods and Examples
Let's explore different scenarios and apply the principles of similar triangles to solve for 'x'.
Example 1: Using AA Similarity
Imagine two triangles, ΔABC and ΔDEF. We know that ∠A = ∠D = 60° and ∠B = ∠E = 40°. Therefore, by AA similarity, ΔABC ~ ΔDEF. Let's say AB = 8, BC = 10, and DE = 4. We need to find the length of EF (which we'll represent as 'x').
Solution:
Since the triangles are similar, the ratio of corresponding sides is constant:
AB/DE = BC/EF
8/4 = 10/x
Cross-multiply:
8x = 40
x = 5
Therefore, EF = 5.
Example 2: Using SAS Similarity
Consider triangles ΔGHI and ΔJKL. We know that GH = 6, HI = 8, ∠H = ∠J = 70°, JK = 3, and JL = x.
Solution:
Since we have two sides and the included angle, we can use SAS similarity. The ratio of the corresponding sides must be equal:
GH/JK = HI/JL
6/3 = 8/x
Cross-multiply:
6x = 24
x = 4
Therefore, JL = 4.
Example 3: Using SSS Similarity
Let's say we have triangles ΔMNO and ΔPQR. We know that MN = 12, NO = 15, MO = 9, PQ = 8, QR = 10, and PR = 6. Are the triangles similar? If so, find the value of x if we introduce a side in ΔPQR that corresponds to side NO in ΔMNO and is represented by x.
Solution:
We check the ratios of corresponding sides:
MN/PQ = 12/8 = 1.5 NO/QR = 15/10 = 1.5 MO/PR = 9/6 = 1.5
Since all three ratios are equal, the triangles are similar by SSS similarity. Since NO corresponds to x, we can use the same ratio:
NO/x = 1.5
15/x = 1.5
x = 15/1.5 = 10
Therefore, the length of the unknown side is 10.
Example 4: Similar Triangles within a Larger Triangle
A common problem involves similar triangles created by drawing an altitude within a larger triangle. Let's say we have a right-angled triangle ΔABC, where ∠B is the right angle. An altitude BD is drawn to the hypotenuse AC. This creates two smaller triangles, ΔADB and ΔBDC, both similar to the larger triangle ΔABC. If AB = 6, BC = 8, and AD = x, we need to find x.
Solution:
Since ΔADB ~ ΔABC, we have:
AD/AB = AB/AC
x/6 = 6/(√(6² + 8²)) = 6/10
x = 6 * (6/10) = 3.6
Therefore, AD = 3.6.
Example 5: Overlapping Triangles
Sometimes, similar triangles overlap, making it crucial to identify the corresponding sides carefully. Imagine two overlapping triangles where it's given that the triangles are similar. By carefully analyzing the diagram and identifying corresponding sides, we can set up a proportion to solve for x. The specific values and diagram would be needed to work through a numerical example in this case.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
-
Trigonometric Ratios: In some cases, trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) can be employed to find missing side lengths or angles, particularly in right-angled triangles. This approach is especially useful when dealing with angles and sides of similar triangles.
-
Scale Factors: The ratio of corresponding sides in similar triangles is called the scale factor. Understanding the scale factor allows for quicker calculation of unknown side lengths.
-
Complex Geometrical Figures: More complex problems might involve multiple similar triangles within a larger figure, requiring careful analysis and application of multiple principles to find the value of 'x'.
-
Algebraic Manipulation: Often, solving for 'x' requires manipulating algebraic equations derived from the proportional relationships between the sides of similar triangles.
Practical Applications of Similar Triangles
Understanding similar triangles has significant practical applications in various fields:
- Surveying and Mapping: Used to measure distances that are difficult to measure directly.
- Architecture and Engineering: Essential for scaling models and blueprints.
- Computer Graphics: Plays a crucial role in image scaling and transformations.
- Photography: Helps understand the relationship between object size and image size.
Conclusion
Solving for 'x' in similar triangles involves understanding the principles of similarity, identifying corresponding sides and angles, and applying appropriate theorems (AA, SAS, SSS). Mastering this skill requires practice and a systematic approach to problem-solving. By understanding the concepts explained here and working through various examples, you can develop the confidence to tackle similar triangle problems of increasing complexity. Remember to carefully analyze the given information, identify corresponding sides and angles, set up accurate proportions, and solve for the unknown value ('x') using algebraic methods. The use of diagrams and visualization is often key to successful problem-solving in this area of geometry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Revolutions Per Second To Radians Per Second
Mar 19, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 60
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Are The Subunits Of Dna
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 1 8 Of A Yard
Mar 19, 2025
-
Find The Limit Of The Sequence
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Triangles Are Similar. What Is The Value Of X . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
